
Concept explainers
a)
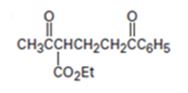
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
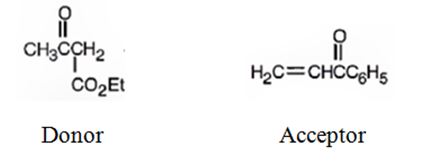
Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and phenyl vinyl ketone (electrophilic acceptor).
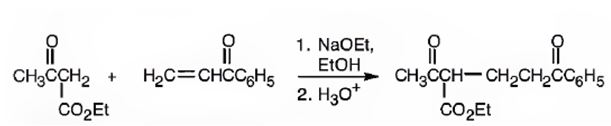
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
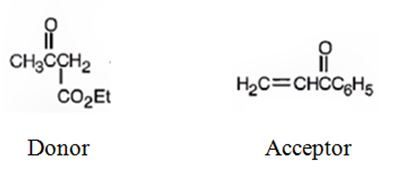
b)
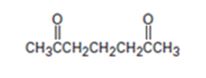
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and methyl vinyl ketone (electrophilic acceptor).
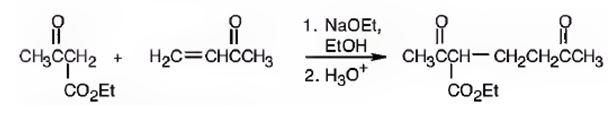
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

c)
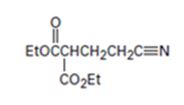
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylacetoacetate (nucleophilic donor) and vinyl nitrile (electrophilic acceptor).
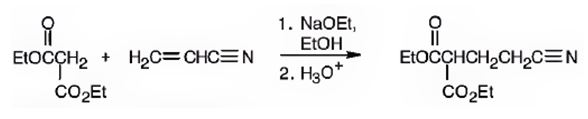
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

d)
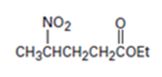
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between nitro ethane (nucleophilic donor) and ethylacrylate (electrophilic acceptor).
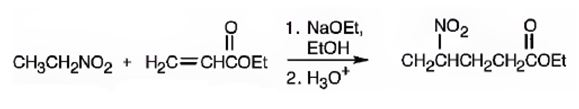
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
e)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

Explanation of Solution
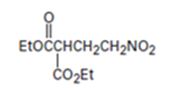
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between the ethylsuccinate (nucleophilic donor) and nitro ethene (electrophilic acceptor).
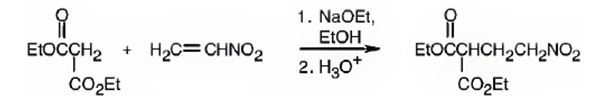
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are

f)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Michael reaction involves the conjugate addition of a stable enolate ion derived from a β-ketoesters or β-diketones or β-ketonitriles or malonic esters (donors) to an unhindered α,β-unsaturated ketones or aldehydes or esters or thioesters or nitriles or amides or nitro compounds (acceptors). The enolate ion from the donor attacks the double bond in acceptor. A new bond is formed between the α-carbon of the donor and the β-carbon of the unsaturated ester.
To give:
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown.
Answer to Problem 62AP
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
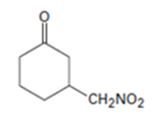
Explanation of Solution
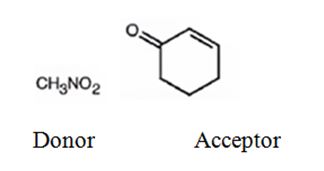
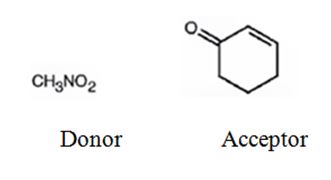
An analysis of the structure of the compound indicates that it is formed by the reaction between nitro methane (nucleophilic donor) and 2-cyclopentenone (electrophilic acceptor).
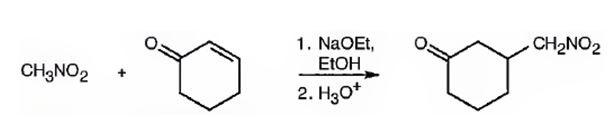
The nucleophilic donor and electrophilic acceptor that react in a Michael reaction to yield the compound shown are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward
- 3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forwardWrite the aldol condensation mechanism and product for benzaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base. Then trans-cinnamaldehyde + acetone in base. Then, trans-cinnamaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


