
Concept explainers
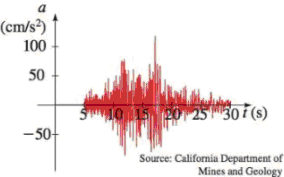
Earthquake The graph shows the vertical acceleration of the ground from the 1994 Northridge earthquake in Los Angeles, as measured by a seismograph. (Here t represents the time in seconds.)
- (a) At what time t did the earthquake first make noticeable movements of the earth?
- (b) At what time t did the earthquake seem to end?
- (c) At what time t was the maximum intensity of the earthquake reached?
(a)
The time at which the earthquake first make the noticeable movements of the earth.
Answer to Problem 44E
The first noticeable movement took place after 5 seconds.
Explanation of Solution
A graph is given which shows the vertical acceleration of the ground from an earthquake as measured by a seismograph.
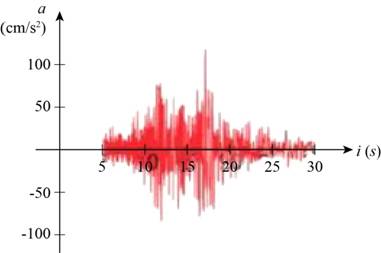
Figure (1)
The acceleration is given on vertical axis and the time in seconds on horizontal axis.
From Figure (1), it is noticed that the acceleration of ground is there right after 5 seconds.
Therefore, the first noticeable movement took place after 5 seconds.
(b)
At what time the earthquake ended.
Answer to Problem 44E
The earthquake ended after 30 seconds.
Explanation of Solution
A graph is given which shows the vertical acceleration of the ground from an earthquake as measured by a seismograph.

Figure (1)
From Figure (1), it is noticed that there is no acceleration of the ground after 30 seconds. It clearly means that the earthquake stopped after 30 seconds.
Therefore, the earthquake ended in 30 seconds.
(c)
At what time the earthquake had maximum intensity.
Answer to Problem 44E
The maximum intensity of the earthquake was reached after 17 seconds.
Explanation of Solution
A graph is given which shows the vertical acceleration of the ground from an earthquake as measured by a seismograph.

Figure (1)
Locate the local maximum point to find the time at which earthquake had the maximum intensity.
The value
From the Figure (1), it is noticed that the value of acceleration is maximum between
The acceleration is more than
This is the point of local maximum.
Therefore, the maximum intensity of the earthquake was reached after 17 seconds.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus - 6th Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Elementary & Intermediate Algebra
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- 4c Consider the function f(x) = 10x + 4x5 - 4x³- 1. Enter the general antiderivative of f(x)arrow_forwardA tank contains 60 kg of salt and 2000 L of water. Pure water enters a tank at the rate 8 L/min. The solution is mixed and drains from the tank at the rate 11 L/min. Let y be the number of kg of salt in the tank after t minutes. The differential equation for this situation would be: dy dt y(0) =arrow_forwardSolve the initial value problem: y= 0.05y + 5 y(0) = 100 y(t) =arrow_forward
- y=f'(x) 1 8 The function f is defined on the closed interval [0,8]. The graph of its derivative f' is shown above. How many relative minima are there for f(x)? O 2 6 4 00arrow_forward60! 5!.7!.15!.33!arrow_forward• • Let > be a potential for the vector field F = (−2 y³, −6 xy² − 4 z³, −12 yz² + 4 2). Then the value of sin((-1.63, 2.06, 0.57) – (0,0,0)) is - 0.336 -0.931 -0.587 0.440 0.902 0.607 -0.609 0.146arrow_forward
- The value of cos(4M) where M is the magnitude of the vector field with potential ƒ = e² sin(лy) cos(π²) at x = 1, y = 1/4, z = 1/3 is 0.602 -0.323 0.712 -0.816 0.781 0.102 0.075 0.013arrow_forwardThere is exactly number a and one number b such that the vector field F = conservative. For those values of a and b, the value of cos(a) + sin(b) is (3ay + z, 3ayz + 3x, −by² + x) is -0.961 -0.772 -1.645 0.057 -0.961 1.764 -0.457 0.201arrow_forwardA: Tan Latitude / Tan P A = Tan 04° 30'/ Tan 77° 50.3' A= 0.016960 803 S CA named opposite to latitude, except when hour angle between 090° and 270°) B: Tan Declination | Sin P B Tan 052° 42.1'/ Sin 77° 50.3' B = 1.34 2905601 SCB is alway named same as declination) C = A + B = 1.35 9866404 S CC correction, A+/- B: if A and B have same name - add, If different name- subtract) = Tan Azimuth 1/Ccx cos Latitude) Tan Azimuth = 0.737640253 Azimuth = S 36.4° E CAzimuth takes combined name of C correction and Hour Angle - If LHA is between 0° and 180°, it is named "west", if LHA is between 180° and 360° it is named "east" True Azimuth= 143.6° Compass Azimuth = 145.0° Compass Error = 1.4° West Variation 4.0 East Deviation: 5.4 Westarrow_forward
- ds 5. Find a solution to this initial value problem: 3t2, s(0) = 5. dt 6. Find a solution to this initial value problem: A' = 0.03A, A(0) = 100.arrow_forward2) Drive the frequency responses of the following rotor system with Non-Symmetric Stator. The system contains both external and internal damping. Show that the system loses the reciprocity property.arrow_forward1) Show that the force response of a MDOF system with general damping can be written as: X liax) -Σ = ral iw-s, + {0} iw-s,arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





