
(a)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
The reagents such as methyl iodide and silver oxide are given and used as the reaction conditions in the given reactions. This reaction is called Hofmann elimination. The
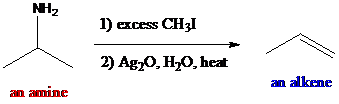
To find: The major product in the reaction (a) via Hofmann elimination
Identify all α- and β-positions in the starting material of the reaction (a)
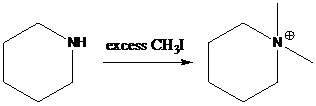
(b)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for primary amine is −NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
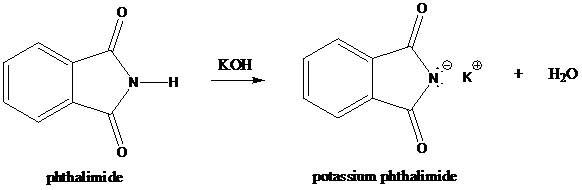
Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary
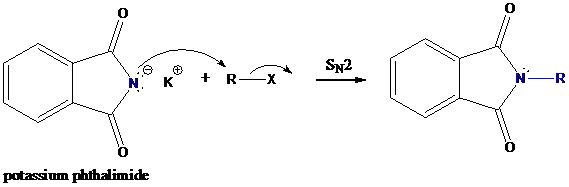
Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.
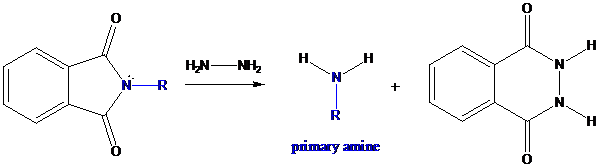
To find: Using a Gabriel synthesis, prepare the major product of (b)
Identify the correct alkyl halide involved in the formation of hexylamine
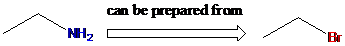
(c)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
When sodium cyanide is reacted with alkyl halide, SN2 nucleophilic reaction of cyanide on alkyl group occurs. So, cyanide is introduced into alkyl group. By adding water to alkyl cyanide, cyanide is converted into
To find: Obtain the major product in the reaction (c)
Draw the nucleophilic attack of cyanide on alkyl group
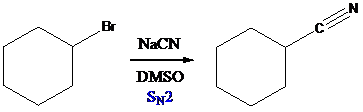
(d)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Sandmeyer reactions use copper salts as the reagents. Here, aryldiazonium salt is converted into aryl halides or aryl cyanides by using copper halides or copper cyanides.
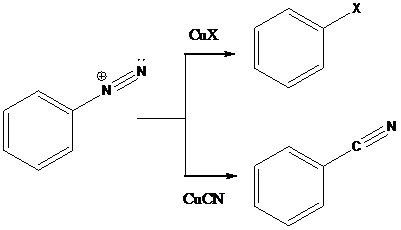
To find: The major product in the reaction (d) via Sandmeyer reaction
Do nitration of benzene

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL) W/ACCESS
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





