
Concept explainers
(a)
The net electric flux through the cube.
(a)
Answer to Problem 32P
Net electric flux through the cube is
Explanation of Solution
Below figure shows the electric field magnitude and its direction in all face’s of the cube.
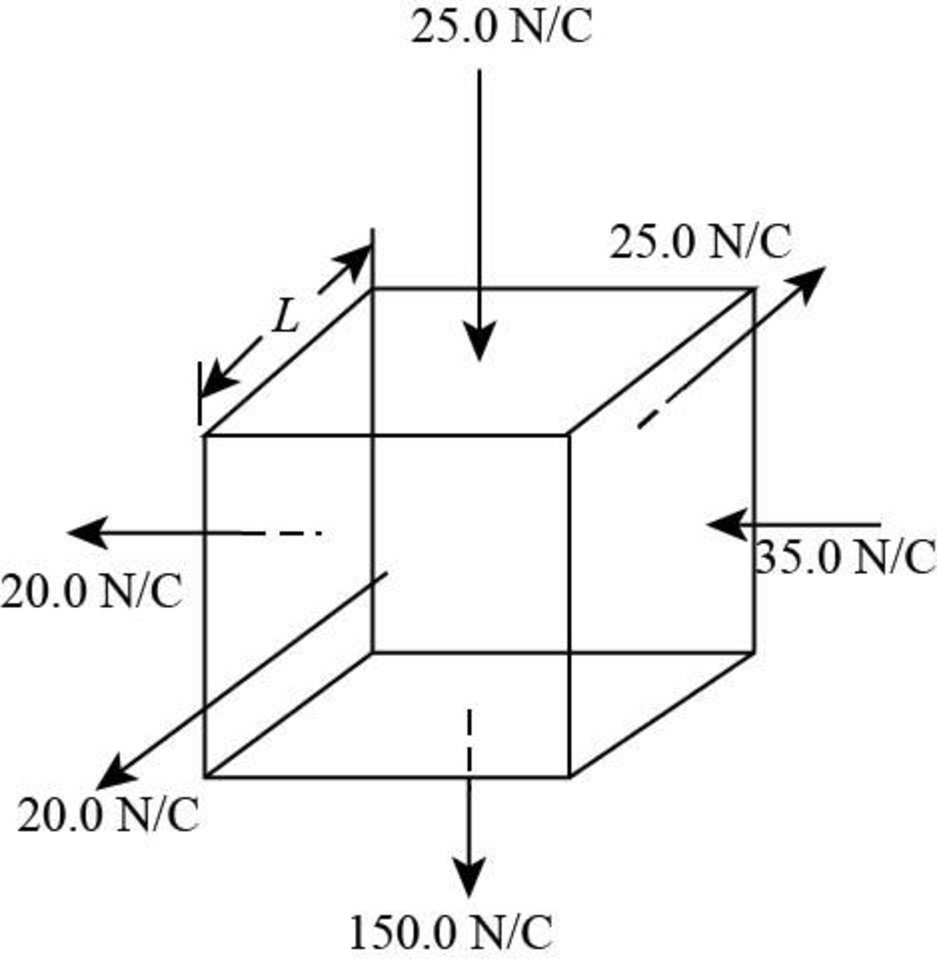
Figure (1)
From Figure (1), it is shown that, the electric fields are perpendicular to the faces of the cube. Therefore, use Gauss law for net flux through the closed Gaussian surface.
Write the expression for net flux through the closed Gaussian surface.
Here,
Write the expression for net electric flux through cube.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, net electric flux through the cube is
(b)
The net charge inside the cube.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32P
The charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is
(c)
Whether the net charge could be a point charge.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32P
No, the net charge can’t be a point charge.
Explanation of Solution
No, single positive charge’s magnitude is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net charge can’t be a point charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- How to solve this, given answerarrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of a square as shown in the figure, 28.0 cm on each side. Find the minimum amount of work required by an external force to move the charge q1 to infinity. Let q1=-2.10 μC, q2=+2.40 μС, q3=+3.60 μC.arrow_forwardA point charge of -4.00 nC is at the origin, and a second point charge of 6.00 nC is on the x axis at x= 0.820 mm . Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at each of the following points on the x axis. x2 = 19.0 cmarrow_forward
- Four point-like charges are placed as shown in the figure, three of them are at the corners and one at the center of a square, 36.0 cm on each side. What is the electric potential at the empty corner? Let q1=q3=+26.0 µС, q2=-28.0 μC, and q4=-48.0μc Varrow_forwardPLS HELparrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





