
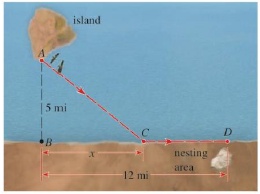
Bird Flight A bird is released from point A on an island, 5 mi from the nearest point B on a straight shoreline. The bird flies to a point C on the shoreline and then flies along the shoreline to its nesting area D (see the figure). Suppose the bird requires 10 kcal/mi of energy to fly over land and 14 kcal/mi to fly over water.
- (a) Use the fact that
to show that the total energy used by the bird is modeled by the function
- (b) If the bird instinctively chooses a path that minimizes its energy expenditure, to what point does it fly?
(a)
To show: The total energy used by the bird is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculation:
The energy of the bird requires
All the distances related to the bird are given in the figure below,
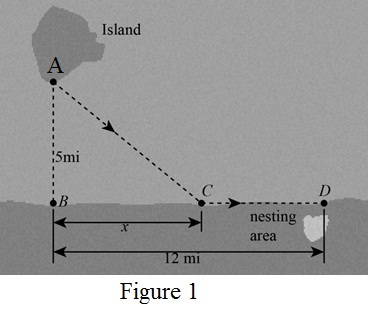
Let x be distance between point B and C.
In
Use the Pythagoras theorem to find the length AC.
The length of the side BD is 12mi and the length of the side BC is x mi.
Then, the length of the side CD is,
The bird flies from the point C to the point D on the land with the energy
To find the energy for
The bird flies from the point A to the point C on the water with the energy
To find the energy for
Then the total energy is,
Substitute
Thus, the total energy is
(b)
To find: The path that minimizes the energy expenditure.
Answer to Problem 31P
The bird flies till the point C on shoreline which is 5.013 miles from point B and then flies along the shoreline.
Explanation of Solution
From the part (a), the total energy is
To find the minimum energy sketch the graph of
The function contains the variable x is the length of the side BC.
The local minimum value of the function is the least finite value where the value of the function at the any number is less than to the original function.
The condition for local minimum is,
Using online graphing calculator, sketch the graph of the function
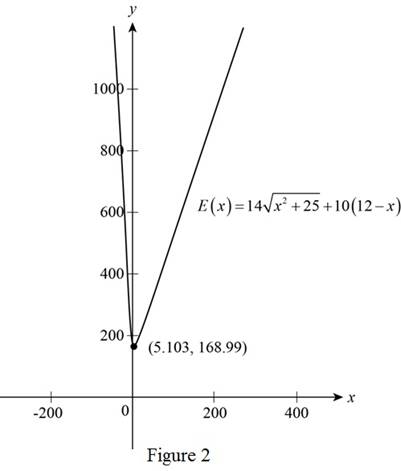
From the above figure, it can be observed that the least peak occurs at the point
Then, the minimum energy expenditure is 168.99 at
Thus, the point C is 5.103 mi away from point B.
Therefore, the bird flies till the point C on shoreline which is 5.013 miles from point B and then flies along the shoreline.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus - 6th Edition
- 4c Consider the function f(x) = 10x + 4x5 - 4x³- 1. Enter the general antiderivative of f(x)arrow_forwardA tank contains 60 kg of salt and 2000 L of water. Pure water enters a tank at the rate 8 L/min. The solution is mixed and drains from the tank at the rate 11 L/min. Let y be the number of kg of salt in the tank after t minutes. The differential equation for this situation would be: dy dt y(0) =arrow_forwardSolve the initial value problem: y= 0.05y + 5 y(0) = 100 y(t) =arrow_forward
- y=f'(x) 1 8 The function f is defined on the closed interval [0,8]. The graph of its derivative f' is shown above. How many relative minima are there for f(x)? O 2 6 4 00arrow_forward60! 5!.7!.15!.33!arrow_forward• • Let > be a potential for the vector field F = (−2 y³, −6 xy² − 4 z³, −12 yz² + 4 2). Then the value of sin((-1.63, 2.06, 0.57) – (0,0,0)) is - 0.336 -0.931 -0.587 0.440 0.902 0.607 -0.609 0.146arrow_forward
- The value of cos(4M) where M is the magnitude of the vector field with potential ƒ = e² sin(лy) cos(π²) at x = 1, y = 1/4, z = 1/3 is 0.602 -0.323 0.712 -0.816 0.781 0.102 0.075 0.013arrow_forwardThere is exactly number a and one number b such that the vector field F = conservative. For those values of a and b, the value of cos(a) + sin(b) is (3ay + z, 3ayz + 3x, −by² + x) is -0.961 -0.772 -1.645 0.057 -0.961 1.764 -0.457 0.201arrow_forwardA: Tan Latitude / Tan P A = Tan 04° 30'/ Tan 77° 50.3' A= 0.016960 803 S CA named opposite to latitude, except when hour angle between 090° and 270°) B: Tan Declination | Sin P B Tan 052° 42.1'/ Sin 77° 50.3' B = 1.34 2905601 SCB is alway named same as declination) C = A + B = 1.35 9866404 S CC correction, A+/- B: if A and B have same name - add, If different name- subtract) = Tan Azimuth 1/Ccx cos Latitude) Tan Azimuth = 0.737640253 Azimuth = S 36.4° E CAzimuth takes combined name of C correction and Hour Angle - If LHA is between 0° and 180°, it is named "west", if LHA is between 180° and 360° it is named "east" True Azimuth= 143.6° Compass Azimuth = 145.0° Compass Error = 1.4° West Variation 4.0 East Deviation: 5.4 Westarrow_forward
- ds 5. Find a solution to this initial value problem: 3t2, s(0) = 5. dt 6. Find a solution to this initial value problem: A' = 0.03A, A(0) = 100.arrow_forward2) Drive the frequency responses of the following rotor system with Non-Symmetric Stator. The system contains both external and internal damping. Show that the system loses the reciprocity property.arrow_forward1) Show that the force response of a MDOF system with general damping can be written as: X liax) -Σ = ral iw-s, + {0} iw-s,arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





