
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110646
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 3CQ
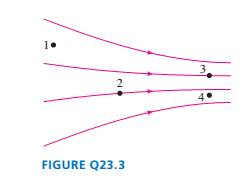
Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the electric field strengths
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Most workers in nanotechnology are actively monitored for excess static charge buildup. The human body acts like an insulator as one walks across a carpet, collecting −50 nC per step. What charge buildup will a worker in a manufacturing plant accumulate if she walks 21 steps?
charge buildup from 21 steps:
nC
How many electrons are present in that amount of charge?
electrons present:
If a delicate manufacturing process can be damaged by an electrical discharge greater than 1012 electrons, what is the maximum number of complete steps that any worker should be allowed to take before touching the components?
maximum number of steps:
A uniform electric field is indicated by electric field lines in the figure. The electric field magnitude is 850 V/m. A charge (-120µC) is moved along a
path from point "a" to point "b", and the length of the path is 10 centimeters. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force acting on
the charge as you move the charge along the path.
E
a
30t
3. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the electric field strengths
E, to E4 at points 1 to 4 in FIGURE Q23.3. Explain.
2
FIGURE Q23.3
Chapter 23 Solutions
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
Ch. 23 - l. You've been assigned the task of determining...Ch. 23 - Reproduce FIGURE Q23.2 on your paper. For each...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A small segment of wire in FIGURE Q23.4 contains...Ch. 23 - An electron experiences a force of magnitude F...Ch. 23 - FIGURE Q23.6 shows a hollow soda straw that has...Ch. 23 - The irregularly shaped area of charge in FIGURE...Ch. 23 - A circular disk has surface charge density 8...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R has charge Q . The electric...Ch. 23 - The ball in FIGURE Q23.10 is suspended from a...
Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor consists of two square...Ch. 23 - A small object is released at point 3 in the...Ch. 23 - A proton and an electron are released from rest in...Ch. 23 - Three charges are placed at the comers of the...Ch. 23 - l. What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from two charges, q ,...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from ± 1.0 nC charges...Ch. 23 - An electret is similar to a magnet, but rather...Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 10.0 cm from a very...Ch. 23 - A 10-cm-long thin glass rod uniformly charged to...Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-long thin glass rods uniformly charged...Ch. 23 - A small glass bead charged to + 6.0 nC is in the...Ch. 23 - The electric field 5.0 cm from a very long charged...Ch. 23 - A 12-cm-long thin rod has the nonuniform charge...Ch. 23 - Two charged rings face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-diameter charged rings face each other,...Ch. 23 - Two charged disks face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 2.0 cm from the...Ch. 23 - A 20cm20cm cm horizontal metal electrode is...Ch. 23 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter insulating spheres have a 6.0...Ch. 23 - You've hung two very large sheets of plastic...Ch. 23 - A 2.0m X 4.0m flat carpet acquires a uniformly...Ch. 23 - Two circular disks spaced 0.50 mm apart form a...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor is formed from two...Ch. 23 - Air "breaks down" when the electric field strength...Ch. 23 - Two parallel plates 1.0 cm apart are equally and...Ch. 23 - a. What is the electric field strength between the...Ch. 23 - Honeybees acquire a charge while flying due to...Ch. 23 - An electron traveling parallel to a uniform...Ch. 23 - The surface charge density on an infinite charged...Ch. 23 - An electron in a vacuum chamber is fired with a...Ch. 23 - A 1.0m -diameter oil droplet (density 900 kg/m3)...Ch. 23 - The permanent electric dipole moment of the water...Ch. 23 - A point charge Q is distance r from a dipole...Ch. 23 - An ammonia molecule (NH3) has a permanent electric...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 23 - Derive Equation 23.11 for the field Edipolein the...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.41 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.42 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 23 - A plastic rod with linear charge density ? is bent...Ch. 23 - An infinite plane of charge with surface charge...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R and surface charge density ?...Ch. 23 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 23 - An electron is launched at a 45 angle and a speed...Ch. 23 - The two parallel plates in FIGURE P23.53 are 2.0...Ch. 23 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 23 - 56. Your physics assignment is to figure out a way...Ch. 23 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 23 - In Problems 63 through 66 you are given the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 66EAPCh. 23 - A rod of length L lies along the y-axis with its...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 23 - 72. A proton orbits a long charged wire, making ...Ch. 23 - Prob. 73EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) What magnitude point charge creates a 10,000 N/C electric field at a distance of 0.250 m? (b) How large is the field at 10.0 m?arrow_forward(a) Find the total electric field at x = 1.00 cm in Figure 18.52(b) given that q =5.00 nC. (b) Find the total electric field at x = 11.00 cm in Figure 18.52(b). (c) If the charges are allowed to move and eventually be brought to rest by friction, what will the final charge configuration be? (That is, will there be a single charge, double charge; etc., and what will its value(s) he?)arrow_forwardA potassium chloride molecule (KCl) has a dipole moment of 8.9 1030 Cm. Assume the KCl molecule is in a uniform electric field of 325 N/C. What is the change in the systems potential energy when the molecule rotates a. from = 170 to 180, b. from = 90 to 100, and c. from = 10 to 0?arrow_forward
- (a) What is the direction and magnitude of an electric field that supports the weight of a free electron near the surface of Earth? (b) Discuss what the small value for this field implies regarding the relative strength of the gravitational and electrostatic forces.arrow_forwardTwo small spherical conductors are suspended from light-weight vertical insulating threads. The conductors are brought into contact (Fig. P23.50, left) and released. Afterward, the conductors and threads stand apart as shown at right. a. What can you say about the charge of each sphere? b. Use the data given in Figure P23.50 to find the tension in each thread. c. Find the magnitude of the charge on each sphere. Figure P23.50arrow_forward(a) Find the electric field at x = 5.00 cm in Figure 18.52 (a), given that q = 1.00 C. (b) at what position between 3.00 and 8.00 cm is the total electric field the same as that for ? 2q alone? (c) Can the electric field be zero anywhere between 0.00 and 8.00 cm? (d) At very large positive or negative values of x, the electric field approaches zero in both (a) and (b). In which does it most rapidly approach zero and why? (e) At what position to the light of 11.0 cm is the total electric field zero, other than at infinity? (Hint: A graphing calculator can yield considerable insight in this problem.)arrow_forward
- Three charged spheres are at rest in a plane as shown in Figure P23.70. Spheres A and B are fixed, but sphere C is attached to the ceiling by a lightweight thread. The tension in the string is 0.240 N. Spheres A and B have charges qA = 28.0 nC and qB = 28.0 nC. What charge is carried by sphere C?arrow_forwardFigure P23.49 shows two identical small, charged spheres. One of mass 4.0 g is hanging by an insulating thread of length 20.0 cm. The other is held in place and has charge q1 = 3.6 C. The thread makes an angle of 18 with the vertical, resulting in the spheres being aligned horizontally, a distance r apart. Determine the charge q2 on the hanging sphere. Figure P23.49arrow_forwardFigure P24.17 shows a dipole. If the positive particle has a charge of 35.7 mC and the particles are 2.56 mm apart, what is the electric field at point A located 2.00 mm above the dipoles midpoint?arrow_forward
- Most workers in nanotechnology are actively monitored for excess static charge buildup. The human body acts like an insulator as one walks across a carpet, collecting −50 nC per step. What charge buildup will a worker in a manufacturing plant accumulate if she walks 17 steps?arrow_forwardDE @ 2 3 W An electric dipole is formed from two charges, tq, spaced 0.800 cm apart. The dipole is at the origin, oriented along the y-axis. The electric field strength at the point (x, y) = (0 cm, 10 cm) is 340 N/C. S X E D 80 C $ 4 888 FA R F O % 5 V FS T G 6 B ▼ T Part A What is the charge q? Give your answer in nC. Express your answer in nanocoulombs. View Available Hint(s) q= Submit Part B Y E= Submit What is the electric field strength at the point (x, y) = (10 cm, 0 cm) ? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) Provide Feedback G| ΑΣΦ MacBook Air H & 7 Value μÅ 4 U N * 4 8 Units DIL FO M ( 9 K MOSISO ? ? nC O O 1- L P > command . M [ Next 11 F12 1arrow_forwardThere are point loads Q1= 7, Q2=10 and Q3=3 at points A(-9,0), O(0,0) and B (9,0) in the OXY plane, respectively. Write the value of the y-component of the electric field in terms of ke numerically at the point P(0, 12) on the-axis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY