
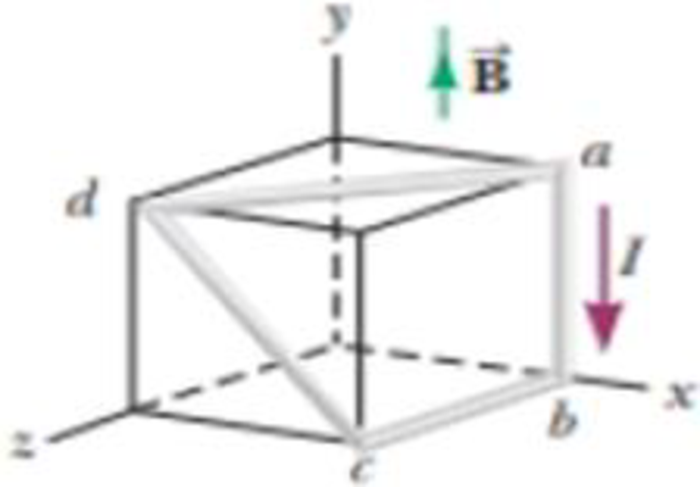
In Figure P28.28, the cube is 40.0 cm on each edge. Four straight segments of wire—ab, bc, cd, and da—form a closed loop that carries a current I = 5.00 A in the direction shown. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.020 0 T is in the positive y direction. Determine the magnetic force vector on (a) ab, (b) bc, (c) cd, and (d) da. (c) Explain how you could find the force exerted on the fourth of these segments from the forces on the other three, without further calculation involving the magnetic field.
Figure P28.28
(a)
The magnetic force vector on
Answer to Problem 28P
The magnetic force vector on
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
As the current flows down and the magnetic from point
Substitute
The magnitude of the force is zero because an equal and opposite force cancels it due to which the magnetic force of
Conclusion:
Therefore, magnetic force vector on
(b)
The magnetic force vector on
Answer to Problem 28P
The magnetic force vector on
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
As the current flows down and the magnetic from point
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the x axis direction. Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is in
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(c)
The magnetic force vector on
Answer to Problem 28P
The magnetic force vector on
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
Use Pythagoras theorem to find
Substitute
As the current flows at an angle and the magnetic from point b is perpendicular so the angle
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the z axis direction. Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is in z direction.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(d)
The magnetic force vector on
Answer to Problem 28P
The magnetic force vector on
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
The formula for the magnetic force is,
Here,
Use Pythagoras theorem to find
Substitute
As the current flows vertically and the magnetic from point b is perpendicular so the angle
Substitute
By using the Flemings right hand rule, the thumb points towards the direction d
The direction of the force is,
Thus, the direction of the magnetic force is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force vector on
(e)
How to find the force exerted on the forth segment from the forces on the other three.
Answer to Problem 28P
The force exerted on the forth segment from the forces on the other three can be calculated by the parallelogram law of vectors.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The length of each edge of the cube is
By the parallelogram law of forces, when the forces on three of the arms of a parallelogram are provided then the magnitude of force on the forth arm is equal to the resultant of the other three forces.
According to the parallelogram law of vectors,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted on the forth segment from the forces on the other three can be calculated by the parallelogram law of vectors.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- According to the provided information answer the question accorrding to grade 11 physics Jerry has decided to give up his part-time job for a new career, cat-burglar! Jerry loves the idea of dressing up like a cat all day and of course the chance of meeting Cat Woman! On Jerry's first "job" he figures out his escape plan. He travels 3.0 km south for 15 minutes and then 8.0 km west for 1.5 hours before reaching his house. Draw a sketch diagram of the path he took with all the appropriate labels.arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer all parts of the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





