
a)
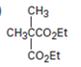
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
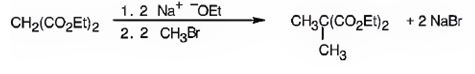
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
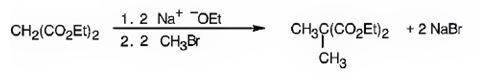
Explanation of Solution
The compound shown is a derivative of carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The acid has two methyl groups attached to the carbon adjacent to ester groups. It can be prepared by replacing the two hydrogens on the active methylene group of malonic ester by two methyl groups. This is achieved by treating the ester with two equivalents of sodium ethoxide and two equivalents of methyl bromide.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
b)
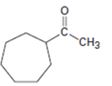
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
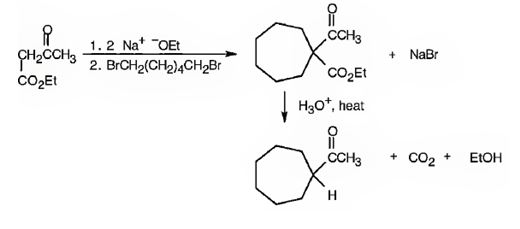
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
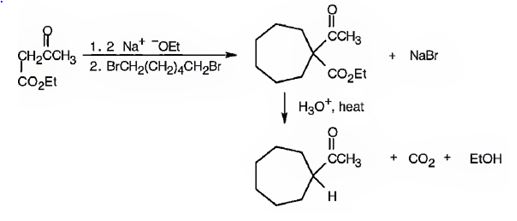
Explanation of Solution
: The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,6- dibromohexane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted acetoacetic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield methyl cycloheptyl ketone.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
c)
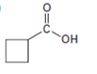
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
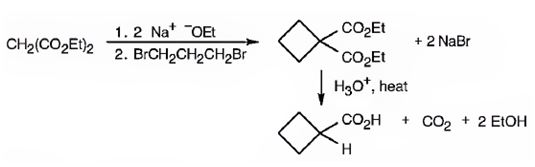
Explanation of Solution
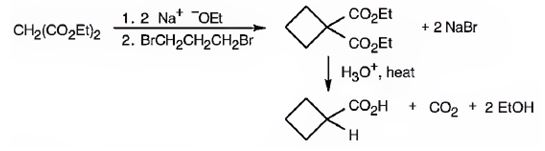
The compound shown is a carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of malonic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,3- dibromopropane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted malonic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic diester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester groups get hydrolyzed to give a dicarboxylic acid. The dicarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield cyclobutylcarboxylic acid.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
d)
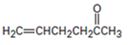
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
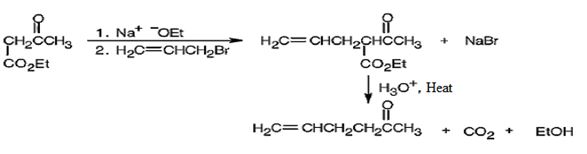
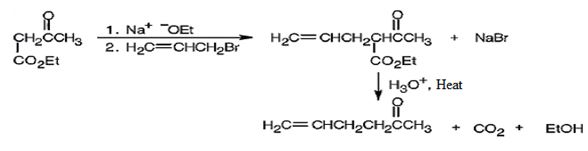
The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on allyl bromide displaces the bromide ion to produce α- allylsubstituted acetoacetic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield hex-5-ene-2-one.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- H CH3 CH3 b) Write the products of your compound and the following reagents. If the reaction would not work for your compound, write "no reaction" and explain the problem. NaCN H* H₂NNHCH5 H* -à NaBH -à CH2MgBr Cro₁₂ --à H3O+ -à c) Would your compound give a positive Tollen's test? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHomework 4 Chem 204 Dr. Hellwig Consider this compound, which will be referred to as "your compound". a) Name your compound according to the IUPAC system. Include stereochemistry (E/Z/R/S) H CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 21.50 Determine the combinations of haloalkane(s) and alkoxide(s) that could be used to synthesize the following ethers through Williamson ether synthesis. (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) H₂COarrow_forward1. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond energy (lowest bond energy first, highest bond energy last). Provide your rationale. C=C, C-F, C=C, C-N, C-C List the bond order for each example.arrow_forwardWhat is the major enolate formed when treated with LDA? And why that one?arrow_forward
- 4. Calculate the total number of sigma bonds and total number of pi bonds in each of the following compounds. a. HH :D: +1 I H-N-C-C-O-H I H b. HH H Н :N=C-C-C=C-CEC-H :0: total o H-C-H H-C = `C-H I H. 11 H-C = C= CH H total o total π total π 1 Harrow_forwardIn the following reaction, what quantity in moles of CH₃OH are required to give off 4111 kJ of heat? 2 CH₃OH (l) + 3 O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O(g) ∆H° = -1280. kJarrow_forwardIndicate the processes in the dismutation of Cu2O.arrow_forward
- 1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 Potential Energy (kJ) 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800 (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt(s) → 2Cl (g) + Pt(s) (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ Ea = 2240 kJ (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2350 kJ AH=-950 kJ ΔΗ = 575 ΚΙ AH=-825 kJ a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ Reaction Progress b. What is the overall chemical equation? c. What is the overall change in enthalpy for the above chemical reaction? d. What is the overall amount of activation energy for the above chemical reaction? e. Which reaction intermediate would be considered a catalyst (if any) and why? f. If you were to add 2700kJ of energy to the reaction (e.g. 2700 kl of heat or electricity), would you be able to make the reaction reverse itself (i.e. have…arrow_forwarddraw the enolate anion and the carbonyl that would be needed to make this product through an aldol addition reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael Adduct and the final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


