
Concept explainers
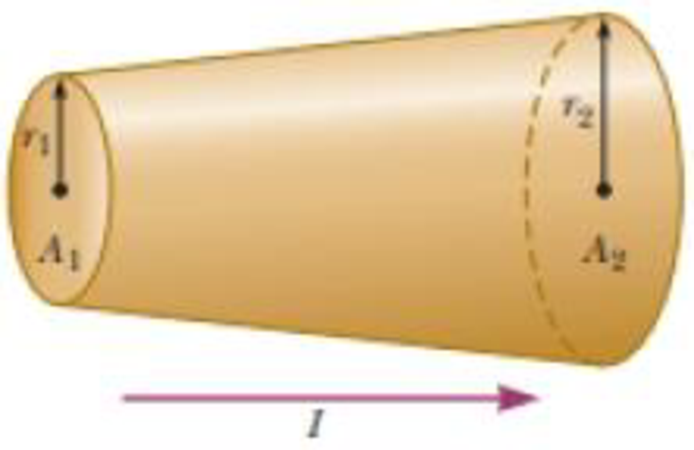
Figure P26.6 represents a section of a conductor of nonuniform diameter carrying a current of I = 5.00 A. The radius of cross-section A1 is r1 = 0.400 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the current density across A1? The radius r2 at A2 is larger than the radius r1 at A1. (b) Is the current at A2 larger, smaller, or the same? (c) Is the current density at A2 larger, smaller, or the same? Assume A2 = 4A1. Specify the (d) radius, (e) current, and (f) current density at A2.
Figure P26.6
(a)
The magnitude of the current density across
Answer to Problem 6P
The magnitude of the current density across
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
Write the expression for the area of cross section of a conductor.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the area of cross section of a conductor is
Formula to calculate the current density across
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the magnitude of the current density across
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the current density across
(b)
The reason that the current at
Answer to Problem 6P
The current at
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
The current is not depending on cross sectional area. So, the current at
Thus, the density at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the density at
area. So, the current at
(c)
The reason that the current density at
Answer to Problem 6P
The current density at
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
From equation (2),
Formula to calculate the current density across
Here,
Formula to calculate the current density across
Here,
From above relations, the current density is inversely proportional to area of cross section. From the figure given in the question, it is shown that:
Hence, the current density at
Thus, the current density at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current density at
(d)
The radius of cross section at
Answer to Problem 6P
The radius of cross section at
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
It is given that the expression for the crossectional area is:
From equation (1),
Write the expression for the area of cross section of a conductor
Write the expression for the area of cross section of a conductor
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the area of cross section of a conductor is
Thus, the radius of cross section at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the radius of cross section at
(e)
The current for cross section at
Answer to Problem 6P
The current for cross section at
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
The current is not depending on cross sectional area. So, the current at
Thus, the current for cross section at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current for cross section at
(f)
The magnitude of the current density across
Answer to Problem 6P
The magnitude of the current density across
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Current carried by a conductor is
Write the expression for the area of cross section of a conductor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the area of cross section of a conductor is
Formula to calculate the current density across
Substitute
Thus, the magnitude of the current density across
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the current density across
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Atoms First
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- RT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





