
Concept explainers
A particle in the cyclotron shown in Figure 28.16a gains energy qΔV from the alternating power supply each time it passes from one dee to the other. The time interval for each full orbit is
so the particle’s average rate of increase in energy’ is
Notice that this power input is constant in time. On the other hand, the rate of increase in the radius r of its path is not constant. (a) Show that the rate of increase in the radius r of the panicle’s path is given by
(b) Describe how the path of the particles in Figure 28.16a is consistent with the result of part (a). (c) At what rate is the radial position of the protons in a cyclotron increasing immediately before the protons leave the cyclotron? Assume the cyclotron has an outer radius of 0.350 m, an accelerating voltage of ΔV = 600 V, and a magnetic field of magnitude 0.800 T. (d) By how much does the radius of the protons’ path increase during their last full revolution?
Figure 28.16 (a) A cyclotron consists of an ion source at P, two does D1 and D2 across which an alternating potential difference is applied, and a uniform magnetic field. (The south pole of the magnet is not shown.) (b) The first cyclotron, invented by E. O. Lawrence and M. S. Livingston in 1934.
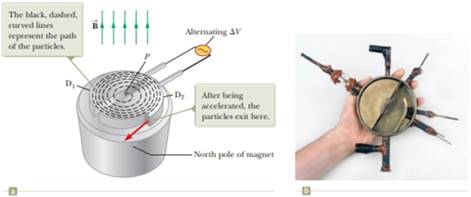
(a)
To prove: The rate of increase in the radius
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the energy is,
Here,
Differentiating equation (1) with respect to time
The above equation can be rewritten as,
Substitute
The formula for the centripetal force is,
The above equation can be rewritten as,
Differentiating equation (3) with respect to time
Deducing from equation (2) and equation (4),
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of increase in the radius
(b)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula of change of radius with time is,
The value of the path of the particle is consistent with respect to time as according to the above formula the path is dependent on the radius of circle and the magnitude of the magnetic field which remains constant for a path.
Thus, the path of the particle is consistent.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the path of the particle is consistent.
(c)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the change of radius with time is,
Substitute
Thus, the rate of increase of the radial direction of proton is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rate of increase of the radial direction of proton is
(d)
Answer to Problem 29.28P
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time interval of full orbit is
The formula for the velocity is,
Substitute
Thus, the velocity of proton is
The formula for the energy is,
Substitute
The formula for the energy at the end is,
Substitute
The formula for the radius at the end is,
Substitute
The formula for the increase in the radius is,
Substitute
Thus the increase in the radius of the path of proton is
Conclusion:
Therefore, increase in the radius of the path of proton is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- I need help with questions 1-10 on my solubility curve practice sheet. I tried to my best ability on the answers, however, i believe they are wrong and I would like to know which ones a wrong and just need help figuring it out.arrow_forwardQuestion: For a liquid with typical values a = 10-3K-¹ K = 10-4 bar-1 V=50 cm³ mol-1, Cp 200 J mol-1K-1, calculate the following quantities at 300 K and 1 bar for one mole of gas: 1. () P ән 2. (9) T 3. (V) T 4. (1) P 5. (9) T 6. Cv 7. (OF)Tarrow_forwardA,B,C AND Darrow_forward
- A bungee jumper plans to bungee jump from a bridge 64.0 m above the ground. He plans to use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 6.00 m above the water. Model his body as a particle and the cord as having negligible mass and obeying Hooke's law. In a preliminary test he finds that when hanging at rest from a 5.00 m length of the cord, his body weight stretches it by 1.55 m. He will drop from rest at the point where the top end of a longer section of the cord is attached to the bridge. (a) What length of cord should he use? Use subscripts 1 and 2 respectively to represent the 5.00 m test length and the actual jump length. Use Hooke's law F = KAL and the fact that the change in length AL for a given force is proportional the length L (AL = CL), to determine the force constant for the test case and for the jump case. Use conservation of mechanical energy to determine the length of the rope. m (b) What maximum acceleration will he…arrow_forward210. Sometimes the Helmholtz free energy F(T, V, N) divided by temperature, T, is an interesting quantity. For example, the quantity is proportional to the logarithm of the equilibrium constant or solubilities. A. Derive a relationship showing that Find the constant of proportionality. a F αυ ƏT T B. Suppose F(T) depends on temperature in the following way: F(T)=2aT²+bT. Find S(T) and U(T).arrow_forwardchoosing East (e) is not correct!arrow_forward
- disks have planes that are parallel and centered Three polarizing On a common axis. The direction of the transmission axis Colish dashed line) in each case is shown relative to the common vertical direction. A polarized beam of light (with its axis of polarization parallel to the horizontal reference direction) is incident from the left on the first disk with int intensity So = 790 W/m². Calculate the transmitted intensity if 81=28.0° O2-35.0°, and O3 = 40.0° w/m² horizontal Өз 02arrow_forwardA polarized light is incident on several polarizing disks whose planes are parallel and centered on common axis. Suppose that the transmission axis of the first polarizer is rotated 20° relative to the axis of polarization of the incident and that the transmission axis of each exis of light, additional analyzer is rotated 20° relative to the transmission axis the previous one. What is the minimum number of polarizer needed (whole number), so the transmitted light through all polarizing sheets has an Striking intensity that is less then 10% that the first polarizer?arrow_forwardA high energy pulsed laser emits 1.5 nano second-long pulse of average power 1.80x10" W. The beam is cylindrical with 2.00 mm in radius. Determine the rms value of the B-field? -Tarrow_forward
- A 23.0-mw (mill:-Watts) laser puts out a narrow cyclindrical beam 50 mm in diameter. What is the average N/C. rms E-field?arrow_forwardThe average intensity of light emerging from a polarizing sheet is. 0.550 W/m², and the average intensity of the horizontally polarized light incident on the sheet is 0.940 W/m². Determine the angle that the transmission axis of the polarizing sheet makes with the horizontalarrow_forwardwe measure an At a particular moment in time and space, electromagnetic wave's electric and magnetic fields. We find the electric field & pointing North and the magnetic field B pointing Down. What is the direction of wave propagation? a. South b. West C. c. Up d. Down e. East f. North.arrow_forward

 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning





