
Interpretation:
The structural isomer, chirality and systematic name should be identified for the given formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomer: Molecule has same molecular formula but different structural arrangement is called isomer.
Chiral: Absence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called chiral molecule, a non-superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral. A carbon atom is attached by the four different groups is called chiral carbon.
Achiral: Presence of a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is called achiral molecule, a superimposable on its mirror image is called achiral. A carbon atom does not have four different groups is called achiral carbon
Geometric isomerism (also known as E-Z isomerism or cis-trans isomerism): same molecular formula but different arrangement in the space. These isomers happen where you have restricted rotation in a molecule (double bond in the molecule). The
Organic compounds are named systematically by using IUPAC rules.
Name of the organic compounds are given according to the number of carbon present in the molecule for example
A molecule having one carbon atom, the molecule name will start with meth etc.…

If any halogens are present in the molecule, the name of the halogens as follows.

Naming the substituted
- (1) Name the parent alkane (long alkyl chain)
- (2) Number the carbon
- (3) Name and number the substituent
If the molecules have the multiple substituents, the compound named as di, tri, tetra, penta, ect.
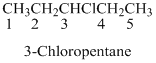
If the molecules having functional group, the name of the compound is given below. Numbering should be starts from the functional group of the given molecule.
The given compound is an alcohol
Example is given below


Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Chemistry
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





