
Concept explainers
Name the following compounds:
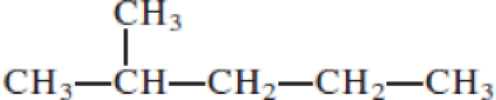
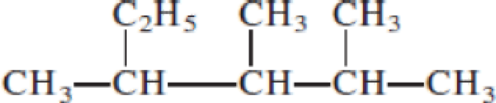
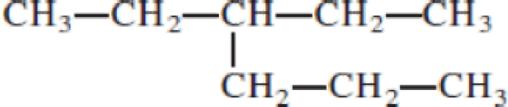
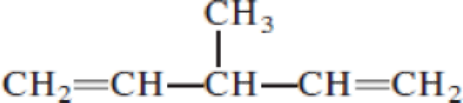
- (a) CH3─C≡C─CH2─CH3
a)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
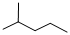
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
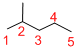
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENTANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:
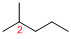
At each Carbon of 2 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituents, then prefix ‘2-methyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 2-methylpentane.
b)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
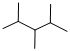
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
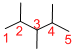
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENTANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:
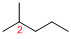
At each Carbon of 2, 3, and 4 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing three identical substituents, then prefix ‘2,3,4-trimethyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 2,3,4-trimethylpentane.
c)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hyphen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
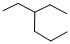
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
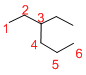
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains six carbons and the parent name is HEXANE. The Suffix ‘ane’ represents the structure contains only single bonds.
Predict substituents and its location:

At each Carbon of 3 one ethyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-ethyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-ethylhexane.
d)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘ene’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hyphen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:
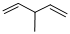
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
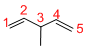
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is 1,4-PENTDIENE. The Suffix ‘diene’ represents the structure contains two double bonds at C-1 and C-4.
Predict substituents and its location:
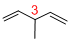
At each Carbon of 3 one methyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-methyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-methyl-1,4-pentadiene.
e)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the substituent should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘yne’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure:

Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
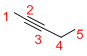
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENT-2-YNE. The Suffix ‘2-yne’ represents the structure contains one triple bond at C-2.
Predict substituents and its location:
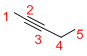
No substituents present and no prefix can be written. Hence, the name is,
IUPAC name: Pent-2-yne.
f)
Interpretation:
The given structure has to be named.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature for alkene:
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms is identified.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent chain is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the chain.
- While numbering the longest chain, the double bond should get least possible number.
- Write the name of the compound; the parent name written as last part of the name by replacing ‘ane’ to ‘ene’. The name of the substituents is written as prefix and a hypen separates the number that the substituents attached with carbon. More than one substituent should be written in alphabetical order.
Geometric isomers of Alkenes:
Cis-isomer: When two particular atoms (group of atoms) are adjacent to each other, the alkene is known as cis-isomer.
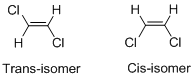
Trans-isomer: When two particular atoms (group of atoms) are across from each other, the alkene is known as cis-isomer.
Explanation of Solution
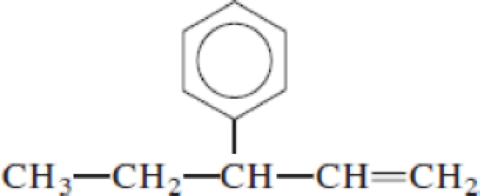
Given structure:
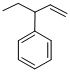
Predict the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms:
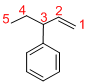
The longest continuous carbon chain of carbon atoms contains five carbons and the parent name is PENT-1-ENE. The Suffix ‘1-ene’ represents the structure contains one double bond at C-1.
Predict substituents and its location:

At each Carbon of 3 one phenyl group is present. Hence, the structure containing one substituent, then prefix ‘3-phenyl’ is added before the parent name. Hyphen separates the number that the substituent attached with carbon.
IUPAC name: 3-phenylpent-1-ene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Chemistry
- + Draw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br Drawing Strong Base H Q Atoms, Bonds Charges and Rings Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Remove Done 語 Reset Undo + Drag To Panarrow_forwardDraw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Drawing Į Strong Base H Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset 謂 Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Br CH3 Q Strong Base Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Undo Reset H "Br H N Br. Remove Done .N. Drag To Panarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the product of this elementary step in an elimination mechanism. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore byproducts. + Br: .. 8 0.01 M NaOH heat Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges and Lone Pairs Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset Remove Done + Drag To Panarrow_forward+ Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Ph CH2CH3 H H3C H Br DBN [૪] Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings H | OH Charges ―00 H. C | Undo Reset Br I Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardReaction A Now the production A Œ In the product of reaction i 12 Dear the product of actionarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learnin When an unknown amine reacts with an unknown acid chloride, an amide with a molecular mass of 163 g/mol (M* = 163 m/z) is formed. In the infrared spectrum, important absorptions appear at 1661, 750 and 690 cm-1. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra are provided. Draw the structure of the product as the resonance contributor lacking any formal charges. 13C NMR DEPT 90 200 160 120 80 40 0 200 160 120 80 DEPT 135 200 160 120 80 40 0 Draw the unknown amide. 40 40 0arrow_forwardDraw the major product karmed when I reach with the epoxide. Use walge dah bonds, including hydrogen al alcach genic center, to show the chemistry of the product Beeldraw any hydrogen akams on coxygen where applicablearrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H I Select to Add Arrows + H H 'H Q H2O H2O CI:O .H H H H I Select to Add Arrows I : C H2O H H H Select to Add Arrows 'Harrow_forward
- + Draw an alkyl halide that produces ONLY the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Drawing Strong Base Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges HO Br H2N Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Panarrow_forwardFor the dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction shown, draw the major organic product. Хок Br tert-butanol heat Select Drew Templates More Erase CH QQQarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Draw the major, neutral organic product for each substitution reaction. For this question, assume that each substitution reaction goes to completion. Disregard elimination. Reaction A. CI H₂O Select Draw Templates More Erase C Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





