
Concept explainers
Which
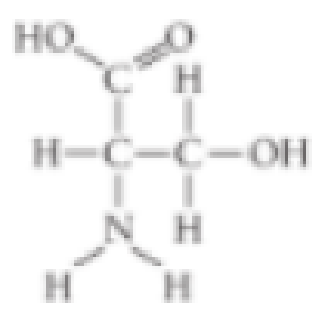
- A. carboxyl
- B. sulfhydryl
- C. hydroxyl
- D. amino
Introduction:
The different properties of an organic molecule not only depend upon the carbon skeleton’s arrangement, it also depends on the different chemical groups attached to the skeleton.
Answer to Problem 1TYU
Correct answer:
The functional group that is not present in the given molecule is sulfhydryl group.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for the correct statement:
Sulfhydryl group is the functional group that comprises of a molecule of sulfur. Hence, the given structure does not have a sulfhydryl group.
Option (B) is given as “sulfhydryl”.
The “functional group that is not present in the given molecule is sulfhydryl group”, it is the right answer.
Hence, the option (B) is correct.
Reasons for the incorrect statements:
Option (A) is given as “carboxyl”.
The carboxyl functional group is present in the given molecule. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (C) is given as “hydroxyl”.
The hydroxyl functional group is present in the given molecule. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (D) is given as “amino”.
The amino group is present in the given molecule. So, it is a wrong answer.
Hence, options (A), (C), and (D) are incorrect.
The functional groups such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, and amino are present in the molecule, whereas the sulfhydryl group is absent in the given molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- 1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forwardwhat are the answer from the bookarrow_forwardwhat is lung cancer why plants removes liquid water intead water vapoursarrow_forward
- *Example 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal dominant trait Trait: Neurofibromatosis Forms of the trait: The dominant form is neurofibromatosis, caused by the production of an abnormal form of the protein neurofibromin. Affected individuals show spots of abnormal skin pigmentation and non-cancerous tumors that can interfere with the nervous system and cause blindness. Some tumors can convert to a cancerous form. i The recessive form is a normal protein - in other words, no neurofibromatosis.moovi A typical pedigree for a family that carries neurofibromatosis is shown below. Note that carriers are not indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Use the letter "N" to indicate the dominant neurofibromatosis allele, and the letter "n" for the normal allele. Nn nn nn 2 nn Nn A 3 N-arrow_forwardI want to be a super nutrition guy what u guys like recommend mearrow_forwardPlease finish the chart at the bottom. Some of the answers have been filled in.arrow_forward
- 9. Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. 18 carbons fatty acids 12 carbons 9 glycerol A. Glycerol is broken down to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, a glycolysis intermediate via the following pathway shown in the figure below. Notice this process costs one ATP but generates one FADH2. Continue generating ATP with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate using the standard pathway and aerobic respiration. glycerol glycerol-3- phosphate…arrow_forwardNormal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO2 level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO2 triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. How might the location and slope of the O₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardforaging/diet type teeth tongue stomach intestines cecum Insectivory numerous, spiky, incisors procumbentExample: moleExample: shrew -- simple short mostly lacking Myrmecophagy absent or reduced in numbers, peg-likeExample: tamandua anteater extremely long simple, often roughened short small or lacking Terrestrial carnivory sharp incisors; long, conical canines; often carnassial cheek teeth; may have crushing molarsExample: dog -- simple short small Aquatic carnivory homodont, spiky, numerousExample: common dolphin -- simple or multichambered (cetaceans only) variable small or absent Sanguinivory very sharp upper incisors; reduced cheek teethExample: vampire bat grooved tubular, highly extensible long small or lacking Herbivory (except nectivores) incisors robust or absent; canines reduced or absent; diastema; cheek teeth enlarged with complex occlusal surfacesExample: beaver -- simple (hindgut fermenters) or multichambered (ruminants) long large Filter feeding none…arrow_forward
- 3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 པར『ན་ cm 30 Species B 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 cm 10 Species C 0/4, 0/0,3/3, 3/3 020arrow_forward3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 cm 30 Species B 0/4, 0/0, 3/3, 3/3 cm 10 Species C 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 E 0 cm 20 AILarrow_forwardNormal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO₂ level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO₂ triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. • How might the location and slope of the O2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





