
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 29, Problem 29.34P
Radical
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
10.
Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the
following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK!
H₂N
CI
OH
CI
カー
11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign
R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as
enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso.
NH2
H
HNH,
-18
b)
8.
Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur
Please explain your rational using 10 words or less
not likely to occur
• The double bond is still in the
Same position
+
Likely
to oc
occur
WHY?
-3
H3C
Brave
Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted
cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable
conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less.
CI
2
-cobs ??
MUST INDICATE H -2
-2
Br
EQ
Cl
OR
AT
Br
H&
most stable
WHY?
- 4
CH
12
Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the
compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the
conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided.
NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below
-4 NOT
HOH
OH
3
Conformer A:
Br
OH
A
Samo
Br H
04
Br
H
H3
CH₂
H
anti
stagere
Br CH
clipsed
H
Brott
H
IV
H
MISSING 2
-2
B
C
D
E
F
X
6
Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY:
13. (1
structure
LOWEST ENERGY:
Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the
corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry
when applicable.
a)
८८
2
"Br
{t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa
Parent name (noname)
4 Bromo
Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane
b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane
# -2
-2
Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 29.2 - Prob. 29.1PCh. 29.5 - Prob. 29.2PCh. 29.6 - Prob. AQCh. 29.6 - Prob. BQCh. 29.6 - Prob. CQCh. 29.6 - Prob. DQCh. 29.6 - Prob. EQCh. 29.6 - Prob. FQCh. 29.6 - Prob. 29.3PCh. 29.6 - Prob. 29.4P
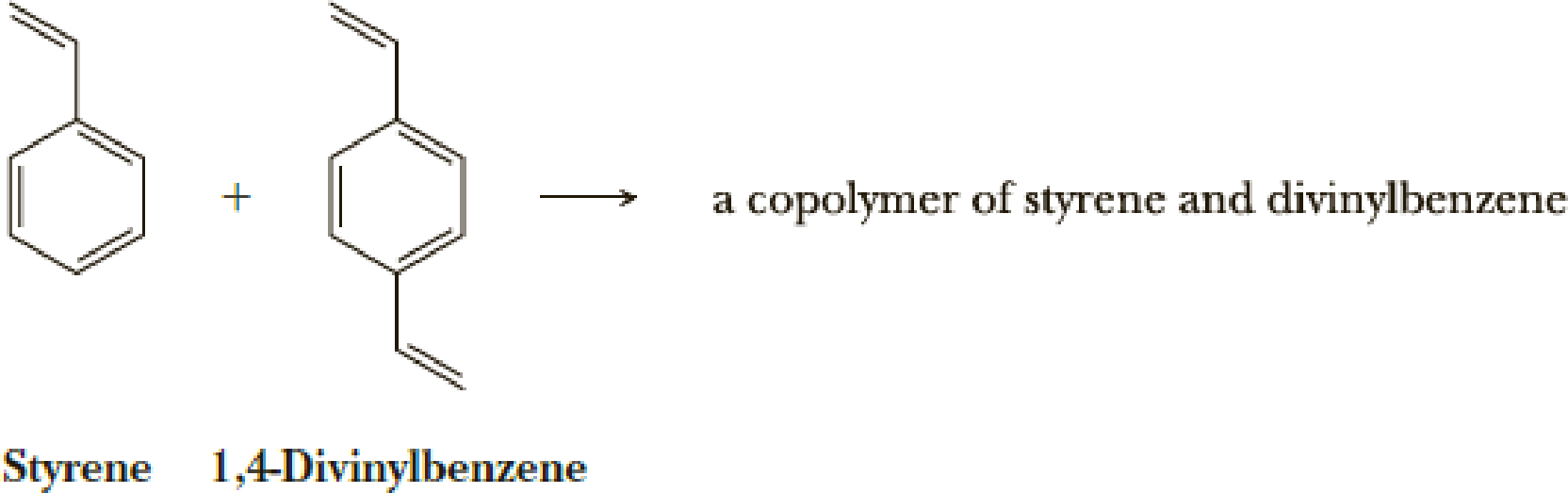
Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.5PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.6PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.7PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.8PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.9PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.10PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.11PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.12PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.13PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.14PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.15PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.16PCh. 29 - Polycarbonates (Section 29.5C) are also formed by...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.18PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.19PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.20PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.21PCh. 29 - Draw a structural formula of the polymer resulting...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.23PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.24PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.25PCh. 29 - Select the monomer in each pair that is more...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.27PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.28PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.29PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.30PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.31PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.32PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.33PCh. 29 - Radical polymerization of styrene gives a linear...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29.35PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.36PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.37PCh. 29 - Prob. 29.38P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry || Polymers || Full Chapter || By Shiksha House; Author: Best for NEET;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxdJlS0xZ0Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY