
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305401969
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 11OQ
The arrow OA in the PV diagram shown in Figure OQ22.11 represents a reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas. The same sample of gas, starting from the same state O, now undergoes an adiabatic free expansion to the same final volume. What point on the diagram could represent the final state of the gas? (a) the same point A as for the reversible expansion (b) point B (c) point C (d) any of those choices (e) none of those choices
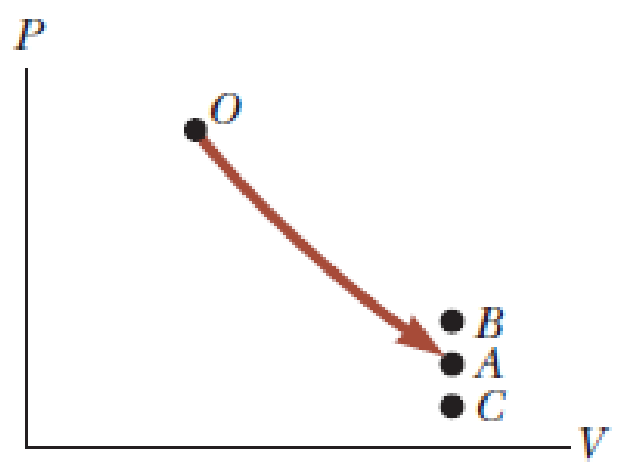
Figure OQ22.11
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote Already
Two objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.
A box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
Ch. 22.1 - The energy input to an engine is 4.00 times...Ch. 22.2 - The energy entering an electric heater by...Ch. 22.4 - Three engines operate between reservoirs separated...Ch. 22.6 - (a) Suppose you select four cards at random from a...Ch. 22.7 - An ideal gas is taken from an initial temperature...Ch. 22.7 - True or False: The entropy change in an adiabatic...Ch. 22 - Prob. 1OQCh. 22 - Prob. 2OQCh. 22 - Prob. 3OQCh. 22 - Of the following, which is not a statement of the...
Ch. 22 - Prob. 5OQCh. 22 - Prob. 6OQCh. 22 - Prob. 7OQCh. 22 - Prob. 8OQCh. 22 - Prob. 9OQCh. 22 - Prob. 10OQCh. 22 - The arrow OA in the PV diagram shown in Figure...Ch. 22 - The energy exhaust from a certain coal-fired...Ch. 22 - Discuss three different common examples of natural...Ch. 22 - Prob. 3CQCh. 22 - The first law of thermodynamics says you cant...Ch. 22 - Energy is the mistress of the Universe, and...Ch. 22 - (a) Give an example of an irreversible process...Ch. 22 - The device shown in Figure CQ22.7, called a...Ch. 22 - A steam-driven turbine is one major component of...Ch. 22 - Discuss the change in entropy of a gas that...Ch. 22 - Prob. 10CQCh. 22 - Prob. 11CQCh. 22 - (a) If you shake a jar full of jelly beans of...Ch. 22 - What are some factors that affect the efficiency...Ch. 22 - A particular heat engine has a mechanical power...Ch. 22 - The work done by an engine equals one-fourth the...Ch. 22 - A heat engine takes in 360 J of energy from a hot...Ch. 22 - A gun is a heat engine. In particular, it is an...Ch. 22 - Prob. 5PCh. 22 - Prob. 6PCh. 22 - Suppose a heat engine is connected to two energy...Ch. 22 - Prob. 8PCh. 22 - During each cycle, a refrigerator ejects 625 kJ of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 10PCh. 22 - Prob. 11PCh. 22 - Prob. 12PCh. 22 - A freezer has a coefficient of performance of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 14PCh. 22 - One of the most efficient heat engines ever built...Ch. 22 - Prob. 16PCh. 22 - Prob. 17PCh. 22 - Prob. 18PCh. 22 - Prob. 19PCh. 22 - Prob. 20PCh. 22 - Prob. 21PCh. 22 - How much work does an ideal Carnot refrigerator...Ch. 22 - Prob. 23PCh. 22 - A power plant operates at a 32.0% efficiency...Ch. 22 - Prob. 25PCh. 22 - Prob. 26PCh. 22 - Prob. 27PCh. 22 - Prob. 28PCh. 22 - A heat engine operates in a Carnot cycle between...Ch. 22 - Suppose you build a two-engine device with the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 31PCh. 22 - Prob. 32PCh. 22 - Prob. 33PCh. 22 - Prob. 34PCh. 22 - Prob. 35PCh. 22 - Prob. 36PCh. 22 - Prob. 37PCh. 22 - Prob. 38PCh. 22 - Prob. 39PCh. 22 - Prob. 40PCh. 22 - Prob. 41PCh. 22 - Prob. 42PCh. 22 - A Styrofoam cup holding 125 g of hot water at 100C...Ch. 22 - Prob. 44PCh. 22 - A 1 500-kg car is moving at 20.0 m/s. The driver...Ch. 22 - Prob. 46PCh. 22 - Prob. 47PCh. 22 - Prob. 48PCh. 22 - Prob. 49PCh. 22 - What change in entropy occurs when a 27.9-g ice...Ch. 22 - Calculate the change in entropy of 250 g of water...Ch. 22 - Prob. 52PCh. 22 - Prob. 53PCh. 22 - Prob. 54PCh. 22 - Prob. 55PCh. 22 - Prob. 56APCh. 22 - Prob. 57APCh. 22 - A steam engine is operated in a cold climate where...Ch. 22 - Prob. 59APCh. 22 - Prob. 60APCh. 22 - Prob. 61APCh. 22 - In 1993, the U.S. government instituted a...Ch. 22 - Prob. 63APCh. 22 - Prob. 64APCh. 22 - Prob. 65APCh. 22 - Prob. 66APCh. 22 - In 1816, Robert Stirling, a Scottish clergyman,...Ch. 22 - Prob. 68APCh. 22 - Prob. 69APCh. 22 - Prob. 70APCh. 22 - Prob. 71APCh. 22 - Prob. 72APCh. 22 - Prob. 73APCh. 22 - A system consisting of n moles of an ideal gas...Ch. 22 - A heat engine operates between two reservoirs at...Ch. 22 - Prob. 76APCh. 22 - Prob. 77APCh. 22 - Prob. 78APCh. 22 - A sample of an ideal gas expands isothermally,...Ch. 22 - Prob. 80APCh. 22 - Prob. 81CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Plz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forwardA box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forward
- What is the meaning of a first order approximation?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgptarrow_forwardA hydrogen atom has just a single electron orbiting the nucleus, which happens to be a single proton without any neutrons. The proton is positively charged, the electron negatively, but both with the same magnitude of charge given by e=1.602x10-19C. The mass of an electron is 9.11x10-31kg, and the proton is 1.67x10-27kg. Find the ratio of the electrostatic to the gravitational force of attraction between the electron and the proton in hydrogen. \arrow_forward
- What is the third law pair to the normal force as you sit in a chair? What effect does the sun's pull on earth have in terms of third law pairs?arrow_forwardUsing Newton's 2nd law, show that all objects subject to the pull of gravity alone should fall at the same rate. What is that rate?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Thermodynamics: Crash Course Physics #23; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4i1MUWJoI0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY