
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of pericyclic reaction required to form benzene from Dewar benzene is to be stated.
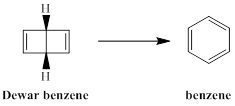
Concept introduction:
The isomer of benzene having bicyclic ring with the molecular formula of C6H6 is termed as Dewar benzene or bicyclo [2, 2, 0] hexa-2, 5-diene. This structure is included in the list of possible structure of benzene and named after James Dewar. However, this bicyclic ring structure is not accepted as the true structure of benzene and Dewar supported the Kekule structure of benzene.
(b)
Interpretation:
Dewar benzene, although a very unstable molecule, is not readily transformed to benzene is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions deal with electrons shift in a concerted manner. Moreover, in these reactions the breaking of reactant bonds and the formation of product bonds are formed at the same time. Notably, the pericyclic reactions are classified as electrocyclic, cycloaddition and sigmatropic reactions based on the activation of reaction, the number of electrons involved and the stereochemistry outcome of the reactions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forwardC. I, II, III Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following questions: 0 0 1. NaOEt, EtOH ΕΙΟ OEt 2 Compound X CO₂Et NaOEt, EtOH CO₂Et Br Compound Y A Compound Z A. Compound X, diethyl propanedioate, is more commonly known as a. ethyl acetoacetate acetoacetic ester b. C. oxalic ester d. malonic ester B. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the conversion of Compound X into Compound Y. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures.arrow_forwardDiethyl malonate can be prepared by the following reaction sequence. Draw the structures of each of the missing intermediates in the boxes provided EtO 0 H3C 11 C 1. Br₂ PBr OH 2 H₂O 010 0 CH3CH₂OH C CH2 OEt Ha CH3CH2OH на NaCN H₂SO4 NC H₂O, heat CH2 OCH2CH3arrow_forward
- Show how you would accomplish each of the following transformations. More than one step may be quired. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. [three only] A. 0 CH3 B. C. D. H 0 0 OCH 3 CH₂CO₂CH2CH3 H3C ➤ HN C NO₂ Clarrow_forwardChoose the BEST reagent for carrying out each of the following conversions. A. CO₂CH3 CO₂CH3 0 CO₂H a. LiAlH4, ether C. CrO3, pyridine B. 0 H a. C. NaBH4, ethanol NaOH, H2O CO₂H OH HD b. NaBH4, ethanol d. H₂/Pd CH₂OH b. CH₂PPh3 d. All of the abovearrow_forwardWrite the complete stepwise mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following amide to yield mandelic acid. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw the structures of all intermediate species. OH H-OH₂ CnH2 :0: OH C OH + NH4 10: The purpose of the acid catalyst in the hydrolysis of an amide is: to enhance the electrophilicity of the amide carbonyl carbon a. to enhance the nucleophilicity of the water molecule b. C. to enhance the electrophilicity of the water molecule d. to shift the equilibrium of the reactionarrow_forward
- 1.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward. Provide IUPAC names for each of the following structures OR draw structures corresponding to each of the following names: [Three only]kk a. H₂N- 0 COCH2CH3 benzocaine b. What is the correct structure for phenylbenzoate? C a. 0 C-O O b. H3C-C-O 0 0 C-O-CH3 d. CH₂O C-CHZ c. Acetyl chloride d. 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloridearrow_forward
- . Draw structures corresponding to each of the following names or Provide IUPAC names for each of the ollowing structures [for 4 ONLY]. A. 2-propylpentanoic acid. B. m-chlorobenzoic acid. C. 0 0 HOC(CH2) COH glutaricadd D. E. F. 0 OH HO OH HO INCO salicylicadd H3C CH3 C=C tgicadd H COOH CH₂C=N 4arrow_forwardThe reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed Fischer esterification. 0 0 C .C. OH + CH3OH OCH3 + H₂O HCI A B C A. The nucleophile in this reaction is B. Compound C functions as a. a base scavenger b. a solvent C. a catalyst in this reaction. d. a neutralizer C. Fischer esterification is an example of: ........ a. nucleophilic acyl addition b. nucleophilic acyl substitution c. nucleophilic acyl elimination d. nucleophilic acyl rearrangementarrow_forwardThe Handbook of Chemistry and Physics gives solubilities of the following compounds in grams per 100 mL of water. Because these compounds are only slightly soluble, assume that the volume does not change on dissolution and calculate the solubility product for each. (a) BaSeO4, 0.0118 g/100 mLarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





