
BIOCHEM. II-EBOOK ACCESS>CUSTOM<
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781337700320
Author: GARRETT
Publisher: CENGAGE LEARNING (CUSTOM)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 22, Problem 7P
Interpretation Introduction
To calculate:
The number of reducing ends and non-reducing ends in given cases.
Introduction:
Glycogen is composed of glucose linked via alpha (1-4) linkages and branches occurring through alpha (1-6) linkages. In glycogen, the free C-1 end on glucose end of the molecule is called a reducing end and all the other ends are non-reducing ends.
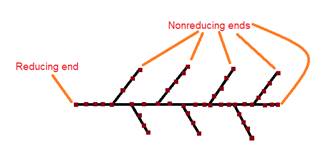
Black line indicate the glycogen chain and red dot indicates the glucose monomers.
Therefore, regardless of the number of residues in the glycogen chain, there is only one reducing end for a glycogen chain. All other ends are non-reducing.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Discuss the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with regards to their genetic materials. Including in your discussion the structure and organisation of genetic material, as well as any implications these differences may have on cellular functions and evolution.
Rubric
Understanding of genetic material differences (provides a comprehensive and accurate explanation of the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in terms of their genetic material, including the structure, organisation and function of genetic material in each cell type. Demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic)
Analysis of implications (analyze the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in terms of their genetic material with depth and insight, discussing the implications of these differences on cellular functions and evolution. Provides specific examples and explanations.)
When was the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker isradipine first patented and by whom? Please provide information on the origin and history of isradipine and who owns it/manufactures it.
9) Below, there is a representation of an SDS-PAGE gel. Assuming the samples in the
MW standard have masses of: 66 kDa, 45 kDa, 36 kDa, 29 kDa, 24 kDa, 20.1 kDa, and
14.2 kDa,
a) Figure 4: indicate where each of the measurements were taken and label as in II.6.
figure 2 above.
b) As in II.7. Table 1 above create Table 2 using the data below. Determine the r.f.
values for the MW standards, plot the relative mobility versus the log of the mass
for the standards, and use the best fit straight line to determine the molecular
weights of the proteins in the whey, peak 1, and peak 2 lanes. (5 pts—this will be
scaled up appropriately if your gel did not develop properly)
dye
MW
Whey
Peak 1 Peak 2
Chapter 22 Solutions
BIOCHEM. II-EBOOK ACCESS>CUSTOM<
Ch. 22 - Prob. 1PCh. 22 - Prob. 2PCh. 22 - Prob. 3PCh. 22 - Prob. 4PCh. 22 - Prob. 5PCh. 22 - Prob. 6PCh. 22 - Prob. 7PCh. 22 - Prob. 8PCh. 22 - Prob. 9PCh. 22 - Understanding Enzyme Mechanisms Related to...
Ch. 22 - Understanding the Mechanisms of Reactions Related...Ch. 22 - Prob. 12PCh. 22 - Prob. 13PCh. 22 - Prob. 14PCh. 22 - Prob. 15PCh. 22 - Prob. 16PCh. 22 - Prob. 17PCh. 22 - Prob. 18PCh. 22 - Prob. 19PCh. 22 - Prob. 20PCh. 22 - Prob. 21PCh. 22 - Prob. 22PCh. 22 - Using the ActiveModel for aldose reductase,...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- what are the different classes and some examples of neuroprotectants that can be used to treat, prevent, or combat neurotoxicity/a neurotoxicant...for example, antioxidants, nutraceuticals, etc.,..?arrow_forwardImagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated. Please draw out the stereochemistry in a fischer projection.arrow_forwardSodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition? Please draw out the mechanism and show how it inhibits this.arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP. Please include a drawing showing the electron flow that occurs.arrow_forward1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following aldol condensation? O NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound. Please show the mechanism by drawing.arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose. Please draw out the structure using curve arrows to show electron flow.arrow_forward3. Which one of the compounds below is the major product formed by the reaction sequence shown here? CH3 + CH3NO2 NaOH H2, Ni ? nitromethane acetophenone OH OH HO HN- u x x x x Ph A HO -NH2 HO H Ph Ph Ph N- H B Ph NH2 D Earrow_forward4. Only ONE of the five compounds below can be prepared by an aldol condensation in which a single carbonyl compound is treated with base. Which one is it? To solve this problem, reverse the aldol condensation that formed each of these molecules to find out what two molecules came together to make the products. The one in which the two molecules are identical is the answer. Ph Ph ཚིག གནས ག ནཱ ཀ ན ཀནཱ A Ph H B Ph Ph H D Ph. Ph Ph E Harrow_forward
- 5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? First, equimolar amounts of cyclopentanone and LDA are mixed at -78°C. Then propionaldehyde (propanal) is added. Addition of aqueous acid completes the process. LDA, -78°C. 1. 2. H₂O* H A B H 0 D H H Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardCH3CH2CHO + propanal PhCH2CHO 2-phenylacetaldehyde mixture of four products NaOH 10. In the crossed aldol reaction of propanal and 2-phenylacetaldehyde shown above, a mixture of four products will be formed. Which ONE of the compounds below will NOT be formed in this crossed aldol reaction? OH Ph A H OH OH Ph H B OH OH H H H Ph Ph C Ph D Earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning