
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
AAU
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:
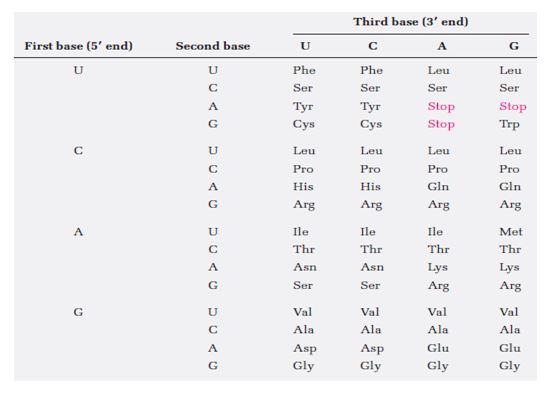
Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
AAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-AAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUU-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
AAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-AAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUU-(3’) |
b)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
GAG
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
GAG
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-GAG-(3’) | (5’)-CUC-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
GAG
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-GAG-(3’) | (5’)-CUC-(3’) |
c)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
UCC
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
UCC
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-UCC-(3’) | (5’)-GGA-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
UCC
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-UCC-(3’) | (5’)-GGA-(3’) |
d)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
CAU
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
CAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-CAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUG-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
CAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-CAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUG-(3’) |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- You are a Quality Manager for a very well-known food ingredient company that produces umami powder, and you are responsible for setting specification limits. The net weight (in grams) of bags of unami powder is monitored by taking samples of six bags on an hourly basis during production. The label on every bag reports a contents of 1KG umami powder. The process mean is μ = 1012 g, and when the process is properly adjusted, it varies with σ = 11 g. QUESTION: Using all the available information, set the upper and lower specification limits.arrow_forward43) 10.00 ml of vinegar (active ingredient is acetic acid) is titrated to the endpoint using 19.32 ml of 0.250 M sodium hydroxide. What is the molarity of acetic acid in the vinegar? YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. NOTE: MA x VA = MB x VBarrow_forward424 Repon Sheet Rates of Chemical Reactions : Rate and Order of 1,0, Deception B. Effect of Temperature BATH TEMPERATURE 35'c Yol of Oh نام Time 485 Buret rend ing(n) 12 194 16. 6 18 20 10 22 24 14 115 95 14738 2158235 8:26 CMS 40148 Total volume of 0, collected Barometric pressure 770-572 ml mm Hg Vapor pressure of water at bath temperature (see Appendix L) 42.2 Slope Compared with the rate found for solution 1, there is Using the ideal gas law, calculate the moles of O; collected (show calculations) times faster 10 Based on the moles of O, evolved, calculate the molar concentration of the original 3% 1,0, solution (sho calculations)arrow_forward
- Steps and explanations pleasearrow_forwardUse diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward

 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





