
(a)
Interpretation:
Reasonable precursors have to be suggested for the formation of compound I in the given problem.
Concept introduction:
Amide bond formation:
Amides, commonly known as acid amides are those compounds which have
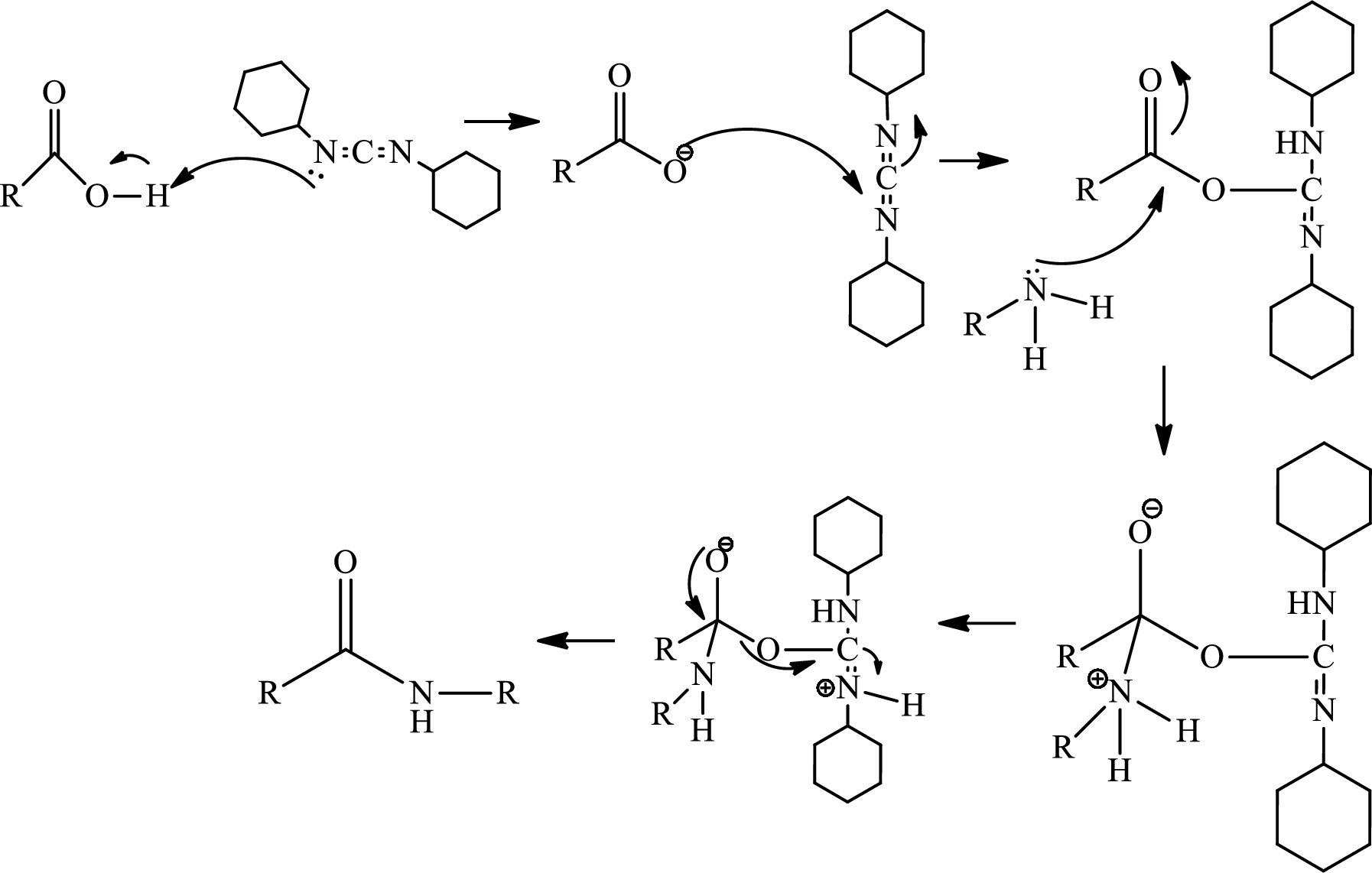
(b)
Interpretation:
Reagents for the reaction along with the mechanism have to be given for the conversion of compound I to II as given in the question.
Concept introduction:
Coupling reaction of aryl halides and phenols catalyzed by palladium and MOP types of ligands:
Palladium catalyzed coupling reactions of aryl halides and phenols are described employing the bulky and electron rich MOP type ligands. When
(c)
Interpretation:
The two isomers of compound II have to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Atropisomers:
Atropisomers are the stereoisomers arising because of the hindered rotation about a single bond where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers.
(d)
Interpretation:
Suitable reagents have to be given for the transformation of compound II to III in the given problem.
Concept introduction:
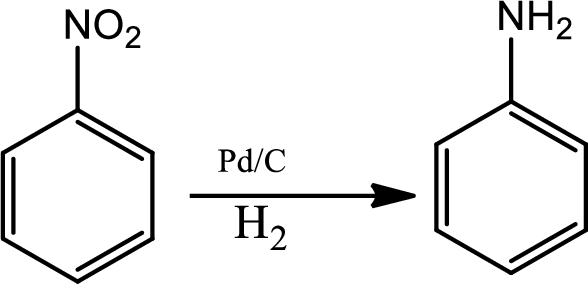
Reduction of nitro group:
Reduction of nitro group can be done by various reagents. In industrial scale reduction of nitrobenzene to anniline is a very common reaction. It is done by catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of palladium hydrogen.
Diazotisation reaction:
Diazonium salta are organic compounds having
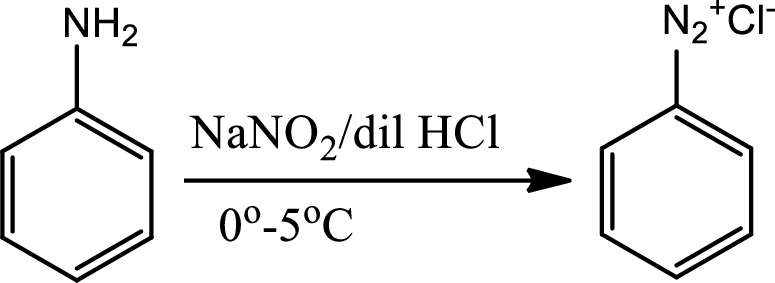
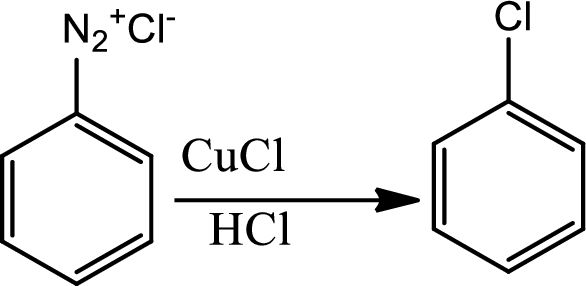
Sandmeyer reaction:
The Sandmeyer reaction is a
(e)
Interpretation:
The reagents and the fragment of the ring A that is useful for the conversion of compound III to IV have to be given.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reaction:
A grignard reagent is a chemical compound with the formula
(f)
Interpretation:
Ring closure reaction of the deprotected free amino group has to be given along with the mechanism.
Concept introduction:
Amide bond formation:
Amides, commonly known as acid amides are those compounds which have
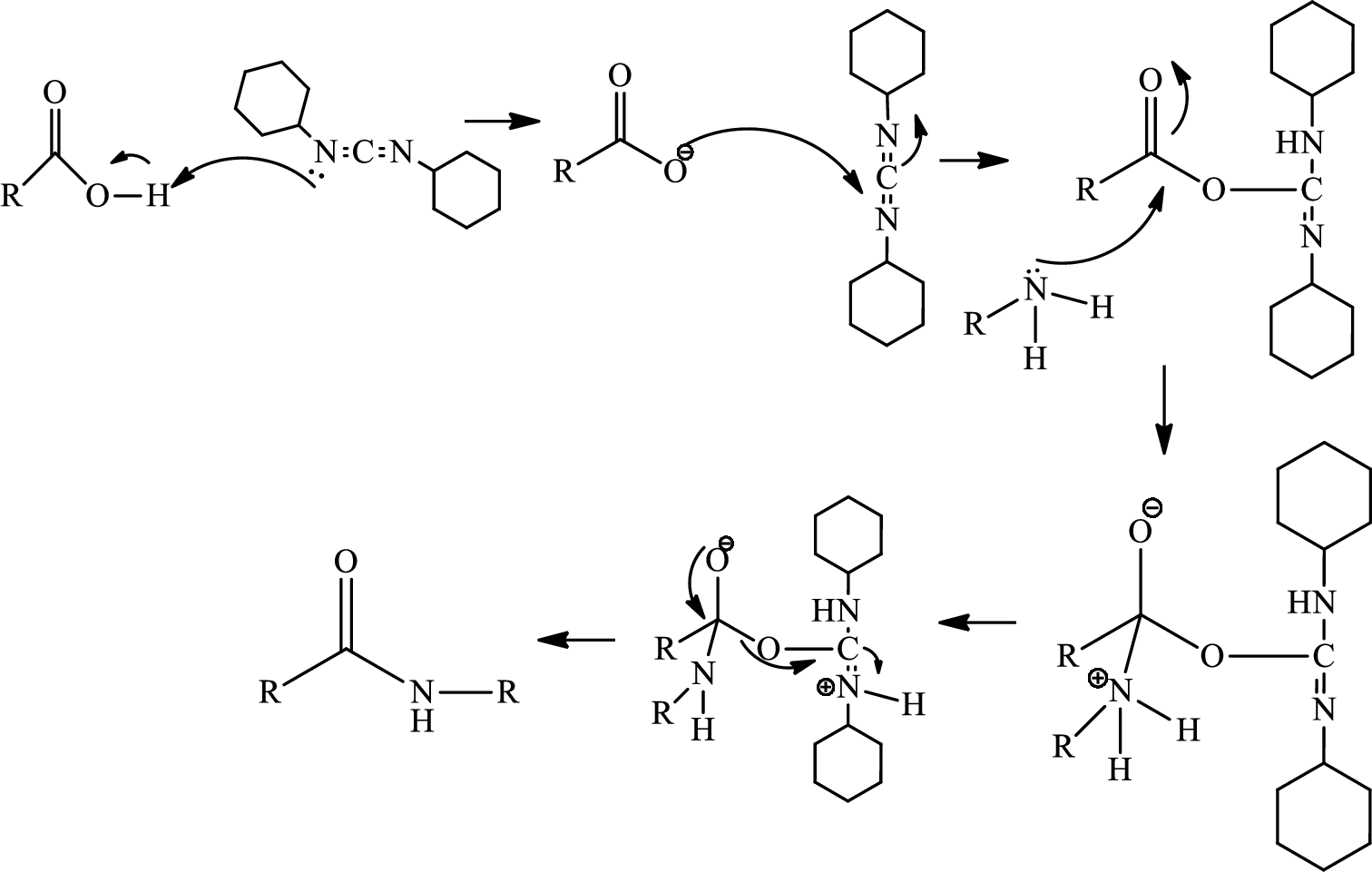
(g)
Interpretation:
The atropisomers have to be drawn and also it has to be shown that only one of them can be converted to vancomycin.
Concept introduction:
Atropisomers:
Atropisomers are the stereoisomers arising because of the hindered rotation about a single bond where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- + Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forwardConsider the following reactants: Br Would elimination take place at a significant rate between these reactants? Note for advanced students: by significant, we mean that the rate of elimination would be greater than the rate of competing substitution reactions. yes O no If you said elimination would take place, draw the major products in the upper drawing area. If you said elimination would take place, also draw the complete mechanism for one of the major products in the lower drawing area. If there is more than one major product, you may draw the mechanism that leads to any of them. Major Products:arrow_forward
- Draw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction. OH + ! : ☐ + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFind one pertinent analytical procedure for each of following questions relating to food safety analysis. Question 1: The presence of lead, mercury and cadmium in canned tuna Question 2: Correct use of food labellingarrow_forwardFormulate TWO key questions that are are specifically in relation to food safety. In addition to this, convert these questions into a requirement for chemical analysis.arrow_forward
- What are the retrosynthesis and forward synthesis of these reactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the given reactions would form meso product? H₂O, H2SO4 III m CH3 CH₂ONa CH3OH || H₂O, H2SO4 CH3 1. LiAlH4, THF 2. H₂O CH3 IVarrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O IV III HCI D = III ა IVarrow_forward
- The reaction of what nucleophile and substrate is represented by the following transition state? CH3 CH3O -Br อ δ CH3 Methanol with 2-bromopropane Methanol with 1-bromopropane Methoxide with 1-bromopropane Methoxide with 2-bromopropanearrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward32. Consider a two-state system in which the low energy level is 300 J mol 1 and the higher energy level is 800 J mol 1, and the temperature is 300 K. Find the population of each level. Hint: Pay attention to your units. A. What is the partition function for this system? B. What are the populations of each level? Now instead, consider a system with energy levels of 0 J mol C. Now what is the partition function? D. And what are the populations of the two levels? E. Finally, repeat the second calculation at 500 K. and 500 J mol 1 at 300 K. F. What do you notice about the populations as you increase the temperature? At what temperature would you expect the states to have equal populations?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning




