
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977596
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 22.80P
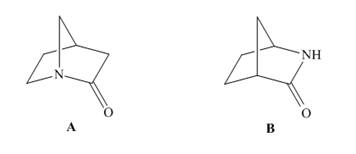
With reference to amides A and B, the carbonyl of one amide absorbs at a much higher wavenumber in its IR spectrum than the carbonyl of the other amide. Which absorbs at higher wavenumber and why?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Provide the product for the reaction
What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between tin(IV) sulfide and nitric acid?
The combustion of 28.8 g of NH3 consumes exactly _____ g of O2.
4 NH3 + 7 O2 ----> 4 NO2 + 6 H2O
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.1PCh. 22 - Draw the three possible resonance structures for...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.3PCh. 22 - Give an IUPAC or common name for each compound. a....Ch. 22 - Problem 22.5 Draw the structure corresponding to...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.6 Explain why the boiling point of is...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.7 How would the compounds in each pair...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.8 Deduce the structures of compounds ...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.9 Without reading ahead in Chapter 22,...Ch. 22 - Rank the compounds in each group in order of...
Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.11PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.12PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.13PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.14PCh. 22 - Problem 22.15 Draw the products of each...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.16 Draw the products of each reaction.
...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.17PCh. 22 - Problem 22.18 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.19PCh. 22 - Problem 22.20 Fenofibrate is a...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.21 What product is formed when the...Ch. 22 - How would you synthesize olestra from sucrose?
Ch. 22 - Problem 22.23 What is the composition of the soap...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.24 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.25PCh. 22 - Problem 22.26 Some penicillins cannot be...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.27PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.28PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.29PCh. 22 - Problem 22.30 Glucosamine is a dietry supplement...Ch. 22 - Draw the products of each reaction. a. c. b.Ch. 22 - Draw a tautomer of each compound.
a. b. c.
Ch. 22 - Draw the product of each reaction. a. b.Ch. 22 - Draw the product of each reaction. a. b.Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.35PCh. 22 - Problem 22.36 Outline two different ways that can...Ch. 22 - 22.37 Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.38PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.39PCh. 22 - 22.40 Give the IUPAC or common name for each...Ch. 22 - 22.41 Give the structure corresponding to each...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.42PCh. 22 - 22.43 Explain why is a stronger acid and a weaker...Ch. 22 - (a) Propose an explanation for the difference in...Ch. 22 - Draw the product formed when phenylacetic acid is...Ch. 22 - Draw the product formed when phenylacetonitrile ...Ch. 22 - 22.47 Draw the organic products formed in each...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.48PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.49PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.50PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.51PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.52PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.53PCh. 22 - 22.54 Draw a stepwise mechanism f or the following...Ch. 22 - 22.55 When acetic acid () is treated with a trace...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.56PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.57PCh. 22 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.59PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.60PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.61PCh. 22 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 22 - 22.63 Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of forms compound...Ch. 22 - 22.64 What carboxylic acid and alcohol are needed...Ch. 22 - Problem 22.65 Devise a synthesis of each compound...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.66PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.67PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.68PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.69PCh. 22 - 22.70 What polyester or poly amide can be prepared...Ch. 22 - 22.71 What two monomers are needed to prepare each...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.72PCh. 22 - 22.73 How can IR spectroscopy be used to...Ch. 22 - 22.74 Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 22 - 22.75 Identify the structures of each compound...Ch. 22 - 22.76 Identify the structures of A and B, isomers...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.77PCh. 22 - 22.78 Identify the structure of compound C...Ch. 22 - 22.79 Identify the structures of D and E, isomers...Ch. 22 - 22.80 With reference to amides A and B, the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.81PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.82PCh. 22 - Prob. 22.83PCh. 22 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 22 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the molecular formula of the bond-line structure shown below OH HO ○ C14H12O2 ○ C16H14O2 ○ C16H12O2 O C14H14O2arrow_forwardCheck all molecules that are acids on the list below. H2CO3 HC2H3O2 C6H5NH2 HNO3 NH3arrow_forwardFrom the given compound, choose the proton that best fits each given description. a CH2 CH 2 Cl b с CH2 F Most shielded: (Choose one) Least shielded: (Choose one) Highest chemical shift: (Choose one) Lowest chemical shift: (Choose one) ×arrow_forward
- Consider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 1H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal.arrow_forwardFor each of the given mass spectrum data, identify whether the compound contains chlorine, bromine, or neither. Compound m/z of M* peak m/z of M + 2 peak ratio of M+ : M + 2 peak Which element is present? A 122 no M + 2 peak not applicable (Choose one) B 78 80 3:1 (Choose one) C 227 229 1:1 (Choose one)arrow_forwardShow transformation from reactant to product, step by step. *see imagearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole
NMR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SBir5wUS3Bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY