
Concept explainers
a)
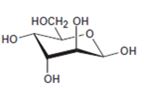
Interpretation:
The open-chain form of the sugar given is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The pyranose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a six membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C1 carbonyl group. The furanose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a five membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C2 carbonyl group.
The orientation of –OH group differs in α- and β- anomers. In α- anomer the OH on C1 is cis to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection while in β- anomer the –OH on C1 is trans to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection.
D sugars have the –O- at C5 on the right in the uncoiled form while L sugars have -O- at C5 on the left.
To draw:
The open-chain form of the sugar given.
b)
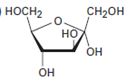
Interpretation:
The open-chain form of the sugar given is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The pyranose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a six membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C1 carbonyl group. The furanose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a five membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C2 carbonyl group.
The orientation of –OH group differs in α- and β- anomers. In the α- anomer the OH on C1 is cis to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection, while in β- anomer the –OH on C1 is trans to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection.
D sugars have the –O- at C5 on the right in the uncoiled form while L sugars have -O- at C5 on the left.
To draw:
The open-chain form of the sugar given.
c)
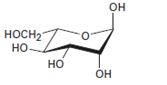
Interpretation:
The open-chain form of the sugar given is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The pyranose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a six membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C1 carbonyl group. The furanose form is a cyclic hemiacetal form with a five membered ring formed by the nucleophilic addition of the –OH group on C5 to the C2 carbonyl group.
The orientation of –OH group differs in α- and β- anomers. In the α- anomer the OH on C1 is cis to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection, while in β- anomer the –OH on C1 is trans to the –OH at the lowest chirality center in Fischer projection.
D sugars have the –O- at C5 on the right in the uncoiled form while L sugars have -O- at C5 on the left.
To draw:
The open-chain form of the sugar given.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 25 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- need help not sure what am doing wrong step by step please answer is 971A During the lecture, we calculated the Debye length at physiological salt concentrations and temperature, i.e. at an ionic strength of 150 mM (i.e. 0.150 mol/l) and a temperature of T=310 K. We predicted that electrostatic interactions are effectively screened beyond distances of 8.1 Å in solutions with a physiological salt concentration. What is the Debye length in a sample of distilled water with an ionic strength of 10.0 µM (i.e. 1.00 * 10-5 mol/l)? Assume room temperature, i.e. T= 298 K, and provide your answer as a numerical expression with 3 significant figures in Å (1 Å = 10-10 m).arrow_forwardInfluence of salt concentrations on electrostatic interactions 2 Answer is 2.17A why not sure step by step please What is the Debye length in a concentrated salt solution with an ionic strength of 2.00 mol/l? Assume room temperature, i.e. T= 298 K, and provide your answer as a numerical expression with 3 significant figures in Å (1 Å = 10-10 m).arrow_forwardThe name of the following molecule is: Νarrow_forward
- The table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which is the most brittle and which is the most tough (or most resistant). Breaking strength Elastic modulus Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain A (MPa) 415 (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) 550 0.15 500 310 B 700 850 0.15 720 300 C Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardMaterials. The following terms are synonyms: tension, effort and stress.arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardThe table shows the tensile stress-strain values obtained for various hypothetical metals. Based on this, indicate which material will be the most ductile and which the most brittle. Material Yield strength Tensile strength Breaking strain Breaking strength Elastic modulus (MPa) (MPa) (MPa) (GPa) A 310 340 0.23 265 210 B 100 120 0.40 105 150 с 415 550 0.15 500 310 D 700 850 0.14 720 210 E - Non-effluence fracture 650 350arrow_forward

 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





