
Concept explainers
Comprehensive cycle problem: Perpetual system
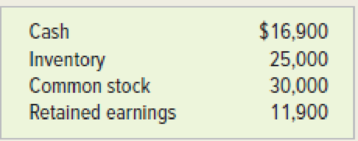
At the beginning of 2018, the Redd Company had the following balances in its accounts:
During 2018, the company experienced the following events:
1. Purchased inventory that cost $15,200 on account from Ross Company under terms 1/10, n/30. The merchandise was delivered FOB shipping point. Freight costs of $200 were paid in cash.
2. Returned $800 of the inventory that it had purchased because the inventory was damaged in transit. The seller agreed to pay the return freight cost.
3. Paid the amount due on its account payable to Ross Company within the cash discount period.
4. Sold inventory that had cost $18,000 for $32,000 on account, under terms 2/10, n/45.
5. Received merchandise returned from a customer. The merchandise originally cost $800 and was sold to the customer for $1,500 cash. The customer was paid $1,500 cash for the returned merchandise.
6. Delivered goods FOB destination in Event 4. Freight costs of $140 were paid in cash.
7. Collected the amount due on the
8. Took a physical count indicating that $21,100 of inventory was on hand at the end of the accounting period.
Required
a. Identify these events as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE).
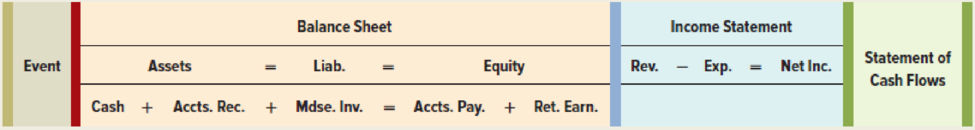
b. Record each event in a statements model like the following one.
c. Prepare a multistep income statement, a statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, a
a.
Identify the events as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE).
Explanation of Solution
Identify the events as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE).
| Event No. | Event type |
| 1a. | AS |
| 1b. | AE |
| 2. | AU |
| 3. | AU |
| 4a. | AS |
| 4b. | AU |
| 5a. | AU |
| 5b. | AS |
| 6. | AU |
| 7. | AU |
| 8. | AU |
Table (1)
- Asset source: All the transactions which increase assets either by borrowing from creditors (increase liabilities), or by earning operating revenues (increase in stockholders’ equity) are referred to as asset source transactions.
- Asset use: All the transactions which decrease assets either by paying off liabilities (decrease in liabilities), or by paying operating expenses (decrease in stockholders’ equity) are referred to as asset use transactions.
- Asset exchange: All the transactions which increase assets and decrease assets simultaneously, with no effect on the total assets value are referred to as asset exchange transactions.
- Claims exchange: All the transactions which include exchange of liabilities for equity are referred to as claims exchange transactions.
b.
Record each event in a statements model.
Explanation of Solution
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements, balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows in one table in a horizontal form, is referred to as, horizontal statements model.
Record each event in a statements model.
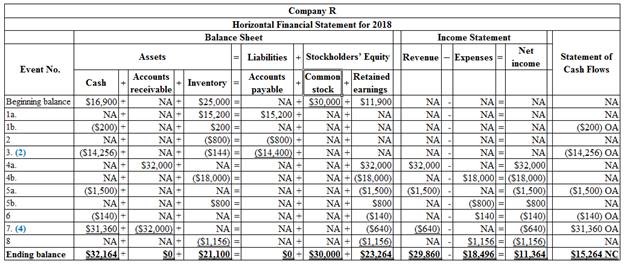
Table (2)
Working Note:
(1) Compute purchase discount.
(2) Compute the cash paid for inventory purchased.
(3) Compute sales discount.
(4) Compute cash received.
c.
Prepare a multistep income statement, statement of stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for Company R.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare a multistep income statement for Company R for the year ended December 31, 2018.
| Company R | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Net sales | $29,860 | |
| Cost of goods sold (5) | ($18,356) | |
| Gross margin | $11,504 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Transportation-out | ($140) | |
| Net income | $11,364 | |
Table (3)
Working Note:
(5) Determine the amount of cost of goods sold.
Statement of stockholders’ equity: The statement which reports the changes in stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock, during the year is referred to as statement of stockholders’ equity.
Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for Company R for the year ended December 31, 2018.
| Company R | ||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Beginning common stock | $30,000 | |
| Add: Stock issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $30,000 | |
| Beginning retained earnings | $11,900 | |
| Add: Net income | $11,364 | |
| Ending retained earnings | $23,264 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $53,264 | |
Table (4)
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for Company R as at December 31, 2018.
| Company R | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| December 31, 2018 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $32,164 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $21,100 | |
| Total assets | $53,264 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $30,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $23,264 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $53,264 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $53,264 | |
Table (5)
Statement of cash flows: Statement of cash flows reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and the result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for Company R for the year ended December 31, 2018.
| Company R | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers (6) | $29,860 | |
| Outflow for inventory (7) | ($14,456) | |
| Outflow for expenses | ($140) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $15,624 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | $0 | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | $0 | |
| Net change in cash | $15,624 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $16,900 | |
| Ending cash balance | $31,164 | |
Table (6)
Working note:
(6) Determine the cash inflow from customers.
(7) Determine the cash outflow for inventory.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- I am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




