
Concept explainers
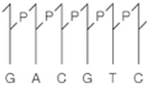
(a) Interpretation:
The other half of a restriction site should be drawn if the one-half is as follows:
Concept Introduction:
The restriction site also known as the restriction sequence is an enzyme that splits DNA into fragments at a recognized site inside a molecule. The restriction site's other part is given and the type II cleavage site with the blunt-ended duplex DNA is shown with heavy arrows. The type II cleavage sites yielding staggered cut is given by light arrows. For the type I restriction endonuclease recognition, the duplex cut is at 1 kilobase away and identical copies of DNA sequence interval is 4096 kilobase pairs as the sequence is 6 base longs with 4 possibility positioned
(b) Interpretation:
Type II cleavage sites producing blunt-ended duplex DNA should be identified using heavy arrows.
Concept Introduction:
The restriction site also known as the restriction sequence is an enzyme that splits DNA into fragments at a recognized site inside a molecule. The restriction site's other part is given and the type II cleavage site with the blunt-ended duplex DNA is shown with heavy arrows. The type II cleavage sites yielding staggered cut is given by light arrows. For the type I restriction endonuclease recognition, the duplex cut is at 1 kilobase away and identical copies of DNA sequence interval is 4096 kilobase pairs as the sequence is 6 base longs with 4 possibility positioned nucleotides.
(c) Interpretation:
Type II cleavage sites producing staggered cuts converted to recombinant DNA molecules by DNA ligase without enzyme involvement should be identified using light arrows.
Concept Introduction:
The restriction site also known as the restriction sequence is an enzyme that splits DNA into fragments at a recognized site inside a molecule. The restriction site's other part is given and the type II cleavage site with the blunt-ended duplex DNA is shown with heavy arrows. The type II cleavage sites yielding staggered cut is given by light arrows. For the type I restriction endonuclease recognition, the duplex cut is at 1 kilobase away and identical copies of DNA sequence interval is 4096 kilobase pairs as the sequence is 6 base longs with 4 possibility positioned nucleotides.
(d) Interpretation:
The place where the duplex be cut when the recognition site for type I restriction endonuclease should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
The restriction site also known as the restriction sequence is an enzyme that splits DNA into fragments at a recognized site inside a molecule. The restriction site's other part is given and the type II cleavage site with the blunt-ended duplex DNA is shown with heavy arrows. The type II cleavage sites yielding staggered cut is given by light arrows. For the type I restriction endonuclease recognition, the duplex cut is at 1 kilobase away and identical copies of DNA sequence interval is 4096 kilobase pairs as the sequence is 6 base longs with 4 possibility positioned nucleotides.
(e) Interpretation:
The average interval of identical copies of the given sequence in DNA which is random should be identified in kilobase pairs.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
- write the ionization equilibrium for cysteine and calculate the piarrow_forwardplease answerarrow_forwardf. The genetic code is given below, along with a short strand of template DNA. Write the protein segment that would form from this DNA. 5'-A-T-G-G-C-T-A-G-G-T-A-A-C-C-T-G-C-A-T-T-A-G-3' Table 4.5 The genetic code First Position Second Position (5' end) U C A G Third Position (3' end) Phe Ser Tyr Cys U Phe Ser Tyr Cys Leu Ser Stop Stop Leu Ser Stop Trp UCAG Leu Pro His Arg His Arg C Leu Pro Gln Arg Pro Leu Gin Arg Pro Leu Ser Asn Thr lle Ser Asn Thr lle Arg A Thr Lys UCAG UCAC G lle Arg Thr Lys Met Gly Asp Ala Val Gly Asp Ala Val Gly G Glu Ala UCAC Val Gly Glu Ala Val Note: This table identifies the amino acid encoded by each triplet. For example, the codon 5'-AUG-3' on mRNA specifies methionine, whereas CAU specifies histidine. UAA, UAG, and UGA are termination signals. AUG is part of the initiation signal, in addition to coding for internal methionine residues. Table 4.5 Biochemistry, Seventh Edition 2012 W. H. Freeman and Company B eviation: does it play abbreviation:arrow_forward
- Answer all of the questions please draw structures for major productarrow_forwardfor glycolysis and the citric acid cycle below, show where ATP, NADH and FADH are used or formed. Show on the diagram the points where at least three other metabolic pathways intersect with these two.arrow_forwardanswer the questions please all of them should be answeredarrow_forward
- Burk plot is shown below. Calculate Km and max for this enzyme. show workarrow_forwardInsert Format Tools Extensions Help Normal text ▾ Arial C 2 10 3 + BIUA Student Guide (continued) Record data and conclusions about the mystery food sample either below or in a lab notebook. Step 2: Protein Test (Biuret Solution) Gelatin Water [Mystery Food (Positive Control) (Negative Control) Sample pink purple no change no change They mystery food sample does not contain protein because the color of the test tube wasn't pink or purple Color Conclusion They mystery food sample does not contain protein because the color of the test tube wasn't pink or purple Step 3: Lipid Test (Sudan Red Solution) Vegetable Oil Water (Positive Control) (Negative Control) Mystery Food Sample floating red no change floating red the mystery food dosnt contain lipids because the test tube has floating red 75 % 87 8 9 7 ChromeOS C Device will pow 26.battery lea powerarrow_forwardThe rate data from an enzyme catalyzed reaction with and without an inhibitor present is found in the image. Question: what is the KM and Vm and the nature of inhibitionarrow_forward
- 1. Estimate the concentration of an enzyme within a living cell. Assume that: (a): fresh tissue is 80% water and all of it is intracellular (b): the total soluble protein represents 15% of the weight (c): all the soluble proteins are enzymes (d): the average molecular weight of the proteins is 150,000 (E): about 100 different enzymes are present please help I am lostarrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P. Question: Estimate the Vmax and Km. What would be the rate at 2.5 and 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] ?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





