
Concept explainers
What two
a. an R-group and a hydroxyl group
b. an N–H group and a carbonyl group
c. an amino group and a hydroxyl group
d. an amino group and a carboxyl group
Introduction:
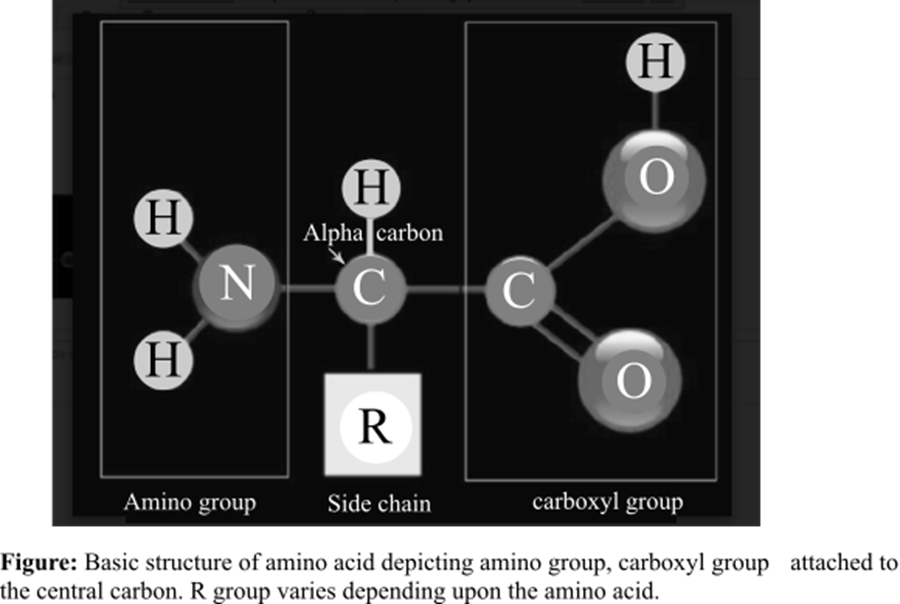
The amino acid is the basic structural unit of the proteins. There are total 20 amino acids found in the living system. At isoelectric point (pH or potential of hydrogen), an amino acid does not have any net charge. The basic structure of amino acids is shown below:
Answer to Problem 1TYK
Correct answer:
An amino group and a carboxyl group
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/Justification for the correct answer:
Option (d) is given as a carboxyl group along with an amino group. Functional groups of amino acids are responsible for bonding between two amino acids. The polypeptide chain consists of several amino acids. When a peptide bond is formed, a hydroxyl (–OH) group is lost from the carboxyl group of an amino acid and an H (hydrogen atom) from the amino group of another amino acid is also lost. This dehydration (loss of one H2O molecule) reaction results in a peptide bond. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Explanation for incorrect answers:
Option (a) is given as an R- group and a hydroxyl group. R group or side chain decides the identity of an amino acid, for example, glycine, which is the simplest amino acid, has a hydrogen atom as its R group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (b) is given as an N-H group and a carbonyl group. Any functional group, which has an O (oxygen) atom attached to the C (carbon) atom through double bond (-C=O) is called carbonyl group. COOH (carboxylic acid) is also a type of the carbonyl group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (c) is given as an amino group and a hydroxyl group. The carboxylic acid of the amino acid contains one hydroxyl group, which gets lost when the amino acid undergoes peptide bond formation with an amino group of another amino acid. So, it is a wrong answer.
Hence, options (a), (b), and (c) are incorrect.
The amino group and a carboxyl group are functional groups bounded to the central carbon of every free amino acid monomer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





