
(a)
Interpretation:
The other products obtained from the highly stereo and regioselective reaction of O-alkylation during the formation of Gilvarin M. has to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
Regioselectivity:
Regioselectivity is the preference of one direction of
Stereoselectivity:
Stereoselectivity is the property of a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
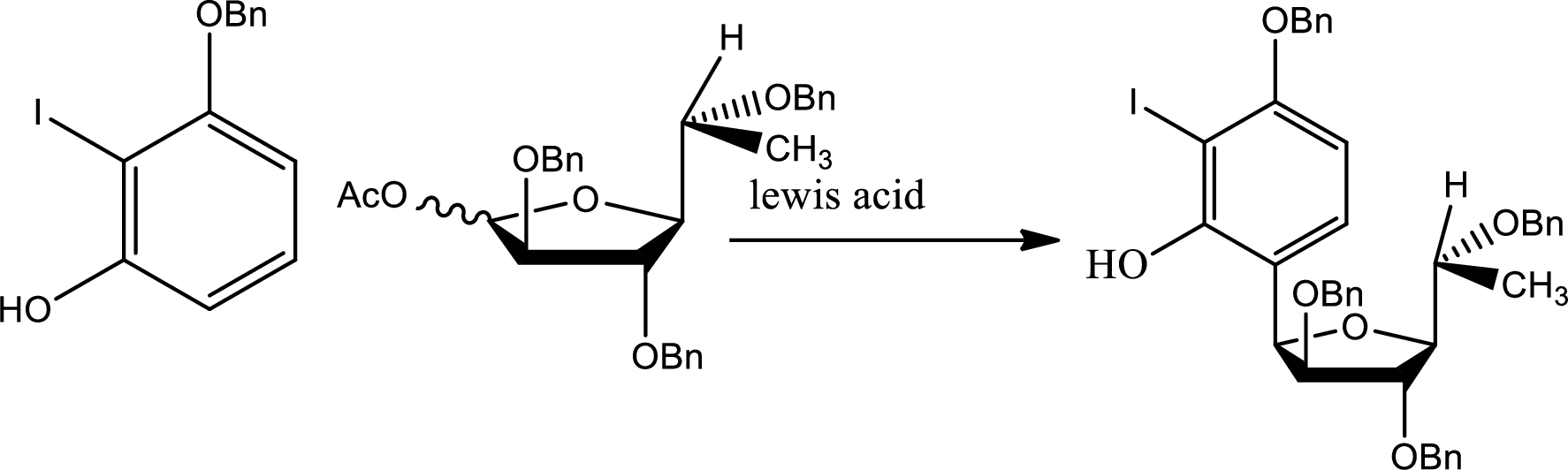
The other possibility is,
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound C has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acid-base reaction:
The species that donates proton or accepts lone pair of electrons are called acids and those who accepts proton or donates lone pair of electrons are called base.
The
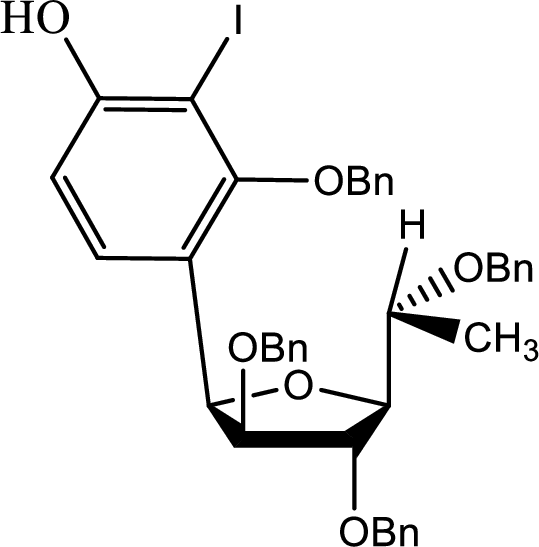
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The pathway of formation of C is,
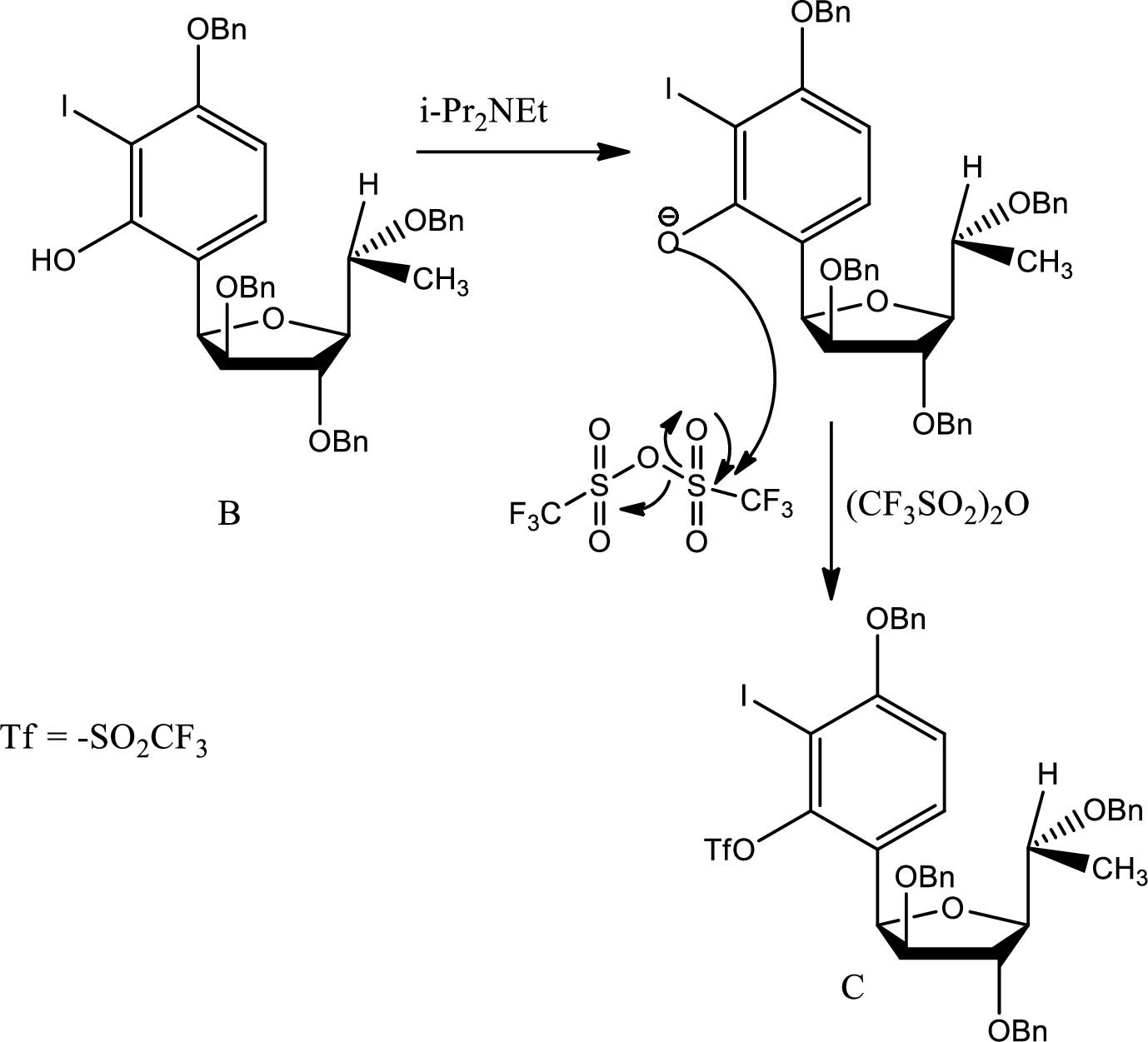
Here the
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of compound D has to be given.
Concept introduction:
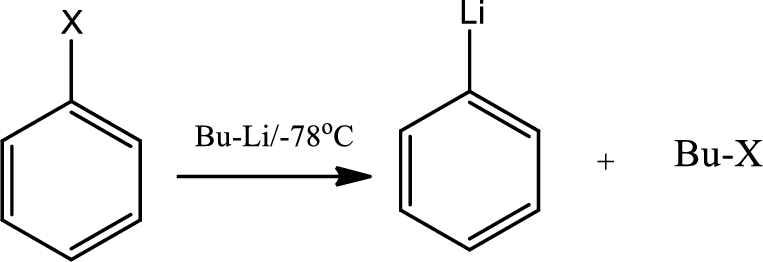
Lithium halogen exchange:
Organolithium reagents are characterised by the presence of
The reaction of lithium metal at low temperature with an
The same reaction happens with the haloarenes also,
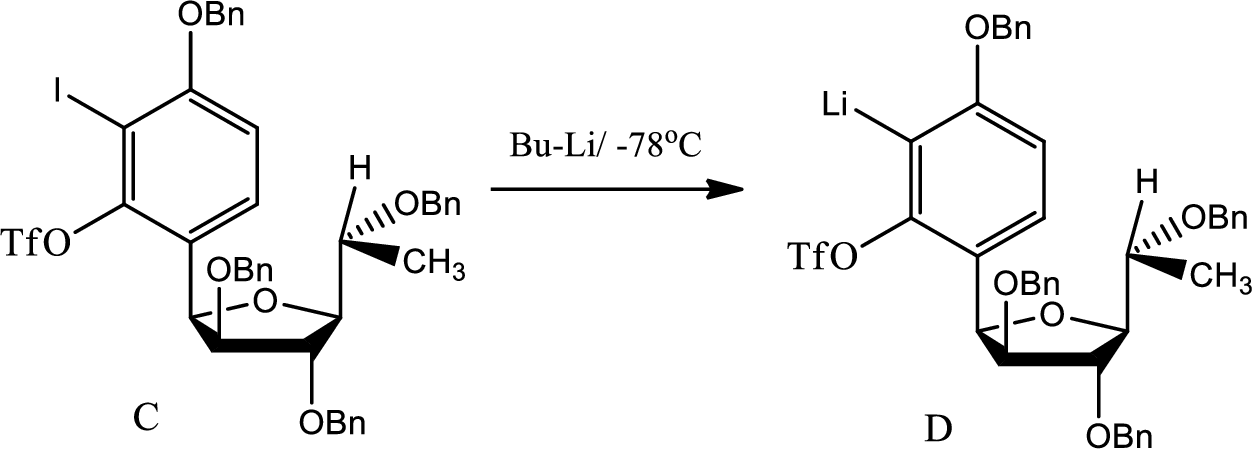
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction for the formation of D is as follows,
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of E has to be given along with the mechanism of formation of E from D.
Concept introduction:
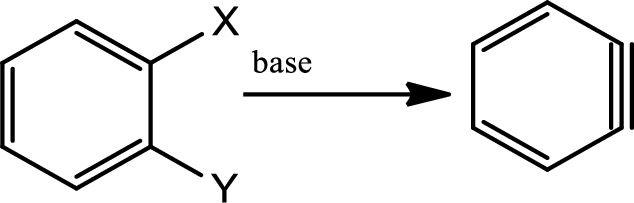
Benzyne formation:
Benzynes are highly reactive intermediate species that are made from
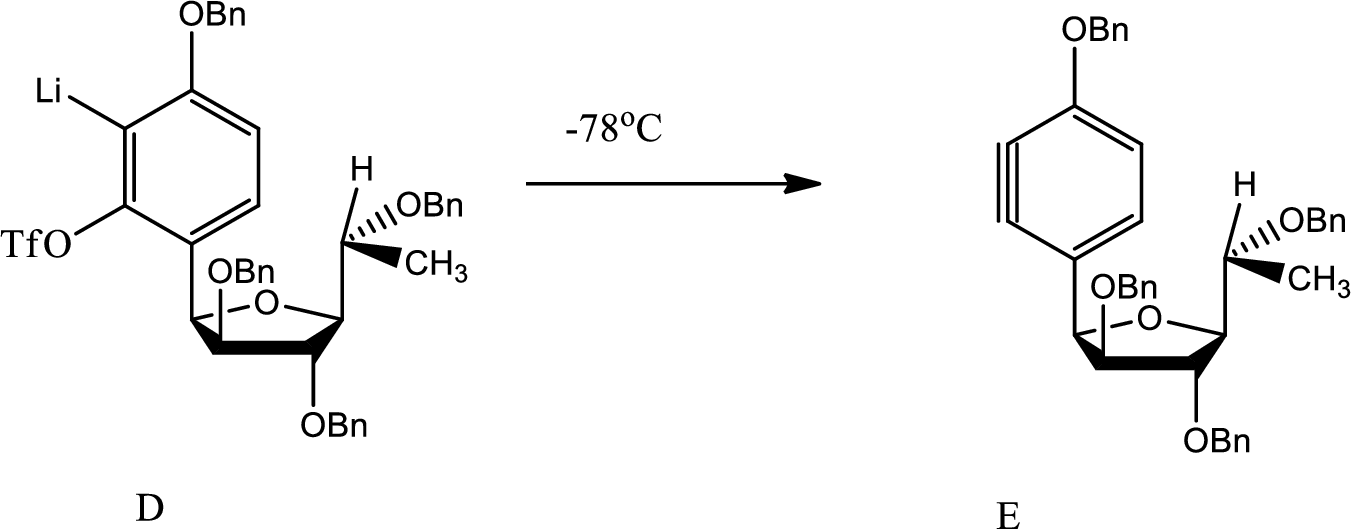
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Here benzyne formation occurs due to removal of
(e)
Interpretation:
A mechanism for formation of F from E has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Diels Alder reaction:
The Diels-Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted
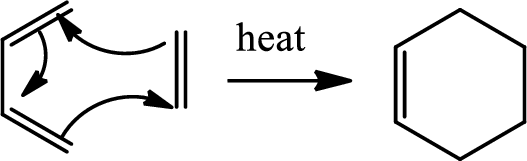
(e)
Explanation of Solution
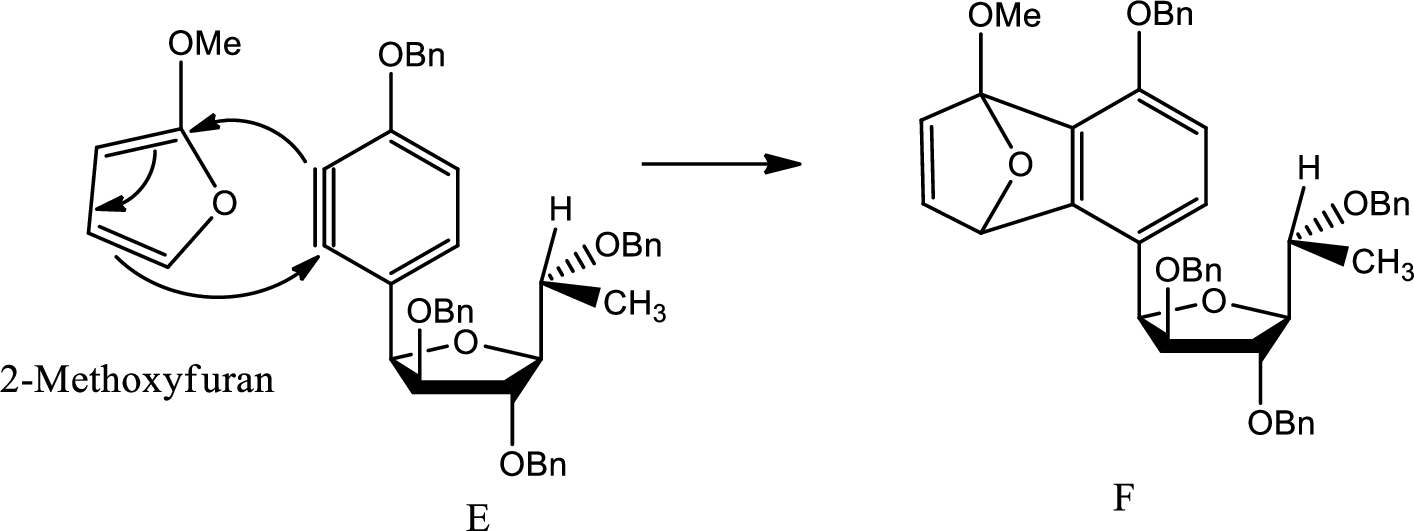
Here Diels Alder reaction occurs between furan and benzyne. A new ring is formed.
(f)
Interpretation:
Mechanism from F to G has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Hydrolysis:
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a water molecule ruptures one or more chemical bonds. This is mainly used for substitution, elimination and fragmentation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Hydrolysis is reverse of condensation reaction because in this process water is added to beak down.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Here aqueous work up leads to breaking of the bridging oxygen bond by protonating the oxygen. Thus the angle strain increases as positive charge on electronegative oxygen is tough. Thus the bond breaks and the charge formed is stabilised by electron donating effect of
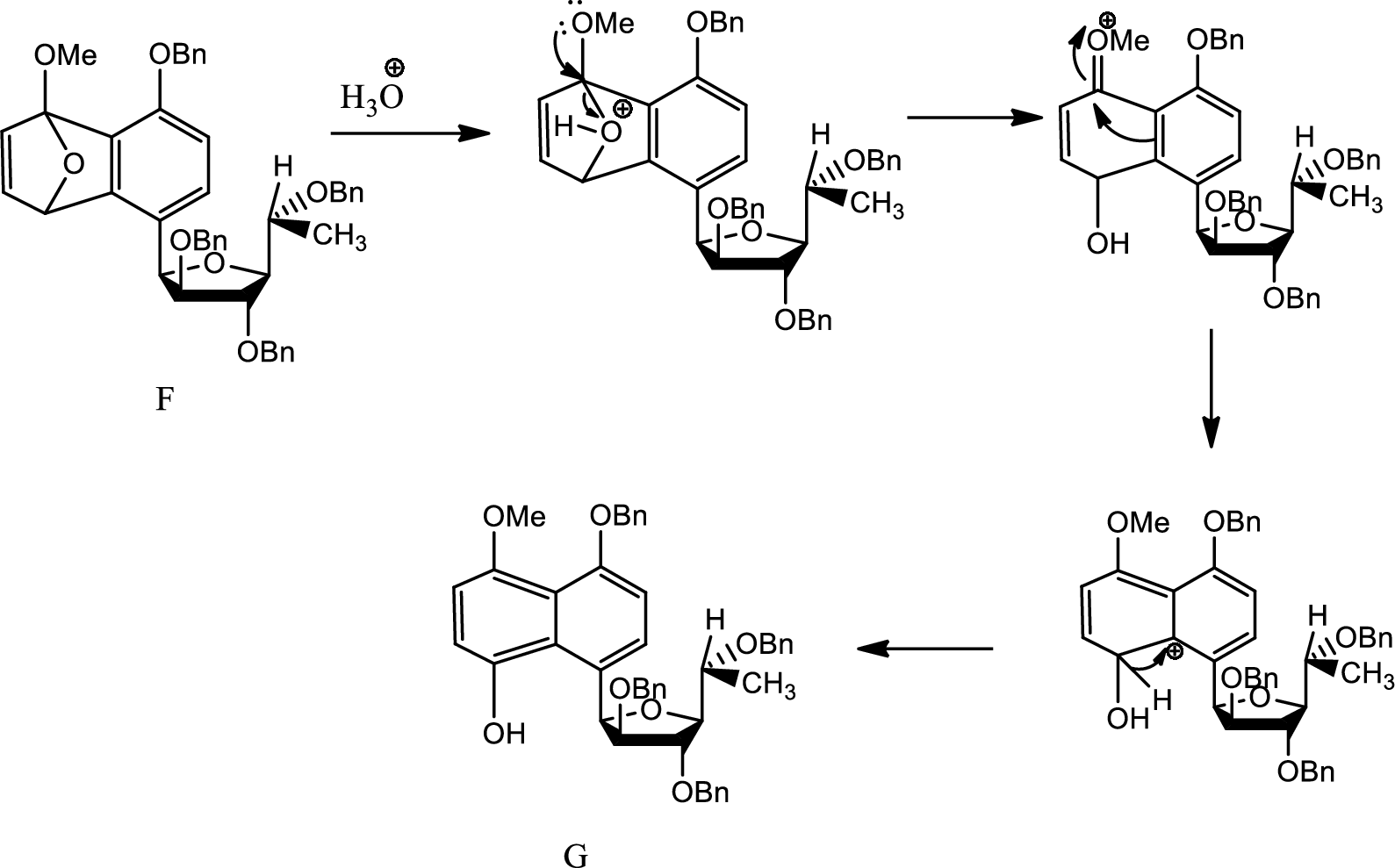
Thus G is formed from F.
(g)
Interpretation:
The reagents and condition from G to H has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acid-base reaction:
The species that donates proton or accepts lone pair of electrons are called acids and those who accepts proton or donates lone pair of electrons are called base.
The
(g)
Explanation of Solution
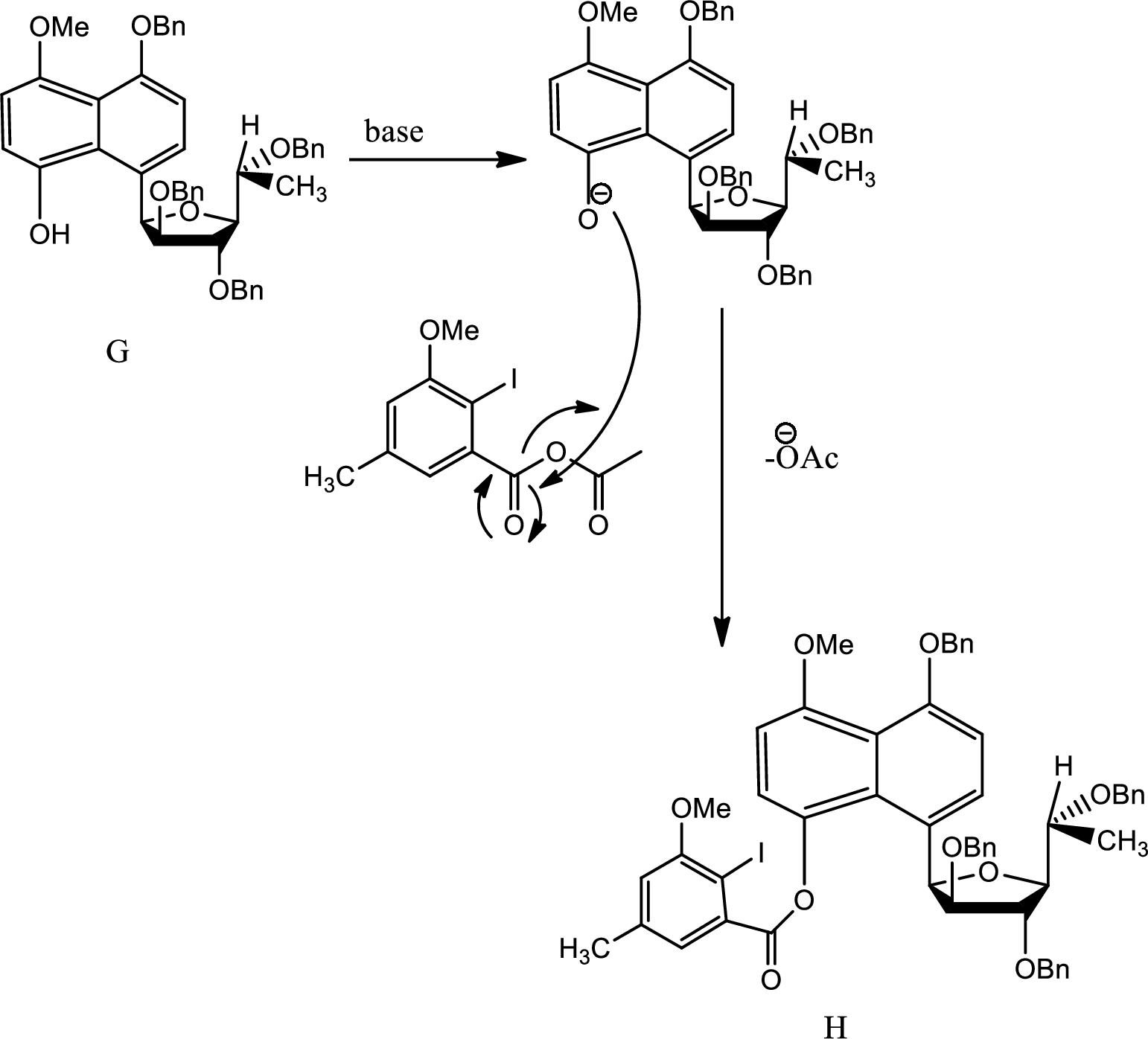
Here on giving base the acidic hydrogen from phenol is removed and the new carbanion formed undergoes
Thus H is formed from G.
(h)
Interpretation:
Reagents and condition for conversion of H to I has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Cross coupling:
A cross coupling reaction is defined as a reaction that creates a
In the case of palladium catalysed cross-coupling reactions the other metal or metalloids are commonly
Suzuki coupling:
The Suzuki coupling uses a boron compound and an alkenyl, aryl or alkyl halide or triflate as the carbon sources with a palladium salt as a catalyst. The reaction is mainly used to form biaryls. The mechanism of the reaction starts with an oxidative addition followed by transmetallation in which the substituent on the borane replaces the ligand on the palladium concluding with the reductive elimination of the palladium to form the new carbon-carbon bond. The base may serve as a new labile ligand to palladium or it may activate the borane by coordination.
Generalized reaction,
Oxidative addition and ligand exchange,
Borane activation
Reaction,
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
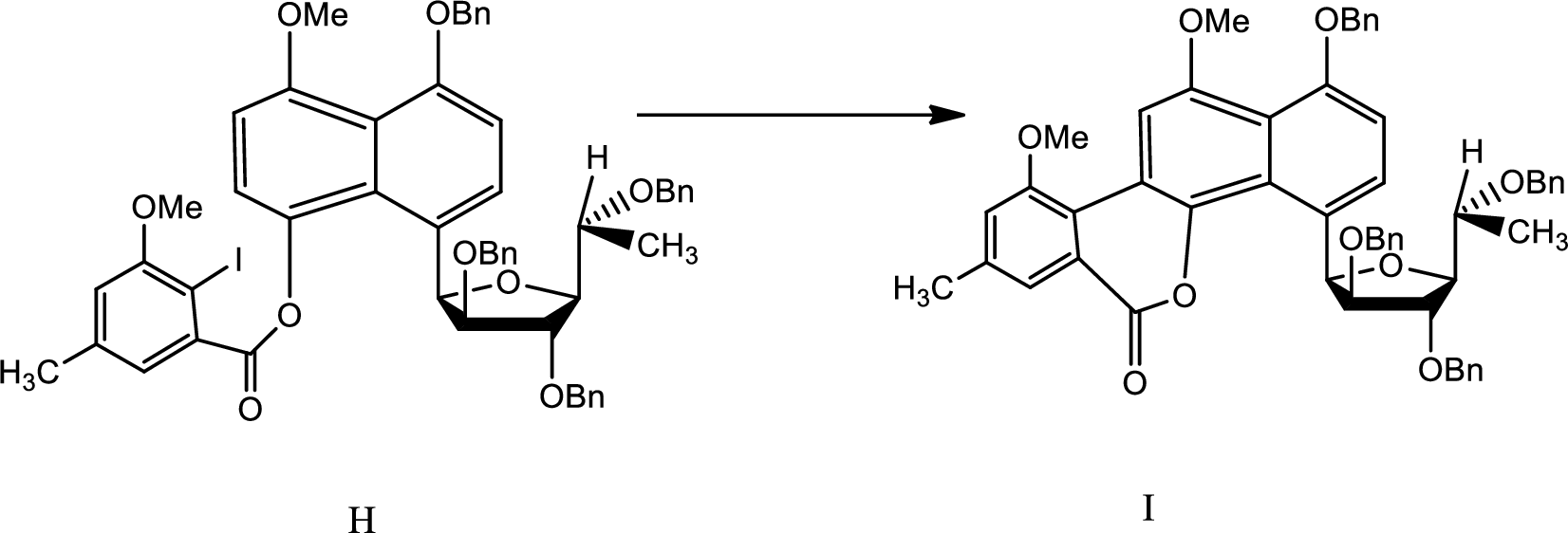
The reaction proceeds as follows,
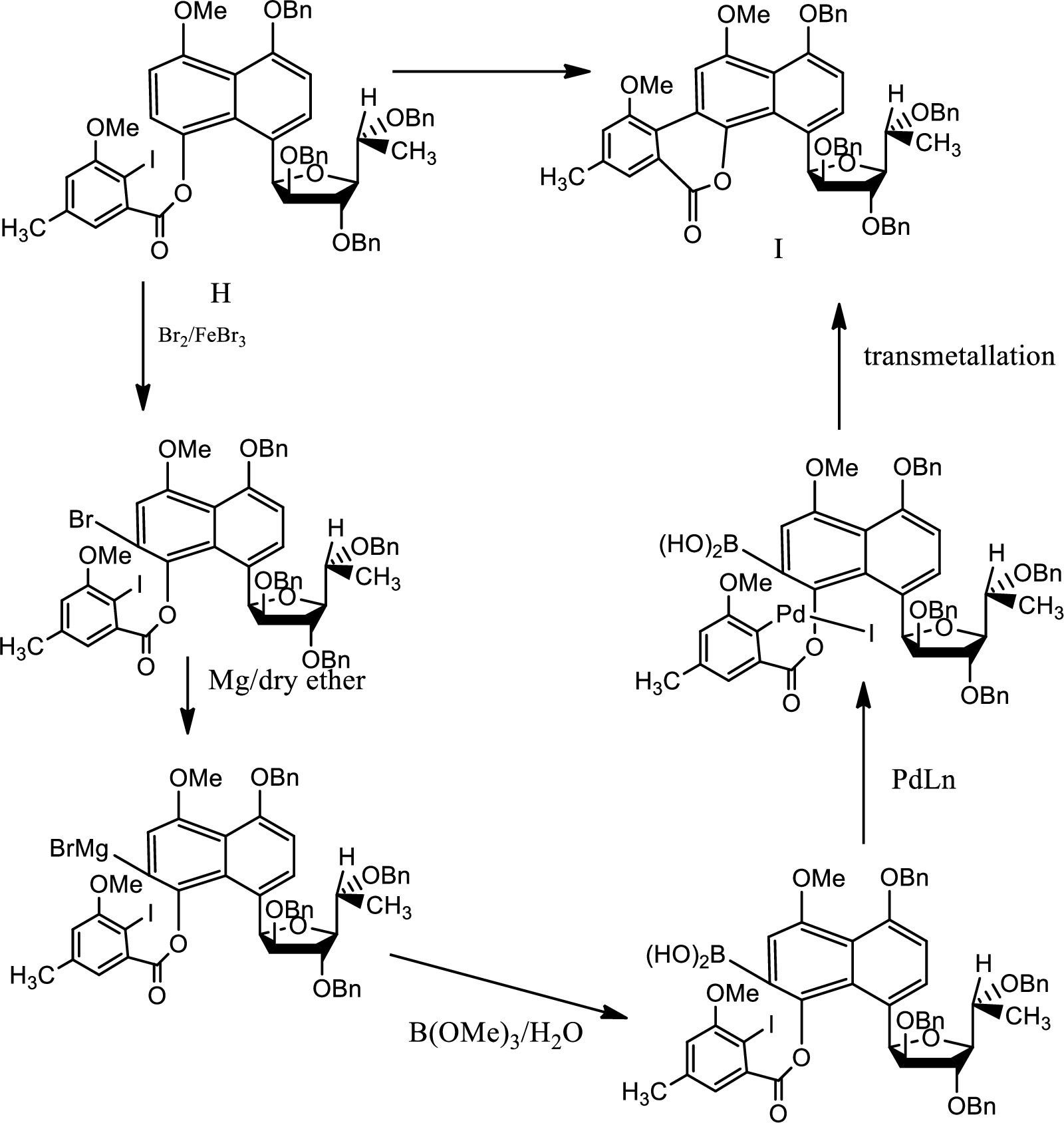
1st boron has to be added so that via transmetallation by intramolecular Suzuki coupling the product can be formed.
(i)
Interpretation:
Reagent needed to form Gilvocarcin M. from I has to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
Protection-deprotection:
A protecting group is introduced to a molecule by chemical modification of a
Hydrogenolysis:
Hydrogenolysis is a chemical reaction whereby a carbon carbon bond or carbon heteroatom single bond is cleaved by hydrogen gas catalytically.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
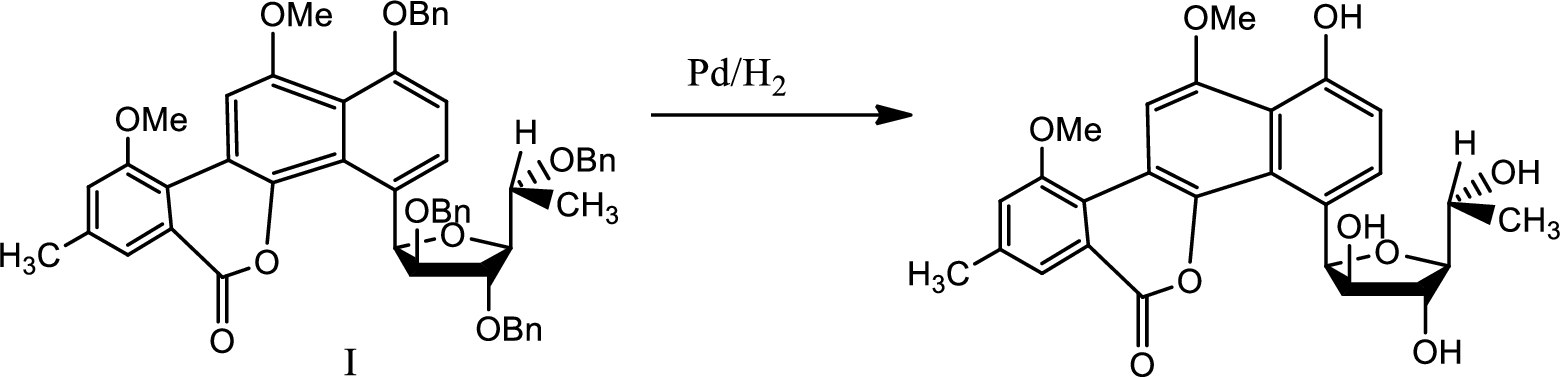
Here deprotection is done by hydrogenolysis with the help of palladium and catalytic amount of hydrogen.
(j)
Interpretation:
Probable source of chiral centres has to be found.
Concept introduction:
Chiral centre:
Chiral centre is defined as an atom bonded to four different chemical species. It is a stereo centre that holds the atom in such way that the structure may not be superimposable to its mirror image. They give optical isomerism.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The source of the chiral centre is only the five membered carbohydrate ring attached to the benzene ring as shown below,
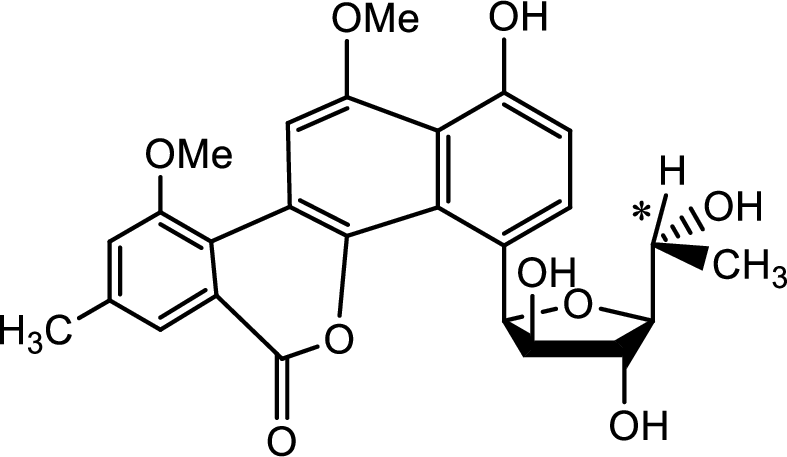
The chiral centre is marked with the asterisk.
(k)
Interpretation:
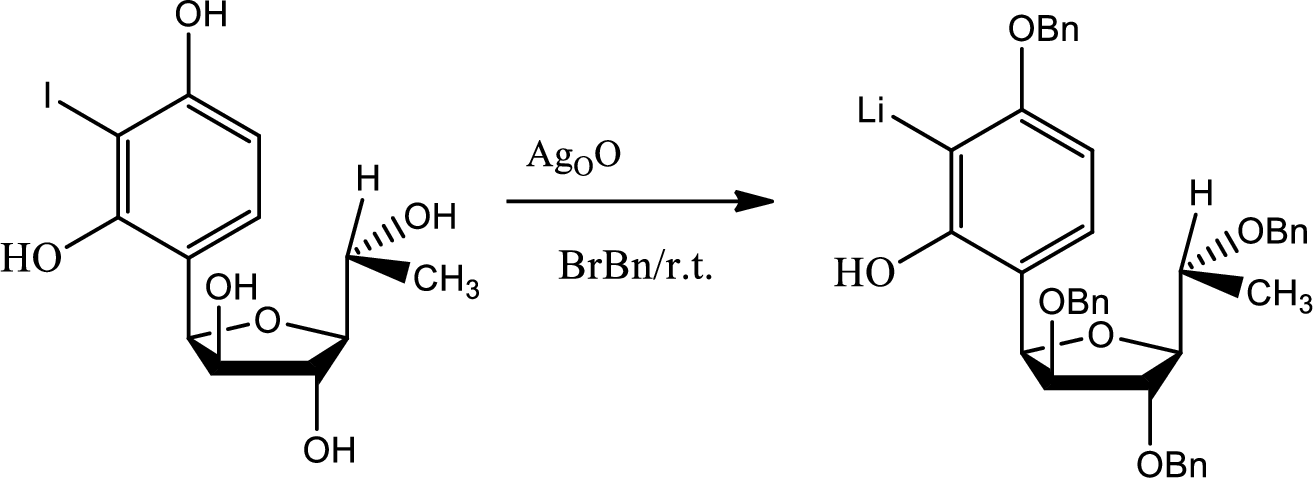
The need of protection of hydroxyl group has to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Protection-deprotection:
A protecting group is introduced to a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction specially in multistep organic synthesis.
(k)
Explanation of Solution
If protection has not been done to the hydroxyl groups then there were possibilities of getting so many unwanted products.
During the acid base reaction all the hydroxyl groups could have lost the proton and thus all the substitution could have taken place in different places. The benzyne formation could have hampered and the stereochemistry could have changed.
The process of protection to the hydroxyl group is given by,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- What are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Write the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forwardHow many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forwardDraw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forward
- Draw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forwardH 14. Draw the line angle form of the following molecule make sure you use the proper notation to indicate spatial positioning of atoms. F F H 15. Convert the following condensed form to line angle form: (CH3)3CCH2COCH2CON(CH2CH3)2arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forward
- In a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward1. Predict the organic product(s) of the following reactions. Assume excess of reagents unless otherwise noted. a) &l BH3 •THF b) 1) NaOH 2) H3O+ solve d) ala 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+ e) H2N سكر CuLi NH2 1) SOCI2 2) EtMgBr 3) H3O+ NC H3O+ Δarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


