
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.

Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
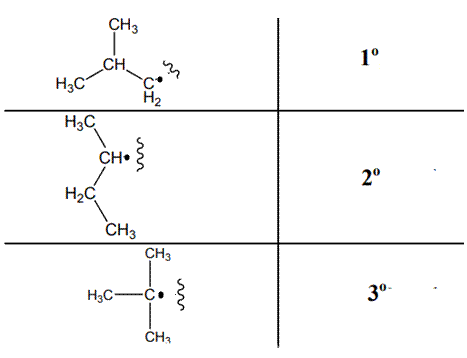
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(b)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
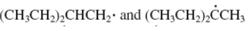
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
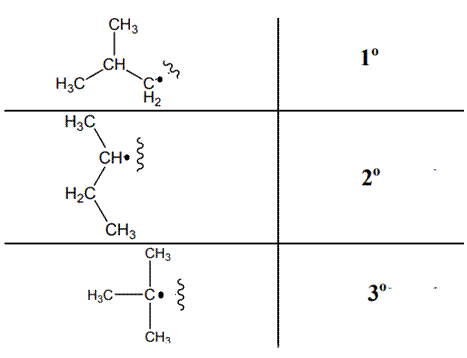
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyperconjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
(c)
Interpretation: Nature of below alkyl radical along with names and most stable radical should be described by orbital description.
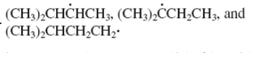
Concept introduction: The carbon radical linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon radical linked to two alkyl/carbon atoms and one
The various kinds of alkyl radicals are indicated below:
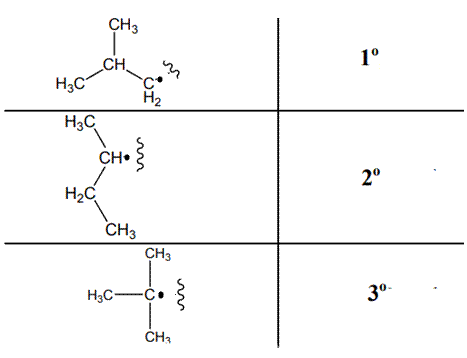
The tertiary radicals are most stable followed by secondary and least stable is primary methyl radical. This is because there is maximum stabilization through delocalization via hyper conjugation. The phenomenon of hyperconjugation refers to donation of
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- ● Biological Macromolecules Naming and drawing cyclic monosaccharides Your answer is incorrect. • Row 1: Your answer is incorrect. Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 4: Your answer is incorrect. Try again... 0/5 Give the complete common name, including anomer and stereochemistry labels, of the following molecules. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS resource. CH2OH OH OH H H I H OH OH H] H CH2OH H OH ẞ-L-sorbose HOCH2 OH OH H HOCH2 H OH OH H OH H H CH2OH OH H H OH H I- H OH H OH Explanation Recheck W E R % 25 α B Y X & 5 D F G H McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Pr Parrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? + R -A HO IN + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardStuc X ctclix ALE X A ALE אן A ALEX Lab (195 X Nut x M Inb x NU X NUT X Unt x + → C www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQ1g8NUi-mObKa_ZLx2twjEhK7mVG6PulJI006NcKTV37JxMpZuyrVCdQolLAKqp_7U3r1GUD3... New Chrome available: Naomi Question 26 of 39 (4 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited Give the IUPAC name. 2,3-dimethylhexane Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of a constitutional isomer of the alkane above that contains a different number of carbons in its longest chain. Skip Part Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 3 Finance headline Q Search mwa Harvard Intensifi... X Save For Later 00 dlo HB Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility a 9:11 PM 4/22/2025arrow_forward
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: + NH2 HO A P+ H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓arrow_forward个 Stuc X ctclix ALE X A ALE × A ALE X Lab x (195 × Nut x M Inbx EF 目 → C www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQ1g8NUi-mObKa_ZLx2twjEhK7mVG6PulJI006NcKTV37JxMpz Chapter 12 HW = Question 27 of 39 (5 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Give the IUPAC name. Check 3 50°F Clear ©2025 McGraw Hill L Q Search webp a عالياكarrow_forward个 Stuck x ctc xALE X A ALE × A ALE X Lab x (19: x - G www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-1Q1g8NUi-mObka ZLx2twjEhK7mVG6PUUIO06 Chapter 12 HW 三 Question 26 of 39 (4 points) 1 Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited Answer the following questions about the given alkane. Part: 0 / 2 Part 1 of 2 Give the IUPAC name. Skip Part 2 53°F Clear Check × Q Search hp hp 02arrow_forward
- Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25.0 oC for the following equation. Cd(s) + Sn+2(aq) ↔Cd+2(aq) + Sn(s) Group of answer choices 3.11x104 1.95x1018 9.66x108 1.40x109arrow_forwardWhat is the pH at the cathode for the following cell written in line notation at 25.0 oC with a Ecell = -0.2749 V? Ni(s)|Ni+2(aq, 1.00 M)||H+1(aq, ?M)|H2(g, 1.00 atm)|Pt(s)arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell for a hydrogen fuel cell at 95.0 oC using the following half-reactions with PH2 = 25.0 atm and PO2 = 25.0 atm. O2(g) + 4H+1(aq) + 4e-1 → 2H2O(l) Eo = 1.229 V 2H2(g) → 4H+1(aq) + 4e-1 Eo = 0.00 Varrow_forward
- Calculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following half-reactions with [Ag+1] = 0.0100 M and [Sn+2] = 0.0200 M. Ag+1(aq) + 1e-1 Ag(s) Sn+2(aq) + 2e-1 Sn(s)arrow_forwardDone 18:19 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 27 of 39 (5 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .. LTE סוי 9 ✓ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Answer the following questions about the given alkane. Part: 0 / 2 Part 1 of 2 Classify each carbon atom as a 1º, 2º, 3º, or 4°. Highlight in red any 1° carbons, highlight in blue any 2° carbons. highlight in green any 3° carbons, and leave any 4° carbons unhighlighted. Skip Part Check Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility ☑ คarrow_forward< Done 19:22 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 4 of 39 (2 points) | Question Attempt: 5 of Unlimited : .. LTE סוי 1 ✓ 2 ✓ 3 = 4 ✓ 5 ✓ 6 ✓ 7 ✓ 8 ✓ 9 = 10 11 ✓ 12 Consider the molecule (CH3)2CHCH2CHCн for the following questions. Part 1 of 2 Which of the following molecules is/are constitutional isomer(s) to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH3? Check all that apply. Part 2 of 2 (CH3),C(CH2)2CH3 CH3 H,C-CH-CH-CH, CH 3 None of the above. ☑ Which of the following molecules is/are identical molecules to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH₁₂? Check all that apply. CH3 H,C-CH-CH₂-CH2-CH, CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 CH2-CH2-CH3 HỌC-CH=CH, 乂 ☑ а None of the above Check Save For Later Submit Assignment © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

