
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 50PQ
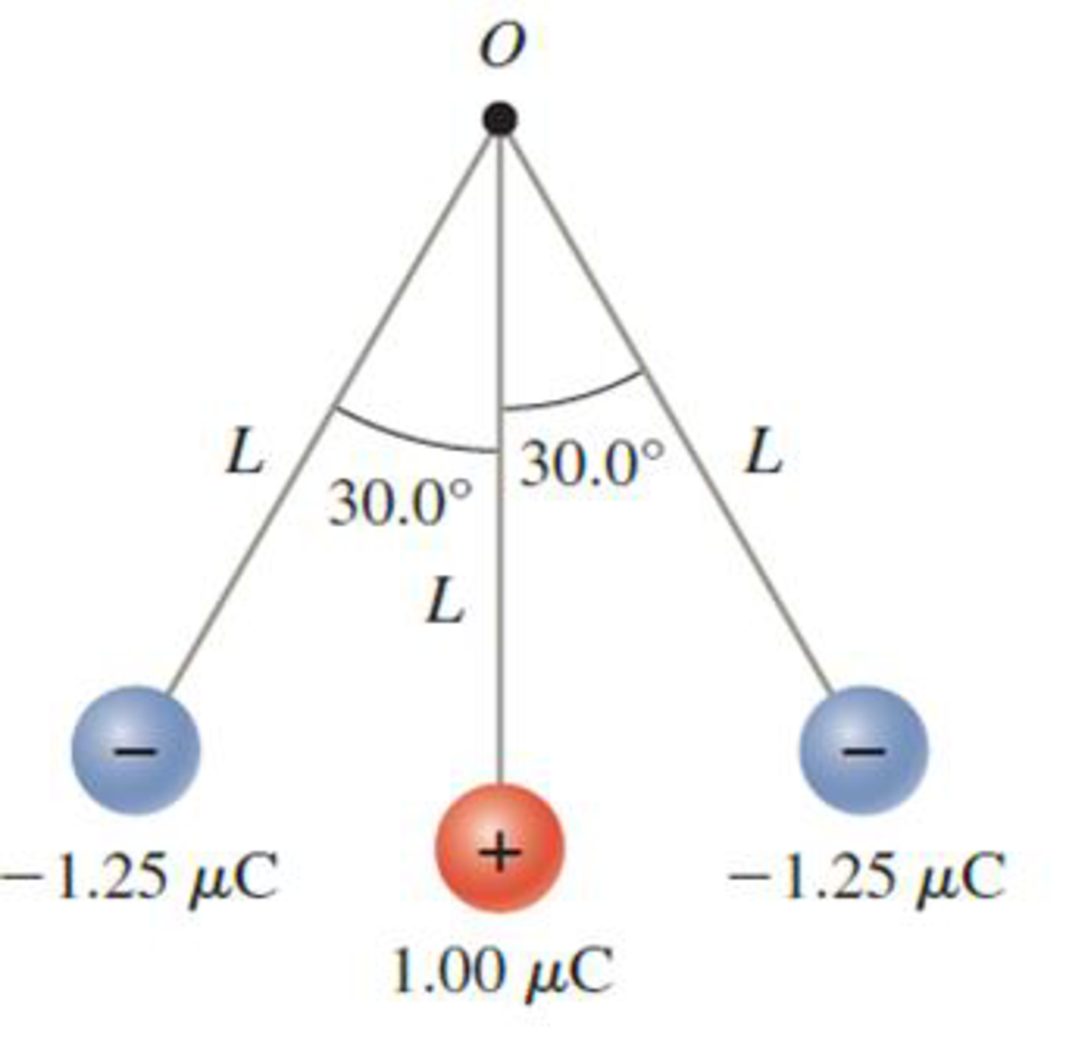
Three charged spheres are suspended by nonconducting light rods of length L = 0.625 m from the point O. The rods are fixed in position so that the middle rod is vertical and the rods on the left and right make an angle of 30.0° with the vertical (Fig. P24.50).
- a. What is the total electric field due to the charged spheres at point O?
- b. What is the electric force on a particle with charge q = +5.00 μC placed at point O?
FIGURE P24.50
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
In each of the following, solve the problem stated. Express your answers in three significant figures. No unit is
considered incorrect.
1. For the circuit shown, determine all the currents in each branch using Kirchhoff's Laws. (3 points)
6
5V 2
B
C
4
A
www
6 VT
ww
T10 V
F
E
2. Compute for the total power dissipation of the circuit in previous item. (1 point)
3. Use Maxwell's Mesh to find Ix and VAB for the circuit shown. (3 points)
Ix
50 V
20
ww
21x
B
4. Calculate all the currents in each branch using Maxwell's Mesh for the circuit shown. (3 points)
www
5ი
10
24V
2A
2002
36V
If the mass of substance (1 kg), initial temperature (125˚C), the final temperature (175˚C) and the total volume of a closed container (1 m3) remains constant in two experiments, but one experiment is done with water ( ) and the other is done with nitrogen ( ). What is the difference in the change in pressure between water and nitrogen?
Using the simplified energy balance in Equation 1, suppose there is heat transfer of 40.00 J to a system, while the system does 10.00 J of work. Later, there is heat transfer of 25.00 J out of the system while 4.00 J of work is done on the system. What is the net change in internal energy of the system?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 24.2 - In a few sentences, explain how you know that...Ch. 24.2 - What is the magnitude of the electric field due to...Ch. 24.3 - Which lines in Figure 24.7 cannot represent an...Ch. 24.4 - Figure 24.10 shows a source that consists of two...Ch. 24.4 - A water molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms...Ch. 24.5 - a. Figure 24.22A shows a rod of length L and...Ch. 24 - The terms electrostatic force and electrostatic...Ch. 24 - Prob. 2PQCh. 24 - A sphere has a charge of 89.5 nC and a radius of...Ch. 24 - Prob. 4PQ
Ch. 24 - A sphere with a charge of 3.50 nC and a radius of...Ch. 24 - Is it possible for a conducting sphere of radius...Ch. 24 - Prob. 7PQCh. 24 - For each sketch of electric field lines in Figure...Ch. 24 - Prob. 9PQCh. 24 - Two large neutral metal plates, fitted tightly...Ch. 24 - Given the two charged particles shown in Figure...Ch. 24 - Prob. 12PQCh. 24 - Prob. 13PQCh. 24 - A particle with charge q on the negative x axis...Ch. 24 - Prob. 15PQCh. 24 - Figure P24.16 shows three charged particles...Ch. 24 - Figure P24.17 shows a dipole. If the positive...Ch. 24 - Find an expression for the electric field at point...Ch. 24 - Figure P24.17 shows a dipole (not drawn to scale)....Ch. 24 - Figure P24.20 shows three charged spheres arranged...Ch. 24 - Often we have distributions of charge for which...Ch. 24 - Prob. 22PQCh. 24 - A positively charged rod with linear charge...Ch. 24 - A positively charged rod of length L = 0.250 m...Ch. 24 - Prob. 25PQCh. 24 - Prob. 26PQCh. 24 - A Find an expression for the position y (along the...Ch. 24 - The electric field at a point on the perpendicular...Ch. 24 - Prob. 29PQCh. 24 - Find an expression for the magnitude of the...Ch. 24 - What is the electric field at point A in Figure...Ch. 24 - A charged rod is curved so that it is part of a...Ch. 24 - If the curved rod in Figure P24.32 has a uniformly...Ch. 24 - aA plastic rod of length = 24.0 cm is uniformly...Ch. 24 - A positively charged disk of radius R = 0.0366 m...Ch. 24 - A positively charged disk of radius R and total...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged conducting rod of length =...Ch. 24 - Prob. 38PQCh. 24 - Prob. 39PQCh. 24 - Prob. 40PQCh. 24 - Prob. 41PQCh. 24 - Prob. 42PQCh. 24 - What are the magnitude and direction of a uniform...Ch. 24 - An electron is in a uniform upward-pointing...Ch. 24 - Prob. 45PQCh. 24 - Prob. 46PQCh. 24 - A very large disk lies horizontally and has...Ch. 24 - An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 24 - In Figure P24.49, a charged particle of mass m =...Ch. 24 - Three charged spheres are suspended by...Ch. 24 - Figure P24.51 shows four small charged spheres...Ch. 24 - Prob. 52PQCh. 24 - A uniform electric field given by...Ch. 24 - A uniformly charged ring of radius R = 25.0 cm...Ch. 24 - Prob. 55PQCh. 24 - Prob. 56PQCh. 24 - A potassium chloride molecule (KCl) has a dipole...Ch. 24 - Prob. 58PQCh. 24 - Prob. 59PQCh. 24 - Prob. 60PQCh. 24 - A total charge Q is distributed uniformly on a...Ch. 24 - A simple pendulum has a small sphere at its end...Ch. 24 - A thin, semicircular wire of radius R is uniformly...Ch. 24 - Prob. 64PQCh. 24 - Prob. 65PQCh. 24 - Prob. 66PQCh. 24 - Prob. 67PQCh. 24 - Prob. 68PQCh. 24 - A thin wire with linear charge density =0y0(14+1y)...Ch. 24 - Prob. 70PQCh. 24 - Two positively charged spheres are shown in Figure...Ch. 24 - Prob. 72PQCh. 24 - Prob. 73PQCh. 24 - Prob. 74PQCh. 24 - A conducting rod carrying a total charge of +9.00...Ch. 24 - Prob. 76PQCh. 24 - A When we find the electric field due to a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 78PQCh. 24 - Prob. 79PQCh. 24 - Prob. 80PQCh. 24 - Prob. 81PQCh. 24 - Prob. 82PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You pour a litre (1 kg) of 25.0˚C water into a 0.500 kg aluminium pan off the stove, but has previously been heated so it starts with a temperature of 120˚C. What is the temperature when the water and the pan reach thermal equilibrium (i.e., what is the temperature of both objects when they reach the same temperature)? Assume that the pan is placed on an insulated pad and a negligible amount of water boils off.arrow_forwardA golf club hits a golf ball and the golf ball’s flight reaches a maximum height of 5.48 m. Calculate the momentum of the golf ball at the maximum height if the mass of the golf ball is 0.459 kg.arrow_forward• Superposition Theorem • Thevenin's and Norton's Theorem 1. Find the unknown voltage V₁, unknown resistances R1 and R2, and currents flowing through R1 and R2 for the circuit shown below using Superposition Theorem. 40 V + R₁₂ w B C ♥16A 10A www 4A F ww 2 E Ꭰ 2. Use Thevenin's Theorem to find the current flowing in 3-ohm resistor and its power dissipation from the circuit shown in the right. + 3. Use Norton's Theorem for the same instruction as for No. 2. 8 V A www 202 B wwww 20 Ω 10 V + 302 202 www C - 12 V 502 www.arrow_forward
- Fill in blanksarrow_forwardA rock is dropped from a height of 2.00 m. Determine the velocity of the rock just before it hits the ground. If the momentum of the rock just before hitting the ground is 14.0 kg m/s, what is the mass of the rock? Is the collision between the rock and the ground elastic or inelastic? Explain.arrow_forwardDescribe how the momentum of a single ball changes as it free falls from a height of approximately 1 m, collides with a hard floor, and rebounds.arrow_forward
- • Nature of Resistance Temperature-Resistance Relationship Ohm's Law, Energy and Power Kirchhoff's Law • • Maxwell's Mesh Analysis 1. The steel of the third rail of a railway system has a resistivity of 21.4 μ-cm. If its cross-sectional area is 8.2 in², calculate the resistance per mile of rail, neglecting the effect of joints between sections. (1 point) 2. An incandescent lamp has a tungsten filament whose resistance is 96 at its operating temperature of 2900°C. Calculate the filament resistance when the lamp is disconnected from the electric source, under which condition its temperature is 24°C. (Use do = 0.0045 02/°C for tungsten) (1 point) 3. For the circuit shown, find the following: 50 V 602 10 V 702 a. the value of resistor R. (1 point) b. the equivalent resistance with respect to the 50-V source. (1 point) 4. For the circuit shown, determine all the currents in each branch using Kirchhoff's Laws. (3 points) A 5V 2 В -ний C 4 6 VT ww F E 5. Use Maxwell's Mesh to find I, and VAB…arrow_forwardFor items 8-9, refer to the problem below. Find all the currents flowing in every resistor, power dissipation in every resistor and the total power of the circuit shown at the right using... 8. Kirchhoff's Laws (5 pts) 9. Maxwell's Mesh Analysis (5 pts) A 8 V 10 V B + 20 Ω 3Ω 202 wwww C wwww 202 + 50 www 12 Varrow_forward• Nature of Resistance Temperature-Resistance Relationship Ohm's Law, Energy and Power Kirchhoff's Law • Maxwell's Mesh Analysis 1. A coil of copper wire (p = 10.37 2-cmil/ft) has a length of 600 ft. What is the length of an aluminum conductor (p 17 cmil/ft), if its cross-sectional area and resistance are the same as those of the copper coil? (Hint: Look for conversion of inches to mils and square inches to square foot. Include it in your solution.) (1 pt) 2. The copper field winding of an electric machine has a resistance of 46 at temperature of 22°C. What will be its resistance at 75°C? (Use do = 0.00427 /°C for copper) (1 pt) 3. The resistivity of a copper rod 50 ft long and 0.25 inch in diameter is 1.76 μ at 20°C. What is its resistance at - 20°C? (1 pt) 4. When two resistors A and B are connected in series, the total resistance is 36 2. When connected in parallel, the total resistance is 8 Q. What is the ratio of the resistance RA to resistance RB? Assume RA < RB. (1 pt) 5. The…arrow_forward
- 2. Two equally strong individuals, wearing exactly the same shoes decide to do a tug of war. The only difference is individual A is 2.5 meters tall and individual B is 1.5 meter tall. Who is more likely to win the tug of war?arrow_forward6. A car drives at steady speed around a perfectly circular track. (a) The car's acceleration is zero. (b) The net force on the car is zero. (c) Both the acceleration and net force on the car point outward. (d) Both the acceleration and net force on the car point inward. (e) If there is no friction, the acceleration is outward.arrow_forward9. A spring has a force constant of 100 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.07 m. One end is attached to a post that is free to rotate in the center of a smooth. table, as shown in the top view in the figure below. The other end is attached to a 1kg disc moving in uniform circular motion on the table, which stretches the spring by 0.03 m. Friction is negligible. What is the centripetal force on the disc? Top View (a) 0.3 N (b) 3.0 N (c) 10 N (d) 300 N (e) 1000 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY