
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with dilute
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
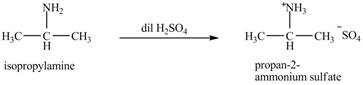
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of amines with dilute

Figure 1
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with dilute
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a dilute
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The reaction does not form any product. The reaction is shown below.
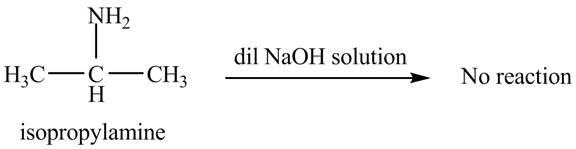
Explanation of Solution
When isopropylamine reacts with a dilute
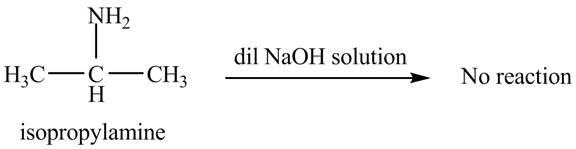
Figure 2
No product is obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a dilute
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product lithium isopropylamide is obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
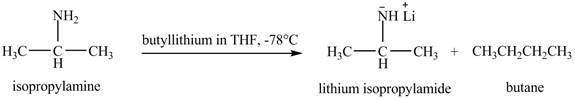
Explanation of Solution
The organolithium base butyllithium in

Figure 3
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with butyllithium in
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride and pyridine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
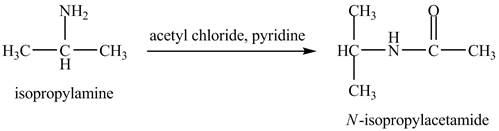
Explanation of Solution
The acid chloride is a very reactive compound. When it reacts with amines it forms amides. The reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride in pyridine results in the formation of
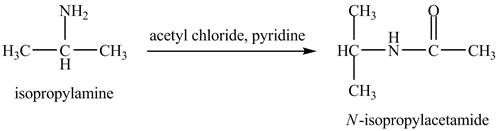
Figure 4
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetyl chloride and pyridine is
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. The formation of diazonium salt from
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
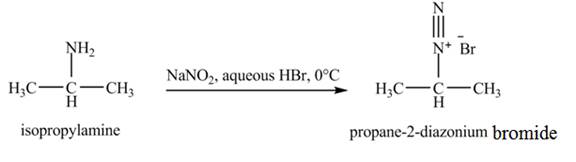
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is an example of a diazotization reaction. When isopropylamine reacts with

Figure 5
The product that obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetone and
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
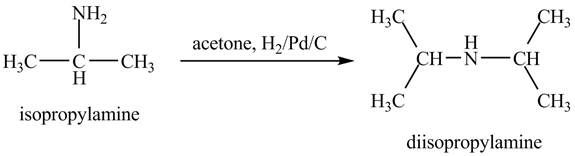
Explanation of Solution
When acetone reacts with isopropylamine, it forms enamine, with double bonds. It is then hydrogenated by

Figure 6
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with acetone and
(g)
Interpretation:
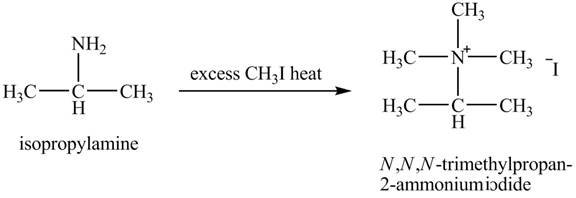
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with excess
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is quaternary ammonium hydroxide. When quaternary ammonium hydroxide is heated,
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
Explanation of Solution
Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is isopropylamine. When it reacts with an excess of

Figure 7
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with excess
(h)
Interpretation:
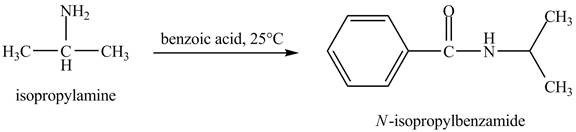
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with benzoic acid at
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction, benzoic acid is a reactive compound. When it reacts with amine it results in the formation of an amide. This reaction is similar to the conversion of carboxylic acid to amides. The reaction is shown below.
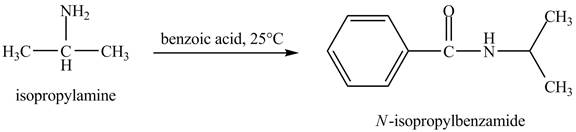
Figure 8
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with benzoic acid at
(i)
Interpretation:
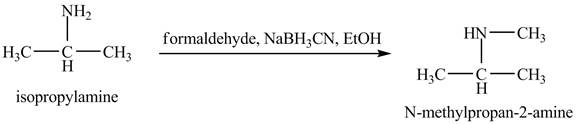
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with formaldehyde,
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
Explanation of Solution
This reaction is an example of a reductive amination reaction. Reductive amination reaction is the conversion of the carbonyl group to the amine or it converts one amine to newer amine. In this reaction, when isopropylamine reacts formaldehyde,

Figure 9
The product that obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with formaldehyde,
(j)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
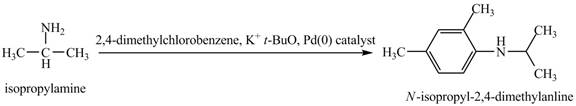
Explanation of Solution
This reaction is an example of a Buchwald-Hartwig reaction. Buchwald Hartwig reaction is used for
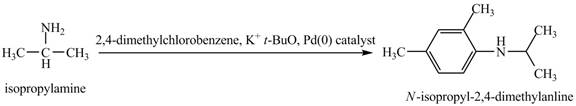
Figure 10
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with
(k)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (g) +
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Hofmann elimination reaction occurs as an anti-elimination reaction. In this reaction, the starting material is quaternary ammonium hydroxide. When quaternary ammonium hydroxide is heated,
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product
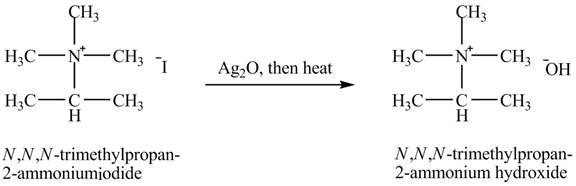
Explanation of Solution
When isopropylamine undergoes Hofmann elimination reaction with a product of part (g)

Figure 11
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (g)
(l)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (d) with
Concept introduction:
Amines are the organic compounds that are formed by replacement of hydrogen from ammonia with a substituent. It may be alkyl or aryl group. Amines are basic in nature because the nitrogen can donate its lone pairs and it also has the ability to accept the proton in water.
Answer to Problem 23.46AP
The product,
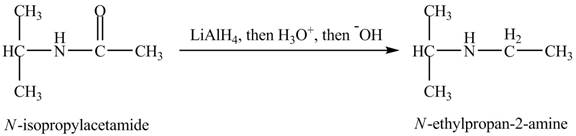
Explanation of Solution
When
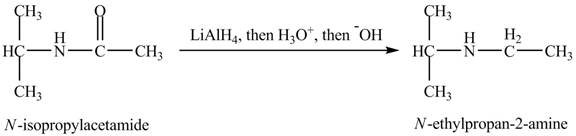
Figure 12
The product obtained in the reaction of isopropylamine with a product of part (d) with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- H-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
