
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
Grignard reaction: The Grignard reaction is an organic reaction used to create a variety of products through the reaction of an organomagnesium compound, also known as a "Grignard reagent" with an electrophile, followed by acid work-up.
Reductive amination: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions.
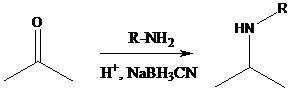
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (a) starting from benzene
Apply retrosynthetic analysis
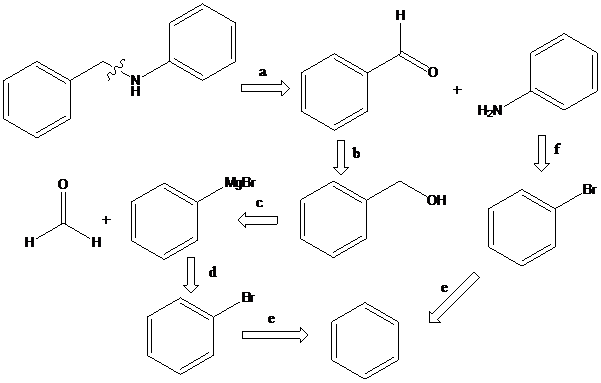
(b)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution: Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. Here are three general steps to an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
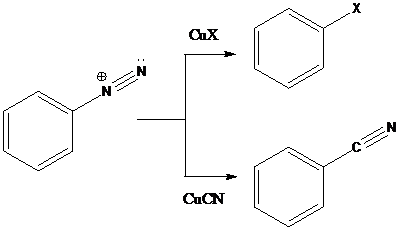
Sandmeyer reaction: Sandmeyer reactions use copper salts as the reagents. Here, aryldiazonium salt is converted into aryl halides or aryl cyanides by using copper halides or copper cyanides.
A compound containing an amino group is treated with sodium nitrite and HCl leading to the formation of diazonium salt.
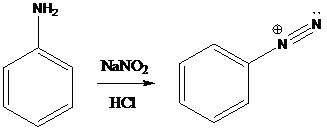
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (b) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis

(c)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution: Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. Here are three general steps to an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
Grignard reaction: The Grignard reaction is an organic reaction used to create a variety of products through the reaction of an organomagnesium compound, also known as a "Grignard reagent" with an electrophile, followed by acid work-up.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction: It is the reaction of an electron pair donor (the nucleophile, Nu) with an electron pair acceptor (the electrophile). A sp3-hybridized electrophile must have a leaving group (X) in order for the reaction to take place. The term SN2 means that two molecules are involved in the actual transition state.
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (c) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis
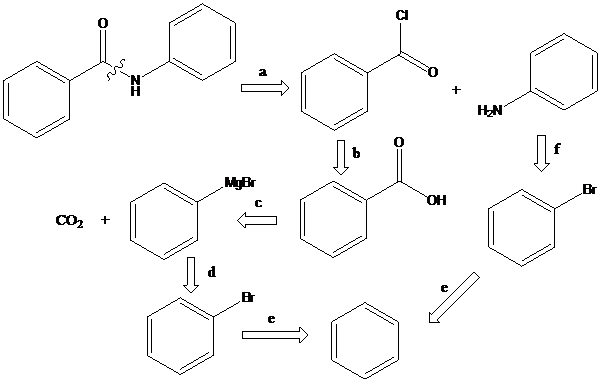
(d)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
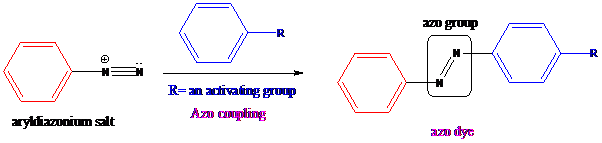
Azo coupling: Aryldiazonium salts on coupling with an activated aromatic ring give an azo dye which produces a deep color in the final product. This color is due to the extended conjugation in it. This reaction occurs by electrophilic substitution reaction. This method is called an azo coupling. The obtained final compound is known as azo dyes.
Friedel–Crafts acylation: The Friedel–Crafts acylation is the reaction of an arene with acyl chlorides or anhydrides using a strong Lewis acid catalyst. This reaction proceeds via electrophilic aromatic substitution to form monoacylated products.
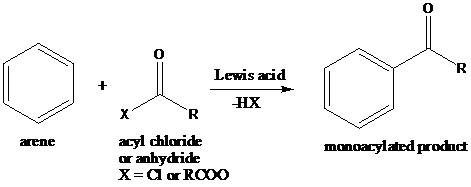
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (d) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis for the given azo dye

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LL BUNDLE
- 1,4-Dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene can undergo 1,2- or 1,4-addition with hydrogen halides. (a) 1,2-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,2-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,2-addition product formed during the reaction in (i)? (b) 1,4-Addition i. Draw the carbocation intermediate(s) formed during the 1,4-addition of hydrobromic acid to 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. ii. What is the major 1,4-addition product formed from the reaction in (i)? (c) What is the kinetic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobromic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (d) What is the thermodynamic product from the reaction of one mole of hydrobro-mic acid with 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene? Explain your reasoning. (e) What major product will result when 1,4-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of hydrobromic acid at - 78 deg * C ? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardGive the product of the bimolecular elimination from each of the isomeric halogenated compounds. Reaction A Reaction B. КОВ CH₂ HotBu +B+ ко HOIBU +Br+ Templates More QQQ Select Cv Templates More Cras QQQ One of these compounds undergoes elimination 50x faster than the other. Which one and why? Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups and to each other Reaction A because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gauche to each other. ◇ Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups gach to each other. Reaction B because the conformation needed for elimination places the phenyl groups anti to each other.arrow_forwardFive isomeric alkenes. A through each undergo catalytic hydrogenation to give 2-methylpentane The IR spectra of these five alkenes have the key absorptions (in cm Compound Compound A –912. (§), 994 (5), 1643 (%), 3077 (1) Compound B 833 (3), 1667 (W), 3050 (weak shoulder on C-Habsorption) Compound C Compound D) –714 (5), 1665 (w), 3010 (m) 885 (3), 1650 (m), 3086 (m) 967 (5), no aharption 1600 to 1700, 3040 (m) Compound K Match each compound to the data presented. Compound A Compound B Compound C Compound D Compoundarrow_forward
- 7. The three sets of replicate results below were accumulated for the analysis of the same sample. Pool these data to obtain the most efficient estimate of the mean analyte content and the standard deviation. Lead content/ppm: Set 1 Set 2 Set 3 1. 9.76 9.87 9.85 2. 9.42 9.64 9.91 3. 9.53 9.71 9.42 9.81 9.49arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product famed when 2,3-dimethylpentan-3-of undergoes an El dehydration. CH₂ E1 OH H₁PO₁ Select Draw Templates More QQQ +H₂Oarrow_forwardComplete the clean-pushing mechanism for the given ether synthesia from propanol in concentrated sulfurica140°C by adding any mining aloms, bands, charges, nonbonding electron pairs, and curved arrows. Draw hydrogen bonded to cayan, when applicable. ore 11,0 HPC Step 1: Draw curved arrows Step 2: Complete the intend carved Q2Q 56 QQQ Step 3: Complete the intermediate and add curved Step 4: Modify the structures to draw the QQQ QQQarrow_forward
- 6. In an experiment the following replicate set of volume measurements (cm3) was recorded: (25.35, 25.80, 25.28, 25.50, 25.45, 25.43) A. Calculate the mean of the raw data. B. Using the rejection quotient (Q-test) reject any questionable results. C. Recalculate the mean and compare it with the value obtained in 2(a).arrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T G OH де OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardMacmillan Leaming Draw the major organic product of the reaction. 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H+ - G Select Draw Templates More H о QQarrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 3-hydroxy-2-butanone. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardGive the expected major product of reaction of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane with each of the following reagents. 2. Reaction with dilute H₂SO, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More CHC Erase QQQ c. Reaction with dilute aqueous HBr. Select Drew Templates More Era c QQQ b. Reaction with NaOCH, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More d. Reaction with concentrated HBr. Select Draw Templates More En a QQQ e. Reaction with CH, Mg1, then H*, H₂O 1. Reaction with CH,Li, then H', H₂Oarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure O OH OH name X ☐arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





