
(a)
Interpretation:
For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If ,
, 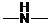 and
and 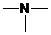 groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
(b)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If ,
, 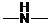 and
and 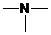 groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
(c)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If ,
, 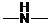 and
and 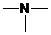 groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
(d)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If ,
, 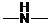 and
and 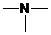 groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
(e)
Interpretation: For a given set of nitrogen containing compounds, the structures have to be drawn using their general or IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction: If ,
, 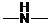 and
and 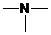 groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
groups are attached to the parent carbon, they are called primary, secondary and tertiary amines respectively.
There are two ways followed to name the compound. First one is the method of giving general name in which name of the alkyl group followed by amine name is given. Second one is the method giving IUPAC name in which name of the alkane group followed by amine name is given.
The length of the chain which is having more number of carbon atoms is selected as the parent or main chain. Other chains are considered as substituents to the main chain. Position of the substituents should be included in the name. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in IUPAC system, then the name of the compound comes as methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, etc. which are the name of alkanes. If one, two, three, four, five, six, etc carbons are activating as the main chain in general name method, then the name of the compound comes as methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, etc. which are the name of alkyl groups. If substituent groups are attached to nitrogen atom as in the case of tertiary or secondary amines, the name is given as N-alkyl name of the substituent.
If any configuration is present in the compound, that should be assigned to it while writing the name. If the compound contains heavier groups on the same side, it gets (Z)-configuration. If they are on the opposite directions, (E)-configurations result.
If a carbon has four different groups attached to it, that carbon shows a chirality nature. If that chiral carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a clockwise direction, it gets (R)-isomer. If that carbon rotates the plane polarized light into a counter-clockwise direction, it gets (S)-isomer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





