
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Based on the reaction, the product has to be predicted, name and formula for the product has to be given.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The product, name and formula for the product of the reaction is given below,
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced equation has to be written for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Balanced Chemical equation:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation which contains same elements in same number on both the sides (reactant and product side) of the chemical equation thereby obeying the law of conservation of mass.
Balancing the equation:
- There is a Law for conversion of mass in a
chemical reaction i.e., the mass of total amount of the product should be equal to the total mass of the reactants. - First write the skeletal reaction from the given information.
- Then count the number of atoms of each element in reactants as well as products.
- Place suitable coefficients in front of reactants as well as products until the number of atoms on each side (reactants and products) becomes equal.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The balanced equation is given below,
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
(c)
Interpretation:
Nature of the reaction (acid-base reaction, precipitation reaction, or an oxidation-reduction reaction) has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the reactant combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
(d)
Interpretation:
Formula of each product has to be predicted.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
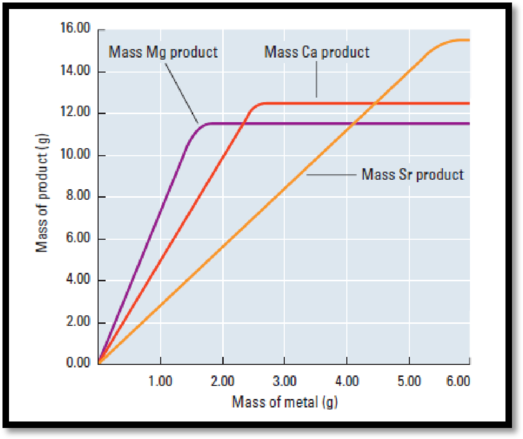
Figure 1
The mass of the metal is directly proportional to the mass of the compound formed.
From the graph, mass of sample is on the y-axis and the mass of the metal is on the x-axis and the fixed mass of the other reactant.
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 11.4 g
Mass of the Mg (metal) is 1.6 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Mg is 24.3050 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Mg is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Mg and bromine is given below,
0.066: 0.123
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 12.4 g
Mass of the Ca (metal) is 2.5 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Ca is 40.078 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Ca is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Ca and bromine is given below,
0.062: 0.124
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 15.3 g
Mass of the Sr (metal) is 5.5 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Sr is 87.62 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Sr is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Sr and bromine is given below,
0.063: 0.123
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: The Molecular Science, 5th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2 with Quick Prep 24-Months Printed Access Card
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





