
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The two product in the given reaction are formed after [1, 7] sigmatropic rearrangement, one due to hydrogen migration and the other to deuterium migration. It should be represented the configuration of product by replacing the A and B with appropriate atoms (H or D)
Concept introduction:
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
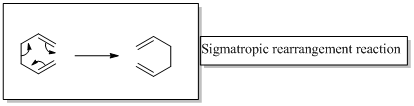
Sigma tropic rearrangement reactions are designated with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigma tropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3
Woodward –Hoffmann rules are the set of rules used to vindicate or predict certain aspects of the stereo chemical outcome and activation energy of pericyclic reactions.
Woodward – Hoffmann rules for sigma tropic rearrangement reactions are listed below
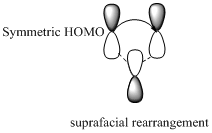
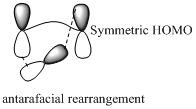
Migration of carbon and hydrogen will occur in a sigmatropic rearrangement reaction. Migration of hydrogen in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,


Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting

Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Modified MasteringChemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card; Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (7th Edition)
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forwardtheres 2 productsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forwardDifferentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forward
- An aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the first photoarrow_forward
- Ggggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forwardExplain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.arrow_forwardBriefly describe a nucleophilic addition.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

