
(a)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
Appropriate curved arrow for the homolysis of the
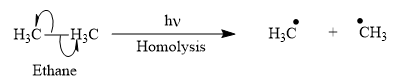
The product for the homolysis of the
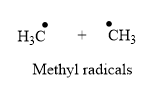
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus, the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus, the product of the homolysis of the
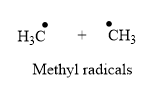
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
(b)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
Appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of the
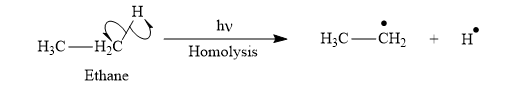
The product for the homolysis of the
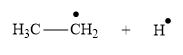
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
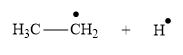
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of a
(c)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
The appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of t the
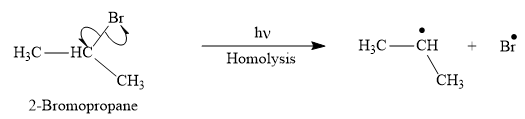
The product for the homolysis of the
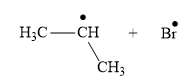
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the

Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
(d)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
The appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of the
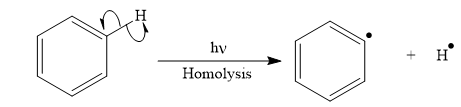
The product for the homolysis of the
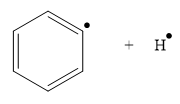
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the

Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. + Drawing Arrows CH3ONA, CH3OH heat : Br:O Na → H H Br Na + H H H H H :0: .H + Undo Reset Done Q CH3 Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardWhat is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 20.19 Predict the structure of the major 1,2-addition product formed by reaction of one mole of Cl₂ with 3-methylenecyclohexene. Also predict the structure of the 1,4-addition product formed under these conditions. 20.20 Which of the two molecules shown do you expect to be the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene? Explain. Cyclopentadiene + HC 3-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic) or 4-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic)arrow_forward20.35 Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and specify the configuration of compound B. EtO₂C 250°C C14H2004 CO₂Et 1. Oso, then NaHSO3 2. HIO4 C14H2006 A Barrow_forward20.21 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene. 20.22 Draw structural formulas for the two constitutional isomers with the molecular for- mula C₂H,Br, formed by adding one mole of Br, to cyclopentadiene.arrow_forward
- Add substituents to draw the conformer below (sighting down the indicated bond), then rotate the back carbon to provide the conformation that will be capable of an E2 elimination. R/S stereochemistry is graded. + I I H CH3 Ph Досн Br OCH 3 Drawing Q H Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Tap a node to see suggestions. H H H H H Undo Reset Remove Done Rotatearrow_forward20.17 Predict the structure of the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene. 3-Methylenecyclohexene 20.18 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene.arrow_forward+ Draw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br Drawing Strong Base H Q Atoms, Bonds Charges and Rings Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Remove Done 語 Reset Undo + Drag To Panarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





