
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The base, codon, anticodon and the amino acid needed to complete a given table needs to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
The first step of the synthesis of proteins using the information in DNA is transcription.
During transcription, the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA takes place.
Only one DNA strand is needed for RNA synthesis, thus the double helix of DNA unwinds during transcription. The strand used for the RNA synthesis is called template strand. The other strand (the non-template strand) is called informational strand and does not involve in the RNA synthesis.The informational strand of DNA is complementary to the template strand.
The informational strand of DNA is complementary to the template strand; meaning the base sequence of the informational strand consists of the complementary base sequence of the template strand.
complementary base pairs:
Adenine pairs with thymine (A−T base pair).
Cytosine pairs with guanine (C−G base pair).
In addition, the direction of the two strands in the same DNA have different directions. Therefore, if the template strand goes from 3' to 5', the informational strand goes from 5' to 3'.
The mRNA synthesized from transcription has a complementary sequence to the DNA template from which it is prepared. Since the informational strand of DNA is complementary to the template strand, the mRNA is an exact copy of the informational strand, the only exception is that the base T present in the informational strand is replaced by U on the RNA strand.
The information needed to prepare a polypeptide is in the mRNA strand. Each sequence of three
The below table gives the corresponding amino acid of each codon. Based on the codon sequence of the mRNA strand, the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide strand can be determined with the help of the table.
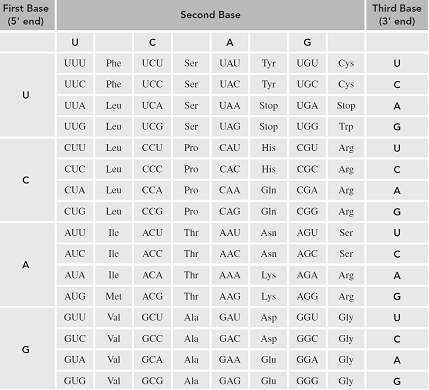
Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings specific amino acids to add to the synthesizing peptide chain. Each individual tRNA contains an anticodon of three nucleotides that is complementary to the codon in mRNA.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- For the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





