
Concept explainers
What two
a. an R-group and a hydroxyl group
b. an N–H group and a carbonyl group
c. an amino group and a hydroxyl group
d. an amino group and a carboxyl group
Introduction:
The amino acid is the basic structural unit of the proteins. There are total 20 amino acids found in the living system. At isoelectric point (pH or potential of hydrogen), an amino acid does not have any net charge. The basic structure of amino acids is shown below:
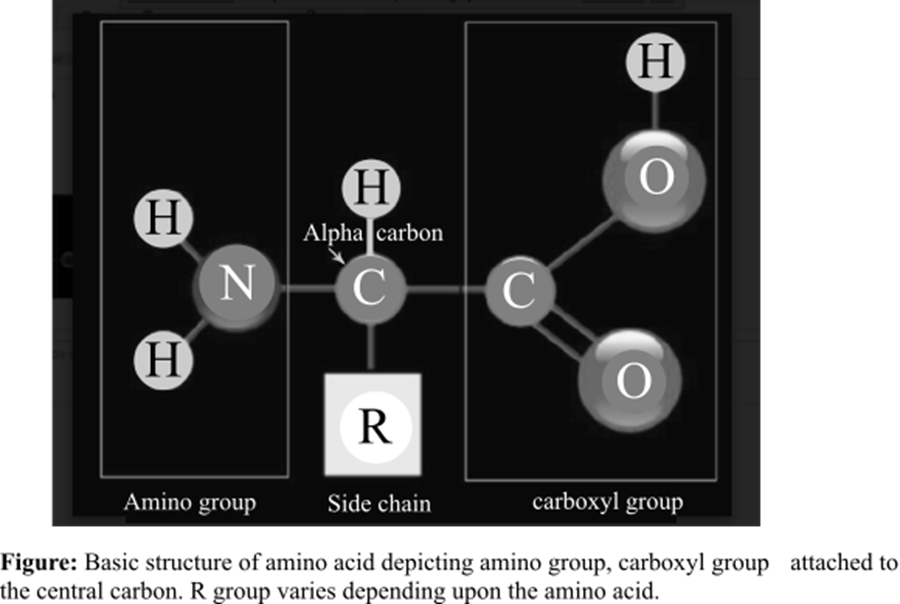
Answer to Problem 1TYK
Correct answer:
An amino group and a carboxyl group
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/Justification for the correct answer:
Option (d) is given as a carboxyl group along with an amino group. Functional groups of amino acids are responsible for bonding between two amino acids. The polypeptide chain consists of several amino acids. When a peptide bond is formed, a hydroxyl (–OH) group is lost from the carboxyl group of an amino acid and an H (hydrogen atom) from the amino group of another amino acid is also lost. This dehydration (loss of one H2O molecule) reaction results in a peptide bond. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Explanation for incorrect answers:
Option (a) is given as an R- group and a hydroxyl group. R group or side chain decides the identity of an amino acid, for example, glycine, which is the simplest amino acid, has a hydrogen atom as its R group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (b) is given as an N-H group and a carbonyl group. Any functional group, which has an O (oxygen) atom attached to the C (carbon) atom through double bond (-C=O) is called carbonyl group. COOH (carboxylic acid) is also a type of the carbonyl group. So, it is a wrong answer.
Option (c) is given as an amino group and a hydroxyl group. The carboxylic acid of the amino acid contains one hydroxyl group, which gets lost when the amino acid undergoes peptide bond formation with an amino group of another amino acid. So, it is a wrong answer.
Hence, options (a), (b), and (c) are incorrect.
The amino group and a carboxyl group are functional groups bounded to the central carbon of every free amino acid monomer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
- can you help? I think its B but not surearrow_forwardSkip to main content close Homework Help is Here – Start Your Trial Now! arrow_forward search SEARCH ASK Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BUY Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition) 11th Edition ISBN: 9780134580999 Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn Publisher: PEARSON 1 The Human Body: An Orientation expand_moreChapter 1 : The Human Body: An Orientation Chapter Questions expand_moreSection: Chapter Questions Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... format_list_bulletedProblem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... See similar textbooks Bartleby Related Questions Icon Related questions Bartleby Expand Icon bartleby Concept explainers bartleby Question Draw a replication bubble with two replication forks.blue lines are DNA single strands and red lines are RNA single strands.indicate all 3' and 5’ ends on all DNA single…arrow_forwardProvide an answerarrow_forward
- Question 4 1 pts Which of the following would be most helpful for demonstrating alternative splicing for a new organism? ○ its proteome and its transcriptome only its transcriptome only its genome its proteome and its genomearrow_forwardIf the metabolic scenario stated with 100 mM of a sucrose solution, how much ATP would be made then during fermentation?arrow_forwardWhat is agricuarrow_forward
- When using the concept of "a calorie in is equal to a calorie out" how important is the quality of the calories?arrow_forwardWhat did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate? What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter? What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment? If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?arrow_forwardWhat kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?arrow_forward
- What is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forwardYou intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





