
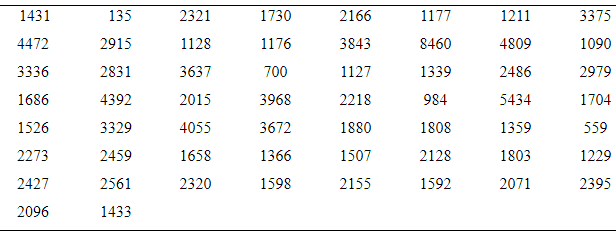
Hail to the chief: There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
- Construct a frequency distribution with approximately five classes.
- Construct a frequency histogram from the frequency distribution in part (a).
- Construct a relative frequency distribution using the same classes as in part (a).
- Construct a relative frequency histogram from this relative frequency distribution.
- Are the histograms skewed to the left, skewed to the right, or approximately symmetric?
- Construct a frequency distribution with approximately nine classes.
- Repeat parts (b)—(d), using the frequency distribution constructed in part (f).
- Do you think that five and nine classes are both reasonably good choices for these data, or do you think that one choice is much better than the other? Explain your reasoning.
a.
To construct:A frequency distribution with approximately 5 classes.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
| 1431 | 135 | 2321 | 1730 | 2166 | 1177 | 1211 | 3375 |
| 4472 | 2915 | 1128 | 1176 | 3843 | 8460 | 4809 | 1090 |
| 3336 | 2831 | 3637 | 700 | 1127 | 1339 | 2486 | 2979 |
| 1686 | 4392 | 2015 | 3968 | 2218 | 984 | 5434 | 1704 |
| 1526 | 3329 | 4055 | 3672 | 1880 | 1808 | 1359 | 559 |
| 2273 | 2459 | 1658 | 1366 | 1507 | 2128 | 1803 | 1229 |
| 2427 | 2561 | 2320 | 1598 | 2155 | 1592 | 2071 | 2395 |
| 2096 | 1433 |
Definition used: Frequency distributions for quantitative data are just like those for qualitative data, except the data are divided into classes rather categories.
Solution:
The class width is 2000. The minimum and maximum values of the ratings are 0 and 9999.
The table of frequency distribution is given by
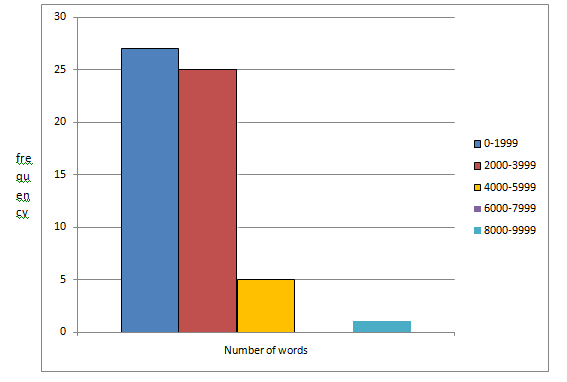
| Number of words | Frequency |
| 0-1999 | 27 |
| 2000-3999 | 25 |
| 4000-5999 | 5 |
| 6000-7999 | 0 |
| 8000-9999 | 1 |
b.
To construct:A frequency histogram from the frequency distribution.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The table of frequency distribution is given by
| Number of words | Frequency |
| 0-1999 | 27 |
| 2000-3999 | 25 |
| 4000-5999 | 5 |
| 6000-7999 | 0 |
| 8000-9999 | 1 |
Definition used: Histograms based on frequency distributions are called frequency histogram.
Solution:
The frequency histogram for the given data is given by
c.
To construct: A relative frequency distribution.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The table of frequency distribution is given by
| Number of words | Frequency |
| 0-1999 | 27 |
| 2000-3999 | 25 |
| 4000-5999 | 5 |
| 6000-7999 | 0 |
| 8000-9999 | 1 |
Formula used:
Solution:
From the given table,
The sum of all frequency is
The table of relative frequency is given by
| Number of words | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| 0-1999 | 27 | |
| 2000-3999 | 25 | |
| 4000-5999 | 5 | |
| 6000-7999 | 0 | |
| 8000-9999 | 1 |
d.
To construct: A relative frequency histogram.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
| 1431 | 135 | 2321 | 1730 | 2166 | 1177 | 1211 | 3375 |
| 4472 | 2915 | 1128 | 1176 | 3843 | 8460 | 4809 | 1090 |
| 3336 | 2831 | 3637 | 700 | 1127 | 1339 | 2486 | 2979 |
| 1686 | 4392 | 2015 | 3968 | 2218 | 984 | 5434 | 1704 |
| 1526 | 3329 | 4055 | 3672 | 1880 | 1808 | 1359 | 559 |
| 2273 | 2459 | 1658 | 1366 | 1507 | 2128 | 1803 | 1229 |
| 2427 | 2561 | 2320 | 1598 | 2155 | 1592 | 2071 | 2395 |
| 2096 | 1433 |
Definition used: Histograms based on relative frequency distributions are called relative frequency histogram.
Solution:
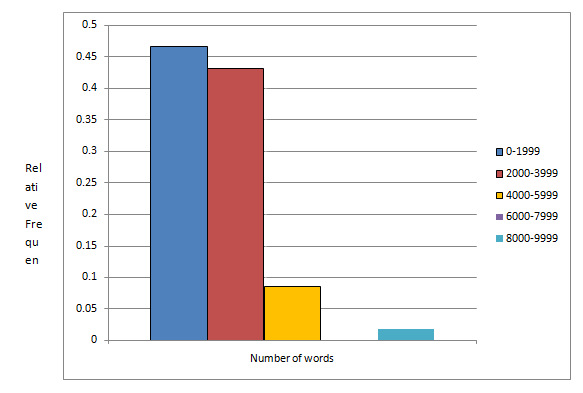
| Number of words | Relative Frequency |
| 0-1999 | 0.466 |
| 2000-3999 | 0.431 |
| 4000-5999 | 0.086 |
| 6000-7999 | 0.000 |
| 8000-9999 | 0.017 |
Therelative frequency histogram for the given data is given by
e.
To find: Whether the histograms are skewed to the right, skewed to the left, or approximately symmetric.
Answer to Problem 33E
The histogram is skewed to the right.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
| 1431 | 135 | 2321 | 1730 | 2166 | 1177 | 1211 | 3375 |
| 4472 | 2915 | 1128 | 1176 | 3843 | 8460 | 4809 | 1090 |
| 3336 | 2831 | 3637 | 700 | 1127 | 1339 | 2486 | 2979 |
| 1686 | 4392 | 2015 | 3968 | 2218 | 984 | 5434 | 1704 |
| 1526 | 3329 | 4055 | 3672 | 1880 | 1808 | 1359 | 559 |
| 2273 | 2459 | 1658 | 1366 | 1507 | 2128 | 1803 | 1229 |
| 2427 | 2561 | 2320 | 1598 | 2155 | 1592 | 2071 | 2395 |
| 2096 | 1433 |
Definition used:
A histogram which has a long right-hand tail is said to be skewed to the right.
A histogram which has a long left-hand tail is said to be skewed to the left.
A histogram is symmetric if its right half is a minor image of its left half.
Solution:
The frequency histogram for the given data is given by
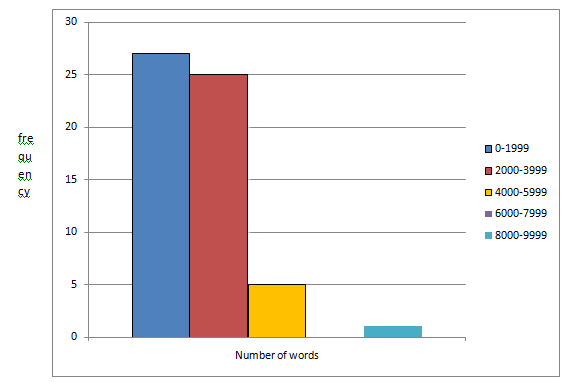
The above histogram has a right-hand tail; therefore, it is skewed to the right.
Hence, the histogram is skewed to the right.
f.
To construct: A frequency distribution with approximately 9 classes.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
| 1431 | 135 | 2321 | 1730 | 2166 | 1177 | 1211 | 3375 |
| 4472 | 2915 | 1128 | 1176 | 3843 | 8460 | 4809 | 1090 |
| 3336 | 2831 | 3637 | 700 | 1127 | 1339 | 2486 | 2979 |
| 1686 | 4392 | 2015 | 3968 | 2218 | 984 | 5434 | 1704 |
| 1526 | 3329 | 4055 | 3672 | 1880 | 1808 | 1359 | 559 |
| 2273 | 2459 | 1658 | 1366 | 1507 | 2128 | 1803 | 1229 |
| 2427 | 2561 | 2320 | 1598 | 2155 | 1592 | 2071 | 2395 |
| 2096 | 1433 |
Definition used: Frequency distributions for quantitative data are just like those for qualitative data, except the data are divided into classes rather categories.
Solution:
Let us take the class width is 1000. The minimum and maximum values of the ratings are 0 and 8999.
The table of frequency distribution is given by
| Number of words | Frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 |
| 1000-1999 | 23 |
| 2000-2999 | 18 |
| 3000-3999 | 7 |
| 4000-4999 | 4 |
| 5000-5999 | 1 |
| 6000-6999 | 0 |
| 7000-7999 | 0 |
| 8000-8999 | 1 |
g.
To construct: A frequency histogram, relative frequency distribution and relative frequency histogram.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The table of frequency distribution is given by
| Number of words | Frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 |
| 1000-1999 | 23 |
| 2000-2999 | 18 |
| 3000-3999 | 7 |
| 4000-4999 | 4 |
| 5000-5999 | 1 |
| 6000-6999 | 0 |
| 7000-7999 | 0 |
| 8000-8999 | 1 |
Solution:
The frequency histogram for the given data is given by
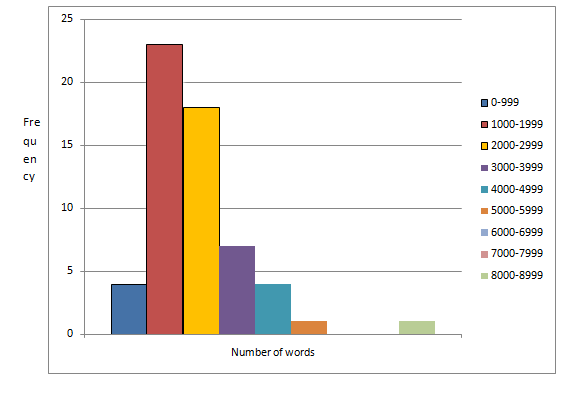
The sum of all frequency is 58
The relative frequency distribution table is given by
| Number of words | Frequency | Relative frequency |
| 0-999 | 4 | |
| 1000-1999 | 23 | |
| 2000-2999 | 18 | |
| 3000-3999 | 7 | |
| 4000-4999 | 4 | |
| 5000-5999 | 1 | |
| 6000-6999 | 0 | |
| 7000-7999 | 0 | |
| 8000-8999 | 1 |
The relative frequency histogram for the given data is given by
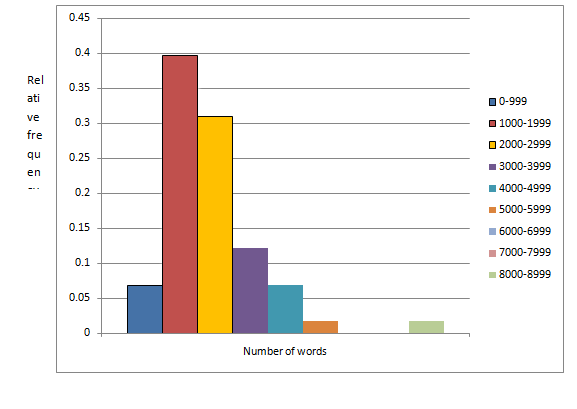
g.
To explain: Whether the good choices for the data are that classes with 5 or 9.
Answer to Problem 33E
The one with 9 classes is the good choice than 5 classes
Explanation of Solution
Given information:There have been 58 presidential inaugurations in U.S. history. At each one, the president has made an inaugural address. Following are the number of words spoken in each of these addresses.
| 1431 | 135 | 2321 | 1730 | 2166 | 1177 | 1211 | 3375 |
| 4472 | 2915 | 1128 | 1176 | 3843 | 8460 | 4809 | 1090 |
| 3336 | 2831 | 3637 | 700 | 1127 | 1339 | 2486 | 2979 |
| 1686 | 4392 | 2015 | 3968 | 2218 | 984 | 5434 | 1704 |
| 1526 | 3329 | 4055 | 3672 | 1880 | 1808 | 1359 | 559 |
| 2273 | 2459 | 1658 | 1366 | 1507 | 2128 | 1803 | 1229 |
| 2427 | 2561 | 2320 | 1598 | 2155 | 1592 | 2071 | 2395 |
| 2096 | 1433 |
The one with 9 classes is more appropriate than the one with only 5 classes.
This is because the one with only 5 classes is too wide and only the most basic features of the data are visible.
Hence, the one with 9 classes is the good choice than 5 classes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
- The U.S. Postal Service will ship a Priority Mail® Large Flat Rate Box (12" 3 12" 3 5½") any where in the United States for a fixed price, regardless of weight. The weights (ounces) of 20 ran domly chosen boxes are shown below. (a) Make a stem-and-leaf diagram. (b) Make a histogram. (c) Describe the shape of the distribution. Weights 72 86 28 67 64 65 45 86 31 32 39 92 90 91 84 62 80 74 63 86arrow_forward(a) What is a bimodal histogram? (b) Explain the difference between left-skewed, symmetric, and right-skewed histograms. (c) What is an outlierarrow_forward(a) Test the hypothesis. Consider the hypothesis test Ho = : against H₁o < 02. Suppose that the sample sizes aren₁ = 7 and n₂ = 13 and that $² = 22.4 and $22 = 28.2. Use α = 0.05. Ho is not ✓ rejected. 9-9 IV (b) Find a 95% confidence interval on of 102. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).arrow_forward
- Let us suppose we have some article reported on a study of potential sources of injury to equine veterinarians conducted at a university veterinary hospital. Forces on the hand were measured for several common activities that veterinarians engage in when examining or treating horses. We will consider the forces on the hands for two tasks, lifting and using ultrasound. Assume that both sample sizes are 6, the sample mean force for lifting was 6.2 pounds with standard deviation 1.5 pounds, and the sample mean force for using ultrasound was 6.4 pounds with standard deviation 0.3 pounds. Assume that the standard deviations are known. Suppose that you wanted to detect a true difference in mean force of 0.25 pounds on the hands for these two activities. Under the null hypothesis, 40 = 0. What level of type II error would you recommend here? Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. 98.7654). Use a = 0.05. β = i What sample size would be required? Assume the sample sizes are to be equal.…arrow_forward= Consider the hypothesis test Ho: μ₁ = μ₂ against H₁ μ₁ μ2. Suppose that sample sizes are n₁ = 15 and n₂ = 15, that x1 = 4.7 and X2 = 7.8 and that s² = 4 and s² = 6.26. Assume that o and that the data are drawn from normal distributions. Use απ 0.05. (a) Test the hypothesis and find the P-value. (b) What is the power of the test in part (a) for a true difference in means of 3? (c) Assuming equal sample sizes, what sample size should be used to obtain ẞ = 0.05 if the true difference in means is - 2? Assume that α = 0.05. (a) The null hypothesis is 98.7654). rejected. The P-value is 0.0008 (b) The power is 0.94 . Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). (c) n₁ = n2 = 1 . Round your answer to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardConsider the hypothesis test Ho: = 622 against H₁: 6 > 62. Suppose that the sample sizes are n₁ = 20 and n₂ = 8, and that = 4.5; s=2.3. Use a = 0.01. (a) Test the hypothesis. Round your answers to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). The test statistic is fo = i The critical value is f = Conclusion: i the null hypothesis at a = 0.01. (b) Construct the confidence interval on 02/022 which can be used to test the hypothesis: (Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).) iarrow_forward
- 2011 listing by carmax of the ages and prices of various corollas in a ceratin regionarrow_forwardس 11/ أ . اذا كانت 1 + x) = 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 + x) هي متعددة حدود محسوبة باستخدام طريقة الفروقات المنتهية (finite differences) من جدول البيانات التالي للدالة (f(x . احسب قيمة . ( 2 درجة ) xi k=0 k=1 k=2 k=3 0 3 1 2 2 2 3 αarrow_forward1. Differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables, providing examples for each type. 2. Consider a discrete random variable representing the number of patients visiting a clinic each day. The probabilities for the number of visits are as follows: 0 visits: P(0) = 0.2 1 visit: P(1) = 0.3 2 visits: P(2) = 0.5 Using this information, calculate the expected value (mean) of the number of patient visits per day. Show all your workings clearly. Rubric to follow Definition of Random variables ( clearly and accurately differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables with appropriate examples for each) Identification of discrete random variable (correctly identifies "number of patient visits" as a discrete random variable and explains reasoning clearly.) Calculation of probabilities (uses the probabilities correctly in the calculation, showing all steps clearly and logically) Expected value calculation (calculate the expected value (mean)…arrow_forward
- if the b coloumn of a z table disappeared what would be used to determine b column probabilitiesarrow_forwardConstruct a model of population flow between metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas of a given country, given that their respective populations in 2015 were 263 million and 45 million. The probabilities are given by the following matrix. (from) (to) metro nonmetro 0.99 0.02 metro 0.01 0.98 nonmetro Predict the population distributions of metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas for the years 2016 through 2020 (in millions, to four decimal places). (Let x, through x5 represent the years 2016 through 2020, respectively.) x₁ = x2 X3 261.27 46.73 11 259.59 48.41 11 257.96 50.04 11 256.39 51.61 11 tarrow_forwardIf the average price of a new one family home is $246,300 with a standard deviation of $15,000 find the minimum and maximum prices of the houses that a contractor will build to satisfy 88% of the market valuearrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


