
(a)
Interpretation: Hexylamines have to be synthesized from various starting compounds.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for hexylamine is C6H13NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
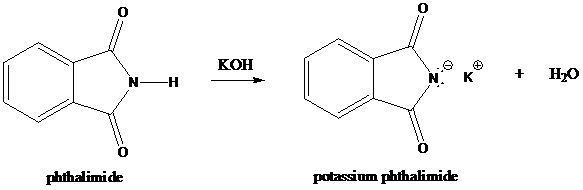
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary
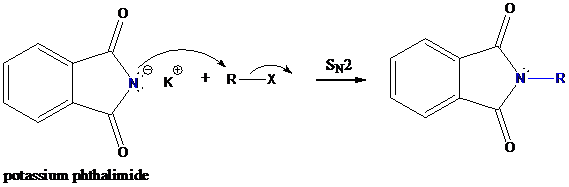
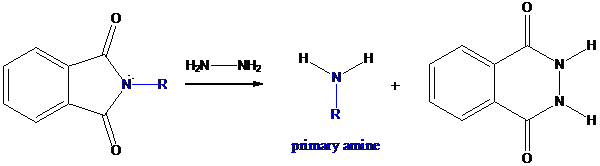
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.
(b)
Interpretation: Hexylamines have to be synthesized from various starting compounds.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for hexylamine is C6H13NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
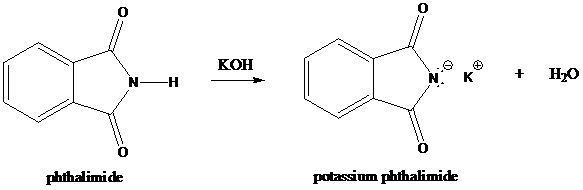
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
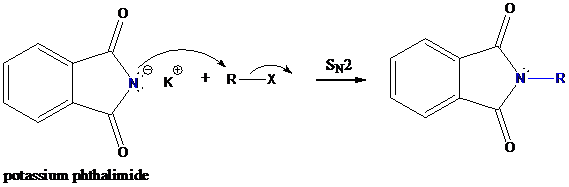
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

(c)
Interpretation: Hexylamines have to be synthesized from various starting compounds.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for hexylamine is C6H13NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
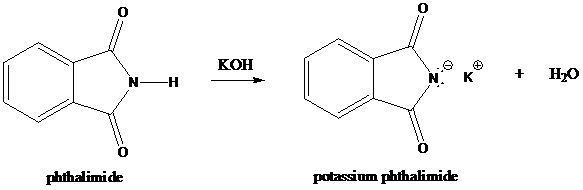
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
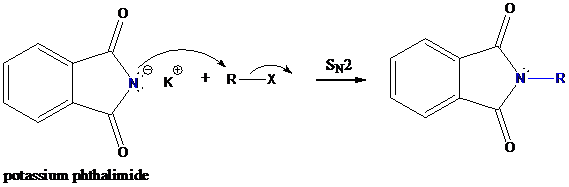
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

(d)
Interpretation: Hexylamines have to be synthesized from various starting compounds.
Concept Introduction: The general formula for hexylamine is C6H13NH2. There are several methods available to prepare primary amines. Among them, Gabriel synthesis plays a very important role for preparing it. In this method, secondary and tertiary amines are not formed as side products. It involves in three steps.
Step-1: Formation of potassium phthalimide (deprotonation)
Potassium phthalimide in alkaline KOH acts as the reagent which has negatively charged phthalimide. It is formed by the reaction between phthalimide and potassium hydroxide.
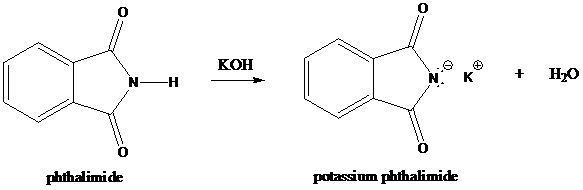
Step-2: Formation of R−N bond by SN2 nucleophilic substitution
The negative charged nitrogen atom in phthalimide can easily attract the positive side of R−X. In primary alkyl halides (R−X), R and X get positive and negative charges, respectively when they ionize. As a result, a bond between nitrogen of phthalimide and carbon of R is formed. This is SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction. Halogen atom is going away as halide anion.
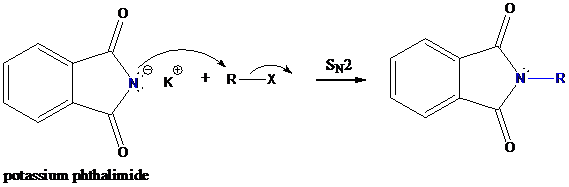
Step-3: Formation of primary amine by hydrolysis
The resultant product further goes for hydrolysis using hydrazine as the reagent. This reaction also follows nucleophilic substitution reaction. Finally, primary amine is formed with a side product of hydrazine derivative.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





