
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of MOs in the given compound
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
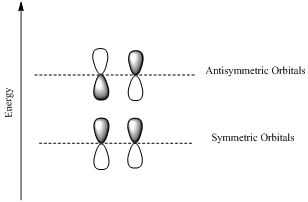
(b)
Interpretation: The designation of HOMO for the given molecule’s molecular orbital has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
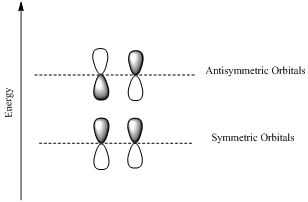
(c)
Interpretation: Number of nodes in the given molecule has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
Node is the site with zero electron density.
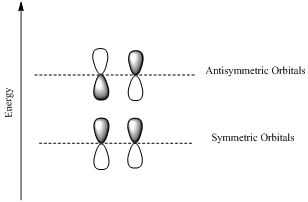
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
- Draw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forwardDraw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forward
- Answer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forward
- Syntheses 22.35 Show how to convert toluene to these compounds. (a) -CH,Br (b) Br- -CH3 22.36 Show how to prepare each compound from 1-phenyl-1-propanone. 1-Phenyl-1-propanone ہتی. Br. (b) Br (racemic) 22.37 Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid. 22.38 Show reagents and conditions to bring about the following conversions. (a) 9 NH2 8 CO₂H NH2 CO₂Et (d) NO2 NH2 S NH₂ NO2 CHS CHarrow_forwardive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardCalculate the stoichiometric amount of CaCl2 needed to convert all of the CuSO4 into CuCl2.arrow_forward
- H CH تنی Cl 1. NaCN, DMF 2. LIAIH4, ether H₂O pyridine N NH₂ 5 CH H 1 HNO, H₂SO 2. Nal NH2 Br Br HNO₂ CuCl H₂SO HCI CH3 H3C NN HSO KCN CuCN 1. HNO₂, H₂SO O₂N NH2 2. OH ཀ་ལས། །ས་ཅན་ :i་དེ་མ་མ་སེ་ NH₂ CH3 1. HNO₂, H₂SO4 2. H3PO₂ 1 HNO2, H2SO4 2. Nalarrow_forwardive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardIf a pharmacy chain sold 65 million 500-mg tablets of aspirin, how many US tons of aspirin does this represent? Report your answer to 2 significant figures.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
