
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of given compound from benzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic
Answer to Problem 23.80P
The given compound is synthesized from benzene as:
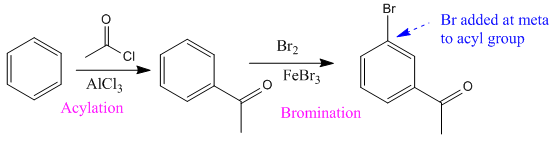
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
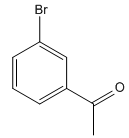
It is noticed that an electron-withdrawing carbonyl group is at meta-position to the bromine atom. Since the bromine atom (halogen) is an ortho/para directing group, acylation (addition of acyl group) of the benzene is carried out in the first step. The next step is the addition of chlorine, as the acyl group is meta directing incoming Cl added at meta to acyl group.
So the complete reaction of synthesis for the given compound is as:

Synthesis of the given compound from benzene is shown on the basis of the directing nature of substituent groups in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of given compound from benzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups, while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.80P
The given compound is synthesized from benzene as:
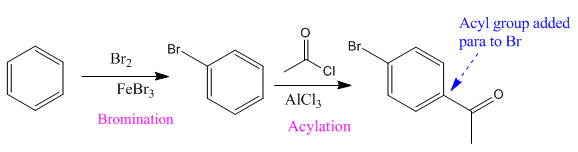
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
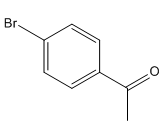
Here acyl group and Br are at para to each other, the Br group is an ortho/para director thus it added first to the benzene ring through bromination. The second step is acylation, the addition of acyl group at the para position.
So the complete reaction of synthesis for the given compound is as:

Synthesis of the given compound from benzene is shown on the basis of the directing nature of substituent groups in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of given compound from benzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups, while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.80P
The given compound is synthesized from benzene as:
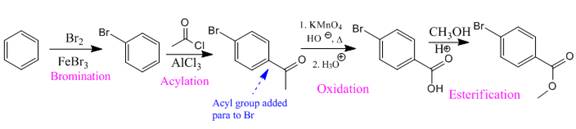
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
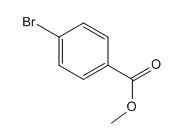
In the above compound both substituents are at para to each other, the Br group is an ortho/para director thus it added first to the benzene ring through bromination. The second step is acylation, addition of acyl group at the para position.

In the next step, the
So the complete reaction of synthesis for the given compound is as:
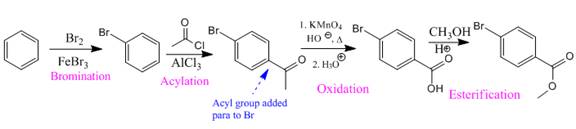
Synthesis of the given compound from benzene is shown on the basis of the directing nature of substituent groups in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of given compound from benzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups, while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.80P
The given compound is synthesized from benzene as:
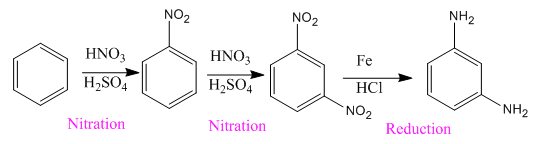
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
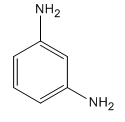
Here both substituents are amino
So the complete reaction of synthesis for the given compound is as:

Synthesis of the given compound from benzene is shown on the basis of the directing nature of substituent groups in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(e)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of given compound from benzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups, while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 23.80P
The given compound is synthesized from benzene as:
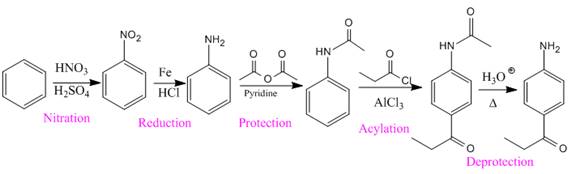
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
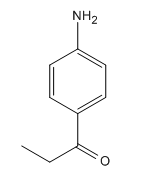
In the above compound, the amino and acyl groups are para to each other. The amino group is an ortho/para director and thus to be added first. The
So the complete reaction of synthesis for the given compound is as:

Synthesis of the given compound from benzene is shown on the basis of the directing nature of substituent groups in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- О δα HO- H -Br δα HO-- + + -Br [B] 8+ HO- -Br δα नarrow_forward1/2 - 51% + » GAY Organic Reactions Assignment /26 Write the type of reaction that is occurring on the line provided then complete the reaction. Only include the major products and any byproducts (e.g. H₂O) but no minor products. Please use either full structural diagrams or the combination method shown in the lesson. Skeletal/line diagrams will not be accepted. H3C 1. 2. CH3 A Acid OH Type of Reaction: NH Type of Reaction: + H₂O Catalyst + HBr 3. Type of Reaction: H3C 4. Type Reaction: 5. H3C CH2 + H2O OH + [0] CH3 Type of Reaction: 6. OH CH3 HO CH3 + Type of Reaction: 7. Type of Reaction: + [H]arrow_forwardhumbnai Concentration Terms[1].pdf ox + New Home Edit Sign in Comment Convert Page Fill & Sign Protect Tools Batch +WPS A Free Trial Share Inter Concreting Concentration forms. Hydrogen peroxide is a powerful oxidizing agent wed in concentrated solution in rocket fuels and in dilute solution as a hair bleach. An aqueous sulation of H2O2 is 30% by mass and has density of #liligime calculat the Ⓒmolality ⑥mole fraction of molarity. 20 9. B. A sample of Commercial Concentrated hydrochloric ETarrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forward
- Draw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forward
- Choose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





