
Concept explainers
Shikimic acid is a key biosynthetic intermediate in plants and microorganisms. In nature, shikimic acid is converted to chorismate, which is then converted to prephenate, ultimately leading to
(a) Comment on the several transformations that occur between d-mannose and 2. What new functional groups are formed?
(b) What is accomplished in the steps from 2 to 3, 3 to 4, and 4 to 5?
(c) Deduce the structure of compound 9 (a reagent used to convert 5 to 6), knowing that it was a carbanion that displaced the trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate) group of 5. Note that it was compound 9 that brought with it the required
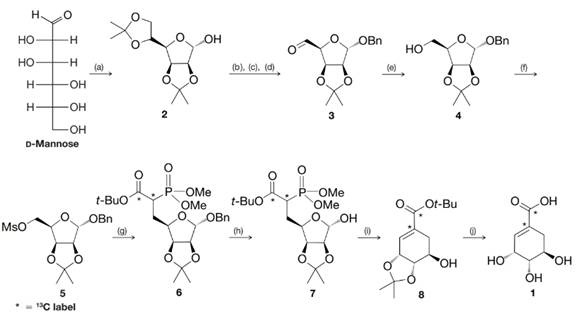
SCHEME 1 The synthesis of
(a) acetone, HA;
(b) BnCl, NaH;
(c) HCl, aq. MeOH;
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g) 9, NaH;
(h)
(i) NaH;
(j) 60% aq.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-WILEYPLUS ACCESS PKG.
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy & Physiology) Standalone Book
- a. Explain Why electron withdrawing groupe tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures 6. Explain why -ll is an ortho -pura drccton evon though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forwardC. Ν Harrow_forwarda. H3C. N H3C CH3 HCNarrow_forward
- ол 2. восцапан (46:00) Curtius rearrangment 1. NaN3, heat -OHarrow_forwardQuestion 1. Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Donnan potential.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



