
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110646
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 42EAP
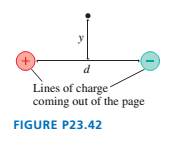
FIGURE P23.42 is a cross section of two infinite lines of charge that extend out of the page. The linear charge densities are
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A fluid with density 263 kg/m3 flows through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At location 1 the flow speed is 13.5 m/s and the diameter of the pipe is 7.4 cm down to location 2 the pipe diameter is 16.9 cm. Location 1 is 6.3 meters higher than location 2.
What is the difference in pressure P2 - P1?
Using units in Pascals and use g = 9.81 m/s2.
The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?
Water is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
Ch. 23 - l. You've been assigned the task of determining...Ch. 23 - Reproduce FIGURE Q23.2 on your paper. For each...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A small segment of wire in FIGURE Q23.4 contains...Ch. 23 - An electron experiences a force of magnitude F...Ch. 23 - FIGURE Q23.6 shows a hollow soda straw that has...Ch. 23 - The irregularly shaped area of charge in FIGURE...Ch. 23 - A circular disk has surface charge density 8...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R has charge Q . The electric...Ch. 23 - The ball in FIGURE Q23.10 is suspended from a...
Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor consists of two square...Ch. 23 - A small object is released at point 3 in the...Ch. 23 - A proton and an electron are released from rest in...Ch. 23 - Three charges are placed at the comers of the...Ch. 23 - l. What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from two charges, q ,...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from ± 1.0 nC charges...Ch. 23 - An electret is similar to a magnet, but rather...Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 10.0 cm from a very...Ch. 23 - A 10-cm-long thin glass rod uniformly charged to...Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-long thin glass rods uniformly charged...Ch. 23 - A small glass bead charged to + 6.0 nC is in the...Ch. 23 - The electric field 5.0 cm from a very long charged...Ch. 23 - A 12-cm-long thin rod has the nonuniform charge...Ch. 23 - Two charged rings face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-diameter charged rings face each other,...Ch. 23 - Two charged disks face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 2.0 cm from the...Ch. 23 - A 20cm20cm cm horizontal metal electrode is...Ch. 23 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter insulating spheres have a 6.0...Ch. 23 - You've hung two very large sheets of plastic...Ch. 23 - A 2.0m X 4.0m flat carpet acquires a uniformly...Ch. 23 - Two circular disks spaced 0.50 mm apart form a...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor is formed from two...Ch. 23 - Air "breaks down" when the electric field strength...Ch. 23 - Two parallel plates 1.0 cm apart are equally and...Ch. 23 - a. What is the electric field strength between the...Ch. 23 - Honeybees acquire a charge while flying due to...Ch. 23 - An electron traveling parallel to a uniform...Ch. 23 - The surface charge density on an infinite charged...Ch. 23 - An electron in a vacuum chamber is fired with a...Ch. 23 - A 1.0m -diameter oil droplet (density 900 kg/m3)...Ch. 23 - The permanent electric dipole moment of the water...Ch. 23 - A point charge Q is distance r from a dipole...Ch. 23 - An ammonia molecule (NH3) has a permanent electric...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 23 - Derive Equation 23.11 for the field Edipolein the...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.41 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.42 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 23 - A plastic rod with linear charge density ? is bent...Ch. 23 - An infinite plane of charge with surface charge...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R and surface charge density ?...Ch. 23 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 23 - An electron is launched at a 45 angle and a speed...Ch. 23 - The two parallel plates in FIGURE P23.53 are 2.0...Ch. 23 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 23 - 56. Your physics assignment is to figure out a way...Ch. 23 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 23 - In Problems 63 through 66 you are given the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 66EAPCh. 23 - A rod of length L lies along the y-axis with its...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 23 - 72. A proton orbits a long charged wire, making ...Ch. 23 - Prob. 73EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forwardWater is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forward
- Jason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. At instant 3, cars P and Q are adjacent to one another (i.e., they have the same position). In the reference frame o f the road, at instant 3 i s the speed o f car Q greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of car P? Explain.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals.arrow_forward
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forwardJust 5 and 6 don't mind 7arrow_forwardIn an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?arrow_forward
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY