
Concept explainers
(a)
The vector electric field created by the
(a)
Answer to Problem 35P
The vector electric field that the
Explanation of Solution
The following figure represents the forces acting on the charges.
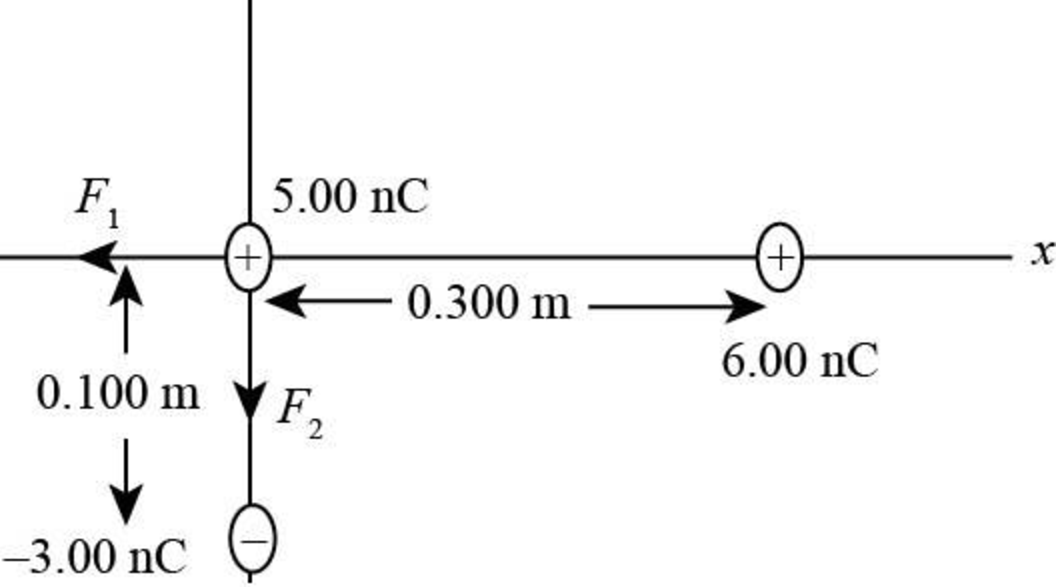
Figure-(1)
Here,
Write the expression for the electric field at origin by the charge
Here,
Write the constant value for the Coulomb constant
Write the expression for the electric field at origin by the charge
Here,
Write the expression for the total vector electric field at origin by the charges
Here, the
Write the expression to convert the units for charge
Write the expression to convert the units for charge
Substitute
Conclusion:
Convert the units for the charge
Convert the units for the charge
Substitute
Further simplify the above equation.
Therefore, the vector electric field that the
(b)
The vector force on the
(b)
Answer to Problem 35P
The vector force on the
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the relation between the electric force and the electric field.
Here,
Write the expression to convert the units for charge
Conclusion:
Convert the units for the charge
Substitute
Therefore, the vector force on the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardhelp me with the experimental set up for the excel i did. the grapharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object? Average acceleration is always halfway between the initial acceleration of an object and its final acceleration. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in velocity of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the displacement of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval.arrow_forward
- The figure shows the velocity versus time graph for a car driving on a straight road. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the car? v (m/s) t(s) The acceleration of the car is negative and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is constant. The acceleration of the car is positive and increasing. The acceleration of the car is positive and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is negative and increasing.arrow_forwardWhich figure could represent the velocity versus time graph of a motorcycle whose speed is increasing? v (m/s) v (m/s) t(s) t(s)arrow_forwardUnlike speed, velocity is a the statement? Poisition. Direction. Vector. Scalar. quantity. Which one of the following completesarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward3.63 • Leaping the River II. A physics professor did daredevil stunts in his spare time. His last stunt was an attempt to jump across a river on a motorcycle (Fig. P3.63). The takeoff ramp was inclined at 53.0°, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. Ignore air resistance. (a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? (b) If his speed was only half the value found in part (a), where did he land? Figure P3.63 53.0° 100 m 40.0 m→ 15.0 marrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





