
Concept explainers
Inhibition of Purine and Pyrimidine
(a)
Interpretation:
A reaction of purine or pyrimidine metabolism is affected by the azaserine.
Concept Introduction:
Azaserine and DON are equivalents of glutamine and bind to glutamine-binding proteins. They can react with nucleophiles, leading to covalent modification and inactivation.
Answer to Problem 4P
Azaserine and DON are equivalents of glutamine and bind to glutamine-binding proteins. They can react with nucleophiles, leading to covalent modification and inactivation. The following reactions in purine synthesis are sensitive to these inhibitors.
There is another reaction that's sensitive to those inhibitors for the synthesis of pyrimidines.
Explanation of Solution
There are 3 structures that are analogs to amino acid, and that they are azaserine (O-diazoacetvl-Lserine) and a connected compound DON, and 6-diaxo-5-oxo-L-norleucine. Their structures are shown below:
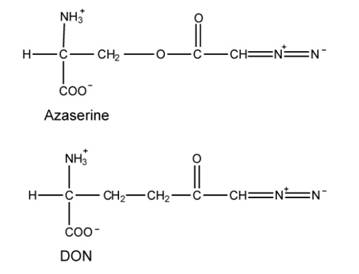
Azaserine and DON are equivalents of glutamine and bind to glutamine-binding proteins. They can react with nucleophiles, leading to covalent modification and inactivation. The following reactions in purine synthesis are sensitive to these inhibitors.
There is another reaction that's sensitive to those inhibitors for the synthesis of pyrimidines.
(b)
Interpretation:
A reaction of purine or pyrimidine metabolism is affected by the methotrexate.
Concept Introduction:
Methotrexate is analogous to dihydrofolate in this it competes with folic acid with high affinity for binding sites on enzymes. Some reactions in purine synthesis are affected.
Answer to Problem 4P
The formation of tTMP in pyrimidine synthesis will be blocked by methotrexate sodium. The reaction is seen below.
Explanation of Solution
Methotrexate is analogous to dihydrofolate in this it competes with folic acid with high affinity for binding sites on enzymes. Some reactions in purine synthesis are affected.
The formation of tTMP in pyrimidine synthesis will be blocked by methotrexate sodium. The reaction is seen below.
(c)
Interpretation:
A reaction of purine or pyrimidine metabolism is affected by the sulfonamides.
Concept Introduction:
Sulfonamides are structurally the same as para-aminobenzoic acid. They inhibit the assembly of folacin in bacterium.
Answer to Problem 4P
Ester synthesis in animals won't be littered with sulfonamides since folacin is an element of a dietary demand for animals.
Explanation of Solution
Sulfonamides are structurally the same as para-aminobenzoic acid. They inhibit the assembly of folacin in bacterium. This inhibition can happen as a result of they cannot produce folacin because of lack of substrate. Ester synthesis in animals won't be littered with sulfonamides since folacin is an element of a dietary demand for animals.
(d)
Interpretation:
A reaction of purine or pyrimidine metabolism is affected by the allupurinol.
Concept Introduction:
Xanthine enzyme can hydroxylate Zyloprim, a suicide substance of organic compound enzyme, to create alloxantine that binds to the catalyst and inactivates it.
Answer to Problem 4P
Organic compound is regenerate to uric acid via the catalyst organic compound enzyme, and excrement acids will not form as a result of its blocked because of each nucleoside and nucleoside that are metabolized to organic compound.
Explanation of Solution
Xanthine enzyme can hydroxylate Zyloprim, a suicide substance of organic compound enzyme, to create alloxantine that binds to the catalyst and inactivates it. Organic compound is regenerate to uric acid via the catalyst organic compound enzyme, and excrement acids will not form as a result of its blocked because of each nucleoside and nucleoside that are metabolized to organic compound.
(e)
Interpretation:
A reaction of purine or pyrimidine metabolism is affected by the 5-fluorouracil.
Concept Introduction:
5-fluorouracil is converted to 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate (FdUMP), which is a powerful inhibitor of thymidylate synthase.
Answer to Problem 4P
Even though 5-fluorouracil is not a significant inhibitor of nucleotide metabolism, it is converted to 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate (FdUMP), which is a powerful inhibitor of thymidylate synthase.
Explanation of Solution
Even though 5-fluorouracil is not a significant inhibitor of nucleotide metabolism, it is converted to 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate (FdUMP), which is a powerful inhibitor of thymidylate synthase.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Biochemistry
- The following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P Question: what would the rate be at 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] and the enzyme concentration was doubled? Also, the rate given in the table is from product accumulation after 10 minuets of reaction time. Verify these rates represent a true initial rate (less than 5% turnover). Please helparrow_forwardThe following data was obtained on isocitrate lyase from an algal species. Identify the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme, deduce the KM and Vmax , and determine the nature of the inhibition by oxaloacetate. Please helparrow_forwardIn the table below, there are sketches of four crystals made of positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. Rank these crystals in decreasing order of stability (or equivalently increasing order of energy). That is, select "1" below the most stable (lowest energy) crystal. Select "2" below the next most stable (next lowest energy) crystal, and so forth. A B 鹽 (Choose one) +2 C +2 +2 (Choose one) D 鹽雞 (Choose one) (Choose one)arrow_forward
- 1. Draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2: w-3 and B. 18:3:49,12,15 2. Name each of the molecules below (image attached)arrow_forwarddraw the structures for the fats A. 16:2:w-3 B 18:3:9,12,15arrow_forward1. Below is a template strand of DNA. Show the mRNA and protein that would result. label the ends of the molecules ( refer to attached image)arrow_forward
- Attach the followina labels to the diagram below: helicase, single stranded binding proteins, lagging strand, leading strand, DNA polymerase, primase, 5' ends (3), 3' ends (3) (image attached)arrow_forward1. How much energy in terms of ATP can be obtained from tristearin (stearate is 18:0) Show steps pleasearrow_forwardMultiple choice urgent!!arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





