
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780135245033
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 2EAP
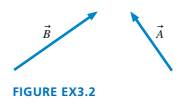
Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.2 onto your paper. Then find
(a)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Please help with this physics problem
Chapter 3 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Ch. 3 - Can the magnitude of the displacement vector be...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B, can C = A + B? Can C>A + B? For each,...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B can C = 0? Can C< O? For each, show how...Ch. 3 - Is it possible to add a scalar to a vector? If so,...Ch. 3 - How would you define the zero vector ?Ch. 3 - Can a vector have a component equal to zero and...Ch. 3 - Can a vector have zero magnitude if one of its...Ch. 3 - Suppose two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can...Ch. 3 - Are the following statements true or false?...Ch. 3 - I. Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.1 onto your...
Ch. 3 - Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.2 onto your paper....Ch. 3 - a. What are the x- and v-components of vector E...Ch. 3 - A velocity vector 40° below the positive x-axis...Ch. 3 - A position vector in the first quadrant has an...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Let C = (3.15 m, 15° above the negative x-axis)...Ch. 3 - A runner is training for an upcoming marathon by...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Let a. Write Vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Din component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - Let A = 4î - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and E = 2 A + 3 B...Ch. 3 - Let A = 41 - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and F = A -4 B . a....Ch. 3 - 17. Let = 2î + 3? and = 2î — 2?. Find the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 3 - 19. What are the x– and y- components of the...Ch. 3 - 20. For the three vectors shown Figure EX3.20, + +...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 3 - 22. Let = (3.0 m, 20° south of east), = (2.0 m,...Ch. 3 - The position of a particle as a function of time...Ch. 3 - a. What is the angle between vectors E and F in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.25 shows vectors A and B . Find vector C...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 3 - The minute hand on a watch is 2.0 cm in length....Ch. 3 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 3 - Ruth sets out to visit her friend Ward, who lives...Ch. 3 - A cannon tilted upward at 30° fires a cannonball...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 3 - A pine cone falls straight down from a pine tree...Ch. 3 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 3 - Your neighbor Paul has rented a truck with a...Ch. 3 - Tom is climbing a 3.0-m-long ladder that leans...Ch. 3 - The treasure map in FIGURE P3.40 gives the...Ch. 3 - The bacterium E. coli is a single-cell organism...Ch. 3 - A flock of ducks is trying to migrate south for...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.43 shows three ropes tied together in a...Ch. 3 - I Four forces are exerted on the object shown in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.45 shows four electric charges located...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me with this physics problemarrow_forwardIn a scene from The Avengers (the first one) Black Widow is boosted directly upwards by Captain America, where she then grabs on to a Chitauri speeder that is 15.0 feet above her and hangs on. She is in the air for 1.04 s. A) With what initial velocity was Black Widow launched? 1 m = 3.28 ft B) What was Black Widow’s velocity just before she grabbed the speeder? Assume upwards is the positive direction.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardTwo objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.arrow_forwardA box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aY8z2qO44WA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY