
Concept explainers
Variance interpretation
Vanadium Audio Inc. is a small manufacturer of electronic musical Instruments. The plant manager received the following variable factory
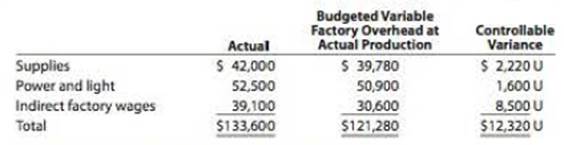
Actual units produced: 15,000 (90% of practical capacity)
The plant manager is not pleased with the $12,320 unfavorable variable factory overhead controllable variance and has come to discuss the matter with the controller. The following discussion occurred;
Plant Manager: I just received this factory report for the latest month of operator. I'm not very pleased with these figures. Before these numbers go to headquarters, you and I will need to reach an understanding.
Controller Go ahead, what's the problem?
Plant Manager: What's the problem? Well, everything. Look at the variance. It’s too large. If I understand the accounting approach being used here, you are assuming that my costs are variable to the units produced. Thus, as the production volume declines, so should these costs. Well I don't believe that these costs are variable at all. I think they are fixed costs. As a result when we operate below capacity, the costs really don't go down at all. I'm being penalized for costs I have no control over at all I need this report to be redone to reflect this fact, if anything, the difference between actual and budget is essentially a volume variance. Listen. I know that you're a tear-payer. You really need to reconsider your assumptions on this one.
If you were in the controller’s position, how would you respond to the plant manager?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




