
a.
To calculate: The points where the function is
a.
Answer to Problem 7E
The function is differentiable at every point of the domain
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The domain is
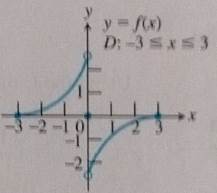
Concept used:
If a function is differentiable at a point it will also be continuous at that point.
If a function is continuous at a point then it may or may not be differentiable.
Calculation:
From the graph it is clear that the graph is smooth without any sharp turns.
There is one exception that is at point
Conclusion: The function is differentiable at every point of the domain
b.
To calculate: The function is continuous but not differentiable.
b.
Answer to Problem 7E
There is no point where the function is continuous but not differentiable.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The domain is
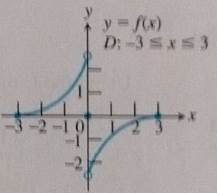
Concept used:
If a function is continuous but not differentiable it can have corner, cusp or vertical tangent.
Calculation:
The graph has a break point at
From the graph it is clear that the graph is not smooth at
Conclusion: There is no point where the function is continuous but not differentiable.
c.
To calculate: The function is neither continuous nor differentiable.
c.
Answer to Problem 7E
No, there are no such points where the function is neither continuous nor differentiable.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The domain is
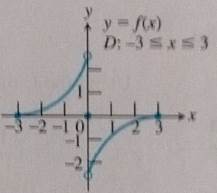
Concept used:
If a function is differentiable at a point it will also be continuous at that point.
If a function is continuous at a point then it may or may not be differentiable.
Calculation:
There is a point
Conclusion: There are no such points where the function is neither continuous nor differentiable.
Chapter 2 Solutions
CALCULUS-W/XL ACCESS
- EXAMPLE 3 Find S X √√2-2x2 dx. SOLUTION Let u = 2 - 2x². Then du = Χ dx = 2- 2x² = 信 du dx, so x dx = du and u-1/2 du (2√u) + C + C (in terms of x).arrow_forwardLet g(z) = z-i z+i' (a) Evaluate g(i) and g(1). (b) Evaluate the limits lim g(z), and lim g(z). 2-12 (c) Find the image of the real axis under g. (d) Find the image of the upper half plane {z: Iz > 0} under the function g.arrow_forwardk (i) Evaluate k=7 k=0 [Hint: geometric series + De Moivre] (ii) Find an upper bound for the expression 1 +2x+2 where z lies on the circle || z|| = R with R > 10. [Hint: Use Cauchy-Schwarz]arrow_forward
- Hint: You may use the following derivative rules: ddxsin(x)=cos(x) ddxcos(x)=−sin(x) ddxln(x)=1x Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve y=4sinx at the point (π6,2).The equation of this tangent line isarrow_forwardQuestion Find the following limit. Select the correct answer below: 1 2 0 4 5x lim sin (2x)+tan 2 x→arrow_forward12. [0/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 5.5.022. Evaluate the indefinite integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) sin(In 33x) dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





