
Organic Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780321803221
Author: Paula Y. Bruice
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 26, Problem 30P
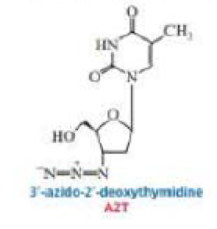
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the retrovirus that causes AIDS. AZT was one of the first drugs designed to interfere with retroviral DNA synthesis. When cells take up AZT, they convert it to AZT-triphosphate. Explain how AZT interferes with DNA synthesis.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
When propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.
Draw mechanism
Does Avogadro's number have units?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 26.1 - In acidic solutions, nucleosides are hydrolyzed to...Ch. 26.1 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 26.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 26.3 - Indicate whether each functional group of the five...Ch. 26.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 26.3 - If one of the strands of DNA has the following...Ch. 26.4 - The 2',3-cyclic phosphodiester that is formed...Ch. 26.5 - Using a dark line for the original parental DNA...Ch. 26.7 - Why do both thymine and uracil specify the...Ch. 26.9 - If methionine is always the first amino acid...
Ch. 26.9 - Four Cs occur in a row in the segment of mRNA...Ch. 26.9 - UAA is a stop codon. Why does the UAA sequence in...Ch. 26.9 - Prob. 13PCh. 26.9 - Write the sequences of bases in the sense strand...Ch. 26.9 - List the possible codons on mRNA that speciy each...Ch. 26.10 - Adenine can be deaminated to hypoxanthine, and...Ch. 26.10 - Explain why thymine cannot be deaminated.Ch. 26.12 - Which of the following base sequences is most...Ch. 26 - Name the following:Ch. 26 - What nonapeptide is coded for by the following...Ch. 26 - What is the sequence of bases in the template...Ch. 26 - Prob. 22PCh. 26 - Prob. 23PCh. 26 - Prob. 24PCh. 26 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 26 - A segment of DNA has 18 base pairs. It has 7...Ch. 26 - Match the codon with the anticodon:Ch. 26 - Prob. 28PCh. 26 - Which of the following pairs of dinucleotides are...Ch. 26 - Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the...Ch. 26 - If a mRNA contained only U and G in random...Ch. 26 - Why is the codon a triplet rather than a doublet...Ch. 26 - RNAase, the enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis...Ch. 26 - The amino acid sequences of peptide fragments...Ch. 26 - Which cytosine in the following sense strand of...Ch. 26 - Prob. 36PCh. 26 - Sodium nitrite, a common food preservative (page...Ch. 26 - Why does DNA not unravel completely before...Ch. 26 - Staphylococcus nuclease is an enzyme that...Ch. 26 - The first amino acid incorporated into a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forwardIndicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alanine and histidine write the amididation reaction mechanism using arrows then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction and the one letter code for the product of the reaction.arrow_forward
- Name the following molecules using iupacarrow_forwardWrite the amididation reaction mechanism of a-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophenarrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
Nucleic acids - DNA and RNA structure; Author: MEDSimplified;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0lZRAShqft0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY