
(a)
Interpretation: The two repeating units of ABS plastic assuming the three monomer units react in a
Concept introduction: The
To determine: The structure of two repeating units of ABS plastic assuming the three monomer units react in a
(a)
Answer to Problem 168CP
Answer
The two repeating units of ABS plastic are shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The structure of the polymer of ABS plastic is shown in figure 1.
The reaction of Abs
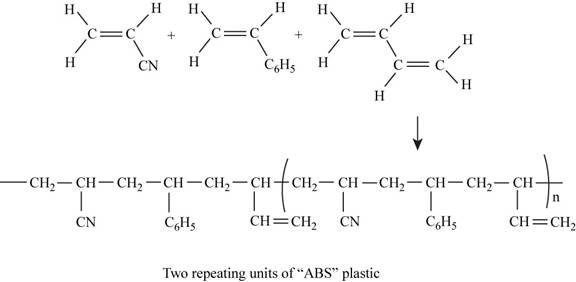
Figure 1
ABS plastic is a terpolymer synthesized by polymerizing styrene, acrylonitrile and polybutadiene. The chemical formula of ABS polymer is
(b)
Interpretation: The two repeating units of ABS plastic assuming the three monomer units react in a
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. ABS plastic is a terpolymer of styrene, acrylonitrile and polybutadiene.
To determine: The percent by mass of acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene in the polymer sample.
(b)
Answer to Problem 168CP
Answer
The mass percent of acrylonitrile is
The mass percent of butadiene is
The mass percent of styrene is
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The mass percent of the three given monomers is calculated below.
Given
The mass of bromine to react completely with ABS plastic is
The mass of ABS plastic is
The molar mass of bromine is
The number of moles is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the given value of the mass and molar mass of bromine in the above expression.
Hence, each molecule in this polymer contains
Therefore,
The ABS plastic is constructed by equimolar ratio of the three molecules. Hence, each molecule is
Therefore,
The mass of acrylonitrile, styrene and butadiene is calculated as,
The molar mass of acrylonitrile is
The molar mass of butadiene is
The molar mass of styrene is
The mass of acrylonitrile, styrene and butadiene is calculated by using the formula,
Substitute the given value of the number of moles and molar mass of in the above expression.
For acrylonitrile,
For butadiene,
For styrene
Therefore,
Mass percent of acrylonitrile, styrene and butadiene is calculated as,
For acrylonitrile,
For butadiene,
For styrene
(c)
Interpretation: The two repeating units of ABS plastic assuming the three monomer units react in a
Concept introduction: The polymers (repeating structural units) are derived from the simple and reactive molecules, called as monomers. ABS plastic is a terpolymer of styrene, acrylonitrile and polybutadiene.
To determine: The relative numbers of monomer units in the given sample of ABS plastic.
(c)
Answer to Problem 168CP
Answer
The three monomer units are in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The relative numbers of the monomer unit in ABS sample is explained below.
On the basis of the above results it is considered that the three monomer unit’s; acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene are present in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry, 10th + Laboratory Handbook for General Chemistry, 3rd + Student Resource Center Printed Access Card + Student Solutions Manual for ... Access Card for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





