
(a)
Interpretation:
The reason for the isotope
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required for breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons.
Explanation of Solution
The graph is represented as follows:
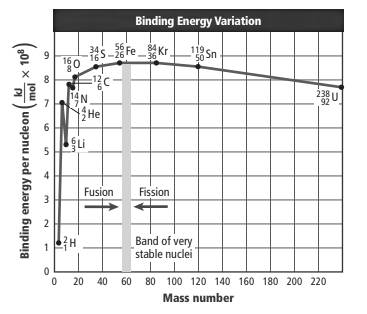
The above graph shows a change in binding energy per nucleon with an increase in mass numbers.
This can be seen from the graph that isotope
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and the nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Here, the element with a mass number near 60 is most stable and it has maximum binding energy per nucleon.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether more stable isotopes are located higher or lower on the curve needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Explanation of Solution
The more stable isotopes have large binding energy per nucleons. The energy increases on moving from bottom to top in the graph thus, the isotopes located higher on the curve have maximum binding energy per nucleons thus, they are more stable isotopes.
(c)
Interpretation:
The stability of Li-6 and He-4 needs to be compared.
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Explanation of Solution
The binding energy curve is represented as follows:
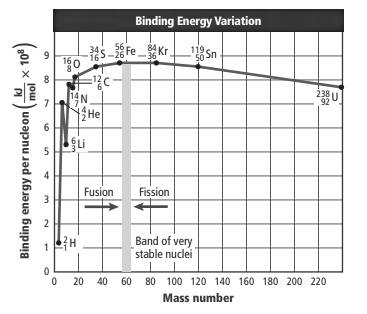
The points are represented for Li-6 and He-4. Here, mass number of Li is more than He but both are less than 60.
The binding energy per nucleon is less for Li-6 and it is approximately
Chapter 24 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- What parameters are included in the specific rotation calculation of a pure substance based on measurement from a polarimeter? Select one or more: Density of the sample Pathlength of the sample container Enantiomeric excess of the sample Measured rotation of lightarrow_forwardV Determine whether the following molecule is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither and select the appropriate box below. Also, highlight the hemiacetal or acetal carbon if there is one. Explanation O CH O Ohemiacetal Oacetal Oneither Check A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Cer 000 Ararrow_forward1. Using Online resources and chemical structures hand draw four different organic compounds (not those already shown in your handout) that are chiral, optically active (a pair of enantiomers will count as one). Pay attention to correct stereochemistry 2. Write or type a short paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the four compounds.arrow_forward
- 1. Using a Model set Build a model for the following compound [CHBRIF] 2. Build another model of the mirror image of your first molecule. 3. Place the two models next to each other and take a picture which shows the differences between the two models. 4. Determine the absolute stereochemistry R or S for the two models. 5. Write or type a paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the two models of CHBгCIF. You must provide an explanation for your conclusions also provide a description for the colors used to representarrow_forwardThe specific rotation of a sample depends upon measured angle of rotation, the density of the sample, and the pathway length of the light. True Falsearrow_forwardConsider the molecule A,B, C and D shown below, (1 x 4) Br NH2 A OH Br 边 H B C D 1. Assign the R/S configuration to each chiral center and identify by circling all the chiral centers. 2. Draw an image for the enantiomer of each of the compounds A, B, C and D.arrow_forward
- Could you crystallize one enantiomer of mandelic acid from a racemic mixture (using the typical achiral solvents found in our lab) without preparing a diastereomeric salt? Why or why not? No, because both enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents. than the other. ооо Yes, because one enantiomer has a higher melting point No, because both enantiomers are liquids. Yes, because one enantiomer is more crystalline than the other.arrow_forwardIf the literature value of specific rotation for a chiral compound is -53.6°, what is the enantiomeric excess of a compound with a measured specific rotation of -40.5°?arrow_forwardThe process to determine the configuration, starts by placing the lowest priority substituent toward the back. If the substituents pointing forward decrease in priority in a clockwise order, the configuration is S. If the substituents decrease in priority in a counterclockwise order, the configuration is R. True Falsearrow_forward
- In the drawing area below, create a hemiacetal with 1 hydroxyl group, 1 methoxy group, and a total of 3 carbon atoms. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check Х PO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardPredict the product of the reaction below (3 pts). hydrazine Ph H₂NNH2 KOH Write the mechanism for the above reaction using curved arrows to show electron movements. show all intermediates in the process (7 pts).arrow_forward↓ Feedback (8/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 2 attempts remaining N H3O+ 0 × Select to Draw + V Retryarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





