
Concept explainers
Figure 25-18 shows plots of charge versus potential difference for three parallel-plate capacitors that have the plate areas and separations given in the table. Which plot goes with which capacitor?
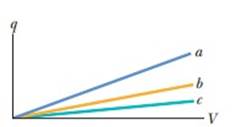
Figure 25-18 Question 1.
| Capacitor | Area | Separation |
| 1 | A | d |
| 2 | 2A | d |
| 3 | A | 2d |
To find:
Which plot goes with which capacitor.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
Plot a goes with the capacitor 2. The plot b goes with capacitor 1 and plot c goes with capacitor 3.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Using Eq.25-9, we can find capacitance of each capacitor from the given values of area and plate separation. Then using Eq.25-1, we can compare the capacitance from the slopes of the plots. Then, comparing the predictions about the capacitance yielded from both the equations, we can find out which plot goes with which capacitor.
2) Formulae:
i) From Eq.25-1, the charge
ii) From Eq.25-9, the capacitance is
3) Given:
i) For capacitor 1, area is
ii) For capacitor 2, area is
iii) For capacitor 3, area is
iv) For capacitor 1, separation is
v) For capacitor 2, separation is
vi) For capacitor 3, separation is
4) Calculations:
From Eq.25-1, the charge
where
Therefore, the capacitance is given by
From Eq.25-9, the capacitance is
where
Let,
Capacitor 1 has capacitance,
Similarly, Capacitor 2 has capacitance,
And Capacitor 3 has capacitance,
From this, we can interpret that capacitance of capacitor 2 has the greatest value and capacitor 1 has the greater capacitance than that of capacitor 3.
From the graph, we can infer that the plot a has the greatest slope. Hence, the capacitance and the slope of plot b is greater than that of plot c. Hence, corresponding capacitance.
Therefore, we can conclude that, Plot a goes with capacitor 2, plot b goes with capacitor 1 and plot c goes with capacitor 3.
Conclusion:
We can predict about the plots between the charge and the voltage corresponding to capacitors having some area and separation between the plates of capacitor from the slope of the graph and the formula for capacitance.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- Three objects with masses m₁ = 3.8 kg, m₂ = 12 kg, and m 19 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m2. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to find the speed of m¸ after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s m m2 mgarrow_forwardIn order for Jane to return to base camp, she needs to swing across a river of width D that is filled with alligators. She must swing into a wind exerting constant horizontal force F, F = 110 N, L = 40.0 m, 0 = 50.0°, and her mass to be 50.0 kg. Wind →F Tarzan! Jane (a) with what minimum speed (in m/s) must Jane begin her swing to just make it to the other side? (If Jane can make it across with zero initial velocity, enter 0.) m/s on a vine having length L and initially making an angle with the vertical (see below figure). Take D = 48.0 m, (b) Shortly after Jane's arrival, Tarzan and Jane decide to swing back across the river (simultaneously). With what minimum speed (in m/s) must they begin their swing? Assume that Tarzan has a mass of 80.0 kg. m/sarrow_forwardR=2.00 12V 2.00 4.00 4.002 What is the current in one of the 4.0 Q resistors? An isolated point charge q is located at point X. Two other points Y and Z are such that YZ2 XY. Y X What is (electric field at Y)/(electric field at Z)?arrow_forward
- Two objects (m₁ = 4.75 kg and m₂ 2.80 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.75-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table mg m (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s (b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.75-kg object hits the table. m/s (c) How much higher does the 2.80-kg object travel after the 4.75-kg object hits the table? marrow_forwardA cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to three identical resistors. The current in the cell is 3.0 A. The resistors are now arranged in series. What is the new current in the cell?arrow_forwardA negatively charged sphere is falling through a magnetic field. north pole of magnet direction of motion south pole of magnet What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the sphere?arrow_forward
- Electrons in a conductor are moving down the page. A proton outside the wire is moving to the right. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton?arrow_forwardWhat is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter and the resistance of an ideal ammeter? Resistance of an ideal voltmeter Resistance of an ideal ammeter infinite A. zero B. zero zero C. infinite infinite D. infinite zeroarrow_forwardvariable resistor with a resistance range of 0 to 6.0 KQ is connected in series with two resistors of fixed value 6.0 KQ. The cell in the circuit has an emf of 18 V and a negligible internal resistance. 18 V X Y 6.0 ΚΩ 6.0 ΚΩ 0 - 6.0 ΚΩ What is the maximum range of potential difference that can be observed between X and Y?arrow_forward
- A positive point charge of magnitude 1.0 μC and a point charge q are separated by a distance d. electron 1.0 με An electron is placed at a distance d from the +1.0 μC charge. The electric force on the electron is zero. What is q?arrow_forwardTwo point charges of +4q and -q are placed a fixed distance apart. Where is the electric field strength equal to zero? B. +49 D. A network of three resistors is connected to a cell of emf 12V and internal resistance R of 2.0 Q as shown.arrow_forwardThree point charges of equal magnitude are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The signs of the charges are shown. Point P is equidistant from the vertices of the triangle. What is the direction of the resultant electric field at P? B.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





